
Hardening Off vs Indoor Growing Illustration
Hardening off prepares plants for outdoor sunlight by gradually exposing them to direct sun and fluctuating temperatures, increasing their tolerance and reducing transplant shock. Indoor growing controls light exposure with artificial sources, allowing steady growth but often resulting in weaker plants less adapted to natural light intensity. Transitioning seedlings through hardening off ensures stronger, healthier plants ready for outdoor conditions compared to those raised exclusively indoors.
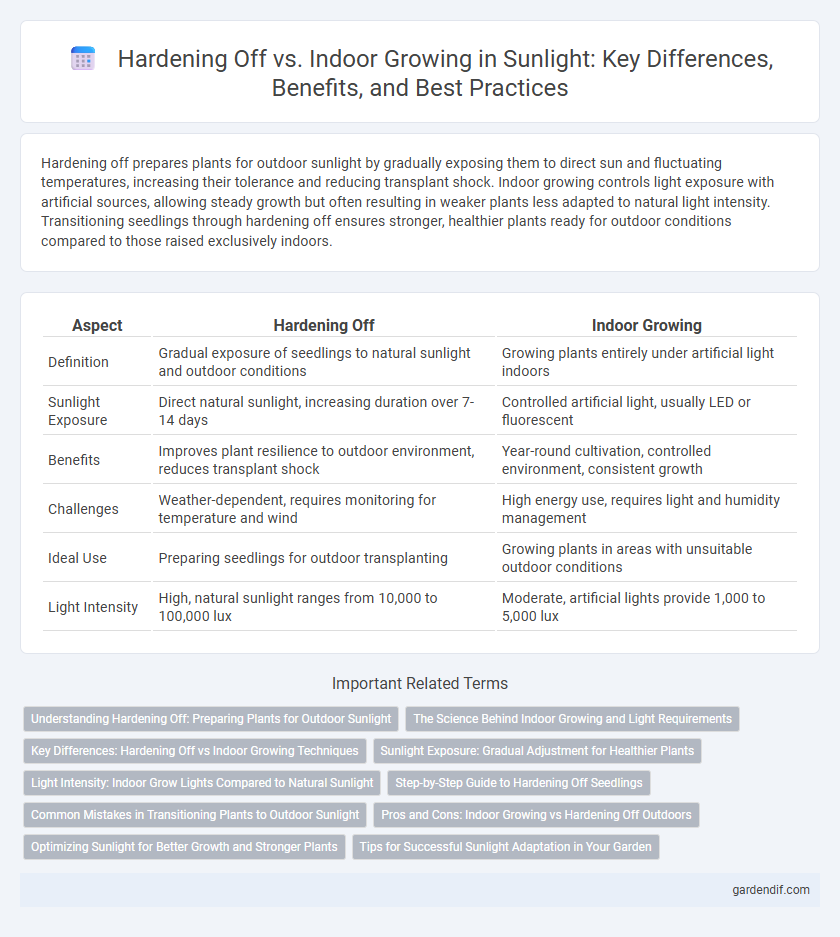
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Hardening Off | Indoor Growing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Gradual exposure of seedlings to natural sunlight and outdoor conditions | Growing plants entirely under artificial light indoors |
| Sunlight Exposure | Direct natural sunlight, increasing duration over 7-14 days | Controlled artificial light, usually LED or fluorescent |
| Benefits | Improves plant resilience to outdoor environment, reduces transplant shock | Year-round cultivation, controlled environment, consistent growth |
| Challenges | Weather-dependent, requires monitoring for temperature and wind | High energy use, requires light and humidity management |
| Ideal Use | Preparing seedlings for outdoor transplanting | Growing plants in areas with unsuitable outdoor conditions |
| Light Intensity | High, natural sunlight ranges from 10,000 to 100,000 lux | Moderate, artificial lights provide 1,000 to 5,000 lux |
Understanding Hardening Off: Preparing Plants for Outdoor Sunlight
Hardening off involves gradually exposing indoor-grown plants to outdoor sunlight and environmental conditions, strengthening their resilience and preventing shock. This process improves plant survival rates by acclimating leaves and stems to direct UV rays, temperature fluctuations, and wind exposure. Properly hardened plants exhibit enhanced photosynthesis efficiency and sturdier cell walls compared to those moved directly outdoors from indoor growing environments.
The Science Behind Indoor Growing and Light Requirements
Indoor growing relies on artificial light sources such as LED, fluorescent, or HID lights that mimic the sun's spectrum to promote photosynthesis and healthy plant development. Hardening off prepares plants for outdoor sunlight by gradually acclimating them to natural light intensity and UV exposure, preventing shock from sudden changes. Optimal light requirements indoors typically involve maintaining 12-16 hours of light per day with sufficient intensity measured in micromoles per square meter per second (umol/m2/s) to support chlorophyll production and growth cycles.
Key Differences: Hardening Off vs Indoor Growing Techniques
Hardening off involves gradually exposing indoor-grown seedlings to outdoor sunlight, wind, and temperature variations to strengthen plant tissues and reduce transplant shock. Indoor growing techniques use controlled environments with artificial light, stable temperature, and humidity to optimize plant growth without natural weather stressors. The key difference lies in hardening off preparing plants for outdoor conditions while indoor growing maintains growth entirely within a regulated indoor space.
Sunlight Exposure: Gradual Adjustment for Healthier Plants
Gradual sunlight exposure during hardening off enables plants to acclimate to natural light intensity, reducing stress and promoting stronger chlorophyll development compared to strictly indoor growing. Direct sunlight fosters robust photosynthesis and enhances plant resilience, which is often limited in indoor environments with artificial lighting. Controlled outdoor light adjustment prevents leaf scorch, helping seedlings transition smoothly and thrive once transplanted.
Light Intensity: Indoor Grow Lights Compared to Natural Sunlight
Indoor grow lights provide controlled light intensity tailored to plant needs, often ranging from 200 to 1000 mmol/m2/s, yet natural sunlight can exceed 2000 mmol/m2/s at peak intensity. Hardening off helps plants adapt gradually from the lower, artificial light conditions indoors to the higher and variable intensity of direct sunlight outdoors. Without proper acclimation, sudden exposure to intense sunlight can cause leaf burn and stress, reducing plant vitality.
Step-by-Step Guide to Hardening Off Seedlings
Gradually exposing seedlings to outdoor sunlight is essential for hardening off, which strengthens plants by acclimating them to natural conditions and preventing shock during transplanting. Start by placing seedlings in a shaded outdoor area for a few hours daily, increasing sunlight and time outside over 7-10 days while monitoring temperature and moisture. Proper hardening off enhances photosynthesis efficiency, improves stem rigidity, and leads to higher survival rates compared to seedlings grown solely indoors.
Common Mistakes in Transitioning Plants to Outdoor Sunlight
Common mistakes when hardening off plants include exposing seedlings to intense direct sunlight too quickly, leading to leaf scorch and stunted growth. Indoor-growing gardeners often neglect gradual acclimation, causing shock from sudden temperature and light intensity changes. Properly timed, incremental exposure to outdoor conditions prevents stress and ensures healthy plant development.
Pros and Cons: Indoor Growing vs Hardening Off Outdoors
Indoor growing offers controlled environments that protect plants from pests, temperature fluctuations, and harsh weather, ensuring consistent growth and year-round cultivation; however, it can limit natural sunlight exposure essential for robust photosynthesis and may increase energy costs. Hardening off outdoors gradually acclimates seedlings to natural conditions, improving their resilience to sunlight, wind, and temperature changes, which enhances overall plant hardiness and reduces transplant shock. The trade-off with hardening off lies in its dependency on suitable weather and increased vulnerability to environmental stressors during the acclimation period.
Optimizing Sunlight for Better Growth and Stronger Plants
Hardening off involves gradually exposing indoor-grown plants to natural sunlight, improving their resilience and photosynthetic efficiency by adapting them to outdoor light intensity and UV levels. Indoor growing allows precise control over light duration and spectrum but lacks the full spectrum and intensity variations of sunlight crucial for strong stem development and chlorophyll production. Optimizing sunlight exposure during hardening off enhances plant structure and stress tolerance, resulting in healthier, more robust plants ready for outdoor conditions.
Tips for Successful Sunlight Adaptation in Your Garden
Gradual exposure to natural sunlight is essential for hardening off seedlings to prevent shock and promote robust growth. Start with short periods of outdoor sun in sheltered spots, increasing duration daily while avoiding intense midday rays to strengthen plant resilience. Indoor growing requires supplemental grow lights mimicking sunlight spectrum and intensity to ensure healthy photosynthesis when natural light is insufficient.
Hardening Off vs Indoor Growing Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com