
Solar Intensity vs Light Duration Illustration
Solar intensity fluctuates throughout the day, reaching its peak when the sun is highest in the sky, while light duration varies based on geographic location and season. Longer daylight hours increase total solar energy received, but intensity determines the strength of sunlight at any given moment. Understanding the balance between solar intensity and light duration is crucial for optimizing solar panel efficiency and plant growth.
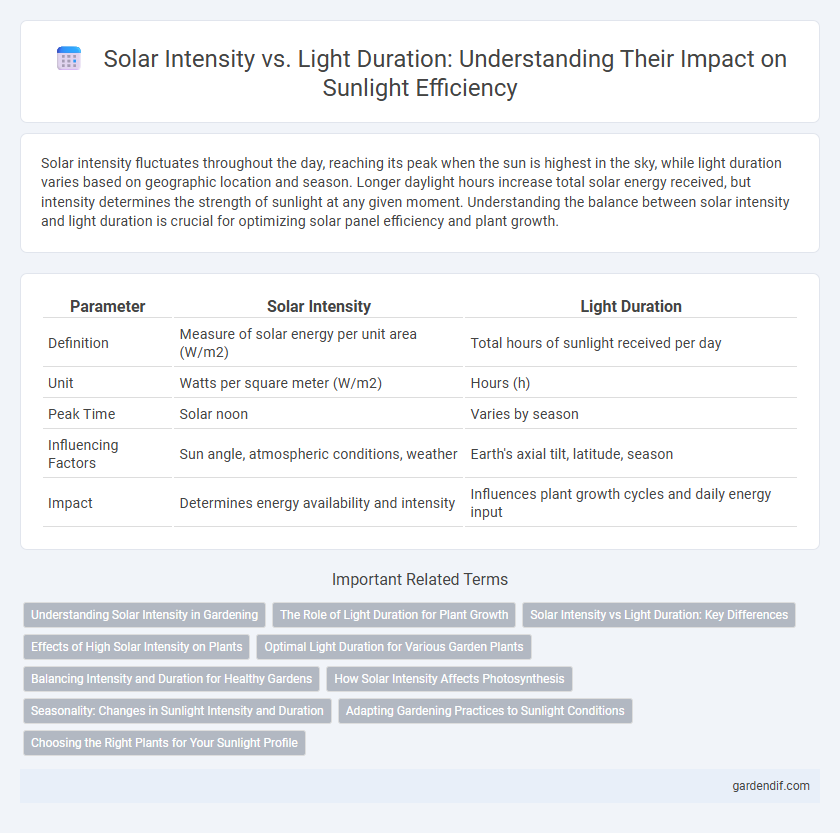
Table of Comparison
| Parameter | Solar Intensity | Light Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Measure of solar energy per unit area (W/m2) | Total hours of sunlight received per day |
| Unit | Watts per square meter (W/m2) | Hours (h) |
| Peak Time | Solar noon | Varies by season |
| Influencing Factors | Sun angle, atmospheric conditions, weather | Earth's axial tilt, latitude, season |
| Impact | Determines energy availability and intensity | Influences plant growth cycles and daily energy input |
Understanding Solar Intensity in Gardening
Solar intensity directly influences photosynthesis rates, impacting plant growth and health in gardening. Understanding the relationship between solar intensity and light duration helps gardeners optimize plant placement and select species suited for specific light conditions. Measuring solar intensity with tools like pyranometers enables accurate assessment of sunlight exposure, improving garden productivity.
The Role of Light Duration for Plant Growth
Light duration significantly influences photosynthesis by regulating the photoperiod, which affects plant growth cycles and flowering. Extended exposure to solar intensity during longer daylight hours enhances chlorophyll production and energy storage, optimizing biomass accumulation. Plants adapt morphologically and physiologically to varying light durations to maximize growth efficiency and reproductive success.
Solar Intensity vs Light Duration: Key Differences
Solar intensity refers to the power per unit area received from the sun, measured in watts per square meter (W/m2), while light duration denotes the total time sunlight is available during the day, usually quantified in hours. The key difference lies in solar intensity affecting the energy concentration at a given moment, whereas light duration influences the cumulative exposure to sunlight. Variations in solar intensity are linked to factors like solar angle and atmospheric conditions, whereas light duration changes primarily due to geographic location and seasonal shifts.
Effects of High Solar Intensity on Plants
High solar intensity significantly impacts plant physiology by increasing photosynthesis rates and accelerating growth when light duration is optimal. Excessive solar intensity, however, can cause photoinhibition, leading to oxidative stress and damage to chlorophyll molecules. Prolonged exposure to intense sunlight without adequate water supply often results in reduced stomatal conductance, impairing transpiration and nutrient uptake.
Optimal Light Duration for Various Garden Plants
Optimal light duration varies significantly among garden plants, with most flowering species thriving under 10 to 14 hours of sunlight daily. Solar intensity directly influences photosynthesis efficiency, where higher intensity within this duration boosts growth rates and flowering potential. Shade-tolerant plants require lower light duration and intensity to prevent stress and maintain optimal health.
Balancing Intensity and Duration for Healthy Gardens
Solar intensity influences photosynthesis rates, while light duration determines the total energy plants receive daily, requiring a precise balance for optimal growth. Maintaining moderate solar intensity with adequate light duration helps prevent plant stress, ensuring healthy development and maximizing nutrient absorption. Gardeners must monitor both factors to create an environment that supports robust foliage and flowering cycles.
How Solar Intensity Affects Photosynthesis
Solar intensity directly influences the rate of photosynthesis by determining the energy available for chlorophyll to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. Higher solar intensity increases the light-dependent reactions, enhancing the production of ATP and NADPH, which are essential for the Calvin cycle. However, prolonged light duration under optimal intensity maximizes photosynthetic efficiency by sustaining continuous energy production and carbon fixation.
Seasonality: Changes in Sunlight Intensity and Duration
Solar intensity varies significantly with seasonality, reaching its peak during summer months when sunlight duration is longest due to the Earth's tilt. Longer daylight hours amplify the total solar energy received, enhancing photosynthesis and influencing climate patterns. Conversely, shorter days and lower solar intensity during winter reduce energy input, impacting ecosystems and human activities.
Adapting Gardening Practices to Sunlight Conditions
Solar intensity directly influences photosynthesis rates, while light duration determines the total energy plants receive daily. To adapt gardening practices effectively, select plant species based on their light requirements and modify planting schedules to maximize exposure during peak sunlight hours. Implementing shade structures or reflective surfaces can optimize light conditions, enhancing growth and crop yield in varying solar environments.
Choosing the Right Plants for Your Sunlight Profile
Solar intensity and light duration are crucial factors in choosing the right plants for your sunlight profile, as they directly influence photosynthesis efficiency and growth rates. Plants like succulents and cacti thrive under high solar intensity and extended light duration, while shade-tolerant species such as ferns and hostas prefer lower intensity and shorter light exposure. Understanding the specific light requirements and tolerance levels of your plants ensures optimal health, flowering, and productivity in your garden.
Solar Intensity vs Light Duration Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com