
Full sun vs partial shade Illustration
Full sun provides plants with at least six hours of direct sunlight daily, promoting vigorous growth and vibrant blooms for sun-loving species. Partial shade offers filtered or indirect light for about three to six hours, ideal for plants that thrive without intense heat or prolonged exposure. Choosing between full sun and partial shade depends on the specific light requirements of your plants to ensure optimal health and development.
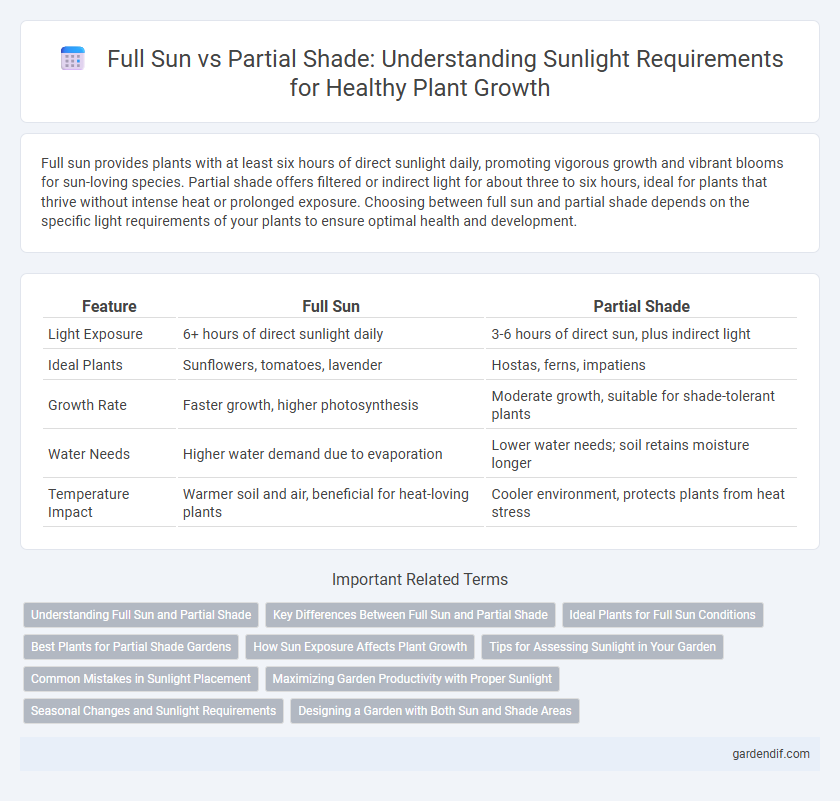
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Full Sun | Partial Shade |
|---|---|---|
| Light Exposure | 6+ hours of direct sunlight daily | 3-6 hours of direct sun, plus indirect light |
| Ideal Plants | Sunflowers, tomatoes, lavender | Hostas, ferns, impatiens |
| Growth Rate | Faster growth, higher photosynthesis | Moderate growth, suitable for shade-tolerant plants |
| Water Needs | Higher water demand due to evaporation | Lower water needs; soil retains moisture longer |
| Temperature Impact | Warmer soil and air, beneficial for heat-loving plants | Cooler environment, protects plants from heat stress |
Understanding Full Sun and Partial Shade
Full sun refers to areas receiving at least six hours of direct sunlight daily, essential for photosynthesis and optimal growth of sun-loving plants such as tomatoes and lavender. Partial shade denotes locations with three to six hours of sunlight or filtered light throughout the day, benefiting shade-tolerant species like hostas and ferns. Recognizing these light exposure requirements is crucial for selecting appropriate plants and ensuring healthy garden development.
Key Differences Between Full Sun and Partial Shade
Full sun areas receive at least six hours of direct sunlight daily, promoting vigorous plant growth and better flowering for sun-loving species. Partial shade zones get three to six hours of direct sunlight, providing a cooler environment suitable for shade-tolerant plants and preventing leaf scorch. Understanding these light conditions is essential for selecting appropriate plants, optimizing growth, and maintaining garden health.
Ideal Plants for Full Sun Conditions
Ideal plants for full sun conditions include vibrant sunflowers, tomatoes, and lavender, which thrive with at least six hours of direct sunlight daily. These sun-loving species develop robust growth, abundant blooms, and high yields when exposed to intense light. Understanding plant-specific sunlight requirements ensures optimal health and productivity in sun-drenched gardens.
Best Plants for Partial Shade Gardens
Best plants for partial shade gardens include hostas, ferns, astilbes, and hellebores, which thrive with filtered sunlight or a few hours of direct morning sun. These plants adapt well to environments where full sun is limited, providing vibrant foliage and blooms without the risk of leaf scorch. Incorporating shade-tolerant species enhances garden diversity while maintaining healthy growth in less intense light conditions.
How Sun Exposure Affects Plant Growth
Sun exposure directly influences photosynthesis rates, with full sun providing the maximum light intensity needed for robust growth, increased flowering, and higher fruit yield. Partial shade reduces light availability, which can slow growth, limit flowering, and sometimes prevent sun-sensitive plants from wilting or scorching. Understanding specific plant light requirements helps optimize garden placement to enhance overall health and productivity.
Tips for Assessing Sunlight in Your Garden
Assess sunlight in your garden by observing the area at different times of the day to determine the duration and intensity of exposure, noting that full sun requires at least six hours of direct sunlight while partial shade receives three to six hours. Use a sunlight meter or smartphone app to obtain precise measurements of light levels, ensuring accurate assessment for plant selection. Pay attention to surrounding structures or trees that may cast shadows, impacting the sunlight availability and influencing plant growth.
Common Mistakes in Sunlight Placement
Placing sun-sensitive plants in full sun often leads to leaf scorch and stunted growth due to excessive light intensity and heat exposure. Choosing locations with partial shade helps moderate sunlight, reducing stress and moisture loss, which is essential for shade-preferring species like ferns and hostas. Ignoring the specific sunlight requirements of each plant results in poor photosynthesis efficiency and increased vulnerability to pests and diseases.
Maximizing Garden Productivity with Proper Sunlight
Maximizing garden productivity depends on matching plant species with their ideal sunlight exposure, where full sun of at least 6 hours daily supports high-yield crops like tomatoes, peppers, and cucumbers. Partial shade, offering 3 to 6 hours of sunlight or filtered light, benefits shade-tolerant plants such as leafy greens, herbs, and certain root vegetables, optimizing growth and preventing stress. Understanding sunlight requirements enhances photosynthesis efficiency, leading to healthier plants and increased harvest quality.
Seasonal Changes and Sunlight Requirements
Full sun exposure supports optimal growth for sun-loving plants such as tomatoes and sunflowers, requiring at least six hours of direct sunlight daily, especially during peak growing seasons in spring and summer. Partial shade benefits plants like ferns and hostas that need filtered light or fewer than four hours of direct sun, adapting well to seasonal changes in sunlight intensity and angle. Understanding the shifting position of the sun across seasons helps gardeners optimize plant placement, ensuring light requirements align with each plant's photosynthetic needs throughout spring, summer, and fall.
Designing a Garden with Both Sun and Shade Areas
Designing a garden that balances full sun and partial shade areas enhances plant diversity and health by accommodating sun-loving species like lavender and sunflowers alongside shade-tolerant ferns and hostas. Strategic placement near structures or trees creates natural transitions between light levels, optimizing photosynthesis and moisture retention for each plant type. Incorporating mulch and drip irrigation further supports varied sunlight zones, ensuring a thriving, visually dynamic garden environment.
Full sun vs partial shade Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com