
Solar radiation vs ambient light Illustration
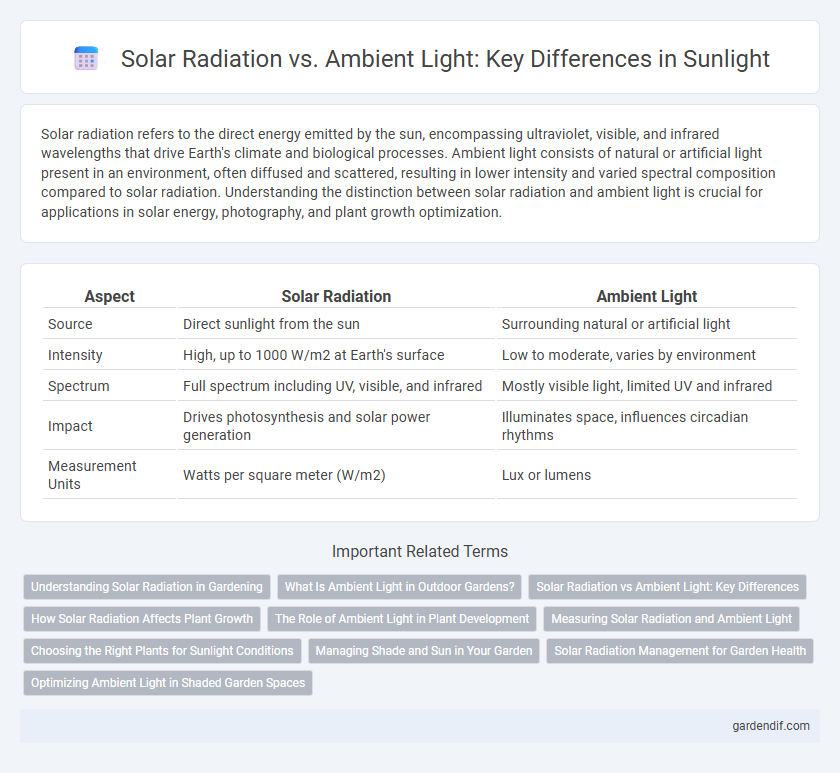
Solar radiation refers to the direct energy emitted by the sun, encompassing ultraviolet, visible, and infrared wavelengths that drive Earth's climate and biological processes. Ambient light consists of natural or artificial light present in an environment, often diffused and scattered, resulting in lower intensity and varied spectral composition compared to solar radiation. Understanding the distinction between solar radiation and ambient light is crucial for applications in solar energy, photography, and plant growth optimization.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Solar Radiation | Ambient Light |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Direct sunlight from the sun | Surrounding natural or artificial light |
| Intensity | High, up to 1000 W/m2 at Earth's surface | Low to moderate, varies by environment |
| Spectrum | Full spectrum including UV, visible, and infrared | Mostly visible light, limited UV and infrared |
| Impact | Drives photosynthesis and solar power generation | Illuminates space, influences circadian rhythms |
| Measurement Units | Watts per square meter (W/m2) | Lux or lumens |
Understanding Solar Radiation in Gardening
Solar radiation, the direct energy emitted by the sun, provides essential wavelengths for photosynthesis, crucial for plant growth and development in gardening. Unlike ambient light, which includes diffuse and reflected light, solar radiation delivers intense, full-spectrum energy that influences seed germination, flowering, and fruiting cycles. Understanding the dynamics of solar radiation helps gardeners optimize plant placement, ensuring maximum exposure for healthier, more productive gardens.
What Is Ambient Light in Outdoor Gardens?
Ambient light in outdoor gardens refers to the natural, diffused illumination from the surrounding environment, excluding direct solar radiation. This lighting includes reflected sunlight from surfaces like soil, foliage, and garden structures, creating a softer and more uniform brightness that supports plant growth without the intensity of direct rays. Understanding ambient light helps gardeners optimize plant placement and choose species adapted to varying light conditions beyond direct sunlight exposure.
Solar Radiation vs Ambient Light: Key Differences
Solar radiation refers to the electromagnetic energy emitted by the sun, primarily consisting of visible light, ultraviolet, and infrared radiation, whereas ambient light is the surrounding light present in any environment, including natural and artificial sources. Solar radiation intensity varies with factors like time of day, geographic location, and atmospheric conditions, while ambient light levels depend on the mix of all light sources and reflective surfaces in the immediate area. Understanding the spectral composition and intensity differences between solar radiation and ambient light is crucial for applications in solar energy, photography, and environmental science.
How Solar Radiation Affects Plant Growth
Solar radiation provides essential wavelengths that directly influence photosynthesis, driving plant growth and development more effectively than ambient light. The intensity and duration of solar radiation determine chlorophyll production, impacting biomass accumulation and flowering cycles in plants. High solar radiation levels increase photosynthetic rates, enhancing energy conversion efficiency critical for robust plant health.
The Role of Ambient Light in Plant Development
Ambient light, consisting of diffuse solar radiation filtered through clouds or vegetation, plays a crucial role in plant development by influencing processes like photosynthesis, phototropism, and circadian rhythms. Unlike direct solar radiation, ambient light provides consistent, lower-intensity illumination that supports steady growth and reduces stress from intense light exposure. This balanced exposure ensures optimal chlorophyll production and enhances overall plant health and productivity in various environments.
Measuring Solar Radiation and Ambient Light
Measuring solar radiation involves quantifying the total energy from the sun that reaches the Earth's surface, typically using pyranometers and solarimeters to assess both direct and diffuse components. Ambient light measurement focuses on the visible spectrum intensity perceived in a specific environment, often captured by photometers or lux meters to determine light levels affecting human vision and plant growth. Accurate differentiation between solar radiation and ambient light is crucial for applications in meteorology, agriculture, and building design to optimize energy efficiency and environmental comfort.
Choosing the Right Plants for Sunlight Conditions
Solar radiation delivers intense, direct energy essential for photosynthesis, favoring sun-loving plants like tomatoes and sunflowers that require full sun exposure. Ambient light, diffused and less intense, supports shade-tolerant species such as ferns and hostas, which thrive under indirect illumination. Selecting plants based on their native light conditions ensures optimal growth, maximizing chlorophyll efficiency and overall health.
Managing Shade and Sun in Your Garden
Solar radiation delivers intense, direct energy essential for photosynthesis, while ambient light provides diffuse illumination that supports plant growth without causing heat stress. Managing shade and sun in your garden involves strategically positioning plants based on their light requirements, ensuring sun-loving species receive ample solar radiation while shade-tolerant plants benefit from filtered ambient light. Utilizing structures like pergolas, shade cloths, or natural tree canopies effectively balances the intensity of solar radiation and ambient light, promoting healthy growth and preventing leaf scorch.
Solar Radiation Management for Garden Health
Solar radiation delivers the full spectrum of light essential for photosynthesis, crucial for robust plant growth in gardens. Ambient light, often diffused and lower in intensity, supports general visibility but lacks the concentrated energy required for optimal plant health. Solar Radiation Management techniques, such as selective shading and reflective mulches, help regulate the intensity and duration of solar radiation, preventing heat stress and promoting efficient photosynthetic activity in garden ecosystems.
Optimizing Ambient Light in Shaded Garden Spaces
Solar radiation provides the primary energy source for plants but can be excessive in shaded garden spaces, limiting growth. Optimizing ambient light involves enhancing diffused light levels using reflective surfaces, light-colored materials, and strategically placed plants to maximize photosynthesis without the harmful effects of direct solar radiation. Balancing UV and visible light spectrums in these microenvironments promotes healthy plant development and improves overall garden aesthetics.
Solar radiation vs ambient light Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com