
Morning sun vs afternoon sun Illustration
Morning sun provides gentle, warm light rich in vitamin D, promoting natural energy and mood enhancement without the intense heat. Afternoon sun tends to be stronger, with increased UV exposure that can cause skin damage and fatigue if proper protection is not used. Balancing time in both helps optimize health benefits while minimizing risks associated with sunlight.
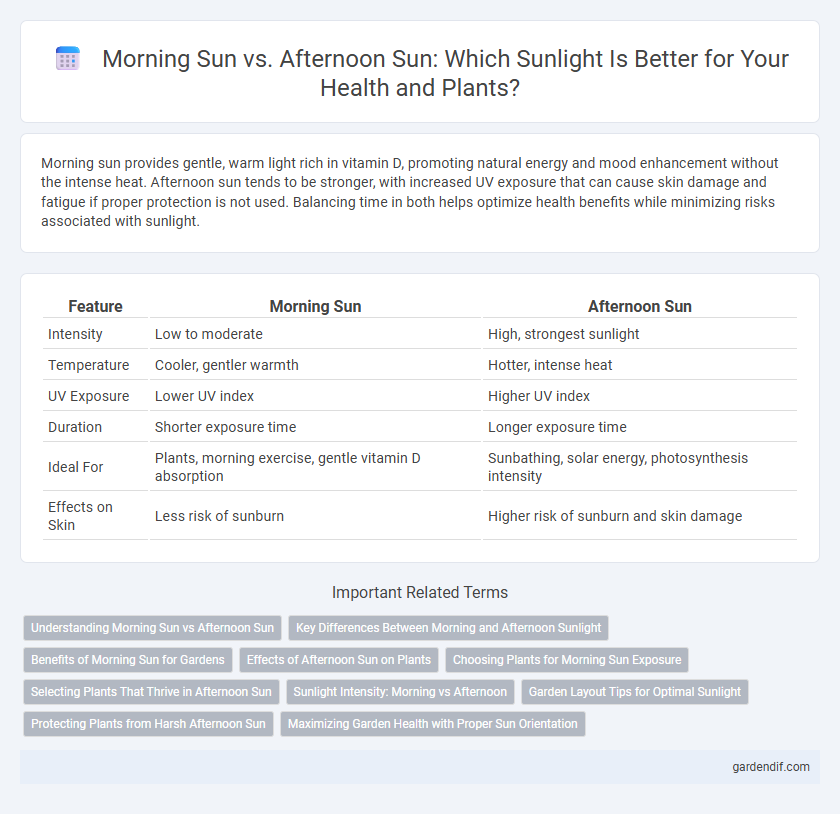
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Morning Sun | Afternoon Sun |
|---|---|---|
| Intensity | Low to moderate | High, strongest sunlight |
| Temperature | Cooler, gentler warmth | Hotter, intense heat |
| UV Exposure | Lower UV index | Higher UV index |
| Duration | Shorter exposure time | Longer exposure time |
| Ideal For | Plants, morning exercise, gentle vitamin D absorption | Sunbathing, solar energy, photosynthesis intensity |
| Effects on Skin | Less risk of sunburn | Higher risk of sunburn and skin damage |
Understanding Morning Sun vs Afternoon Sun
Morning sun provides softer, cooler light with lower ultraviolet (UV) levels, promoting gentle vitamin D synthesis and less risk of skin damage. Afternoon sun emits stronger, more intense rays, with higher UV index values, increasing the potential for sunburn and heat exposure. Understanding these differences helps optimize outdoor activities and skin protection strategies based on sun intensity and timing.
Key Differences Between Morning and Afternoon Sunlight
Morning sunlight offers a softer, cooler spectrum rich in blue light that enhances alertness and supports circadian rhythm regulation, while afternoon sunlight contains higher intensity UV rays and warmer hues due to the sun's position. The angle of morning sun produces less glare and lower heat, making it ideal for photosynthesis and vitamin D synthesis without the risk of overheating or sunburn. Afternoon sun's increased intensity can lead to greater risks of skin damage but also provides abundant energy for robust plant growth and solar power generation.
Benefits of Morning Sun for Gardens
Morning sun provides gentle, consistent light that promotes photosynthesis and reduces the risk of leaf scorch, enhancing plant health and growth. Cooler temperatures in the early hours minimize water evaporation, helping soil retain moisture and reducing irrigation needs. Exposure to morning sunlight also supports strong root development and encourages flowering by regulating plant circadian rhythms effectively.
Effects of Afternoon Sun on Plants
Afternoon sun produces higher intensity and warmer light that can increase photosynthesis but also raises the risk of heat stress and water loss in plants. Prolonged exposure to strong afternoon sunlight can cause leaf scorching, wilting, and reduced growth rates, especially in species sensitive to heat. Proper selection of heat-tolerant plants and adequate watering are crucial to mitigate the adverse effects of intense afternoon sun on plant health.
Choosing Plants for Morning Sun Exposure
Plants that thrive in morning sun exposure benefit from gentle, cooler light that reduces heat stress and prevents leaf scorch. Species such as ferns, impatiens, and begonias flourish under these conditions, as they require filtered or moderate sunlight to maintain vibrant growth. Selecting plants adapted to morning sun ensures healthier foliage and prolonged blooming periods compared to those exposed to the harsher afternoon rays.
Selecting Plants That Thrive in Afternoon Sun
Plants that thrive in afternoon sun typically require full sun exposure of at least 6 hours, tolerating intense heat and strong light. Species such as lavender, succulents, and salvia are well-suited for these conditions due to their drought resistance and ability to withstand high temperatures. Selecting heat-tolerant plants ensures robust growth and vibrant blooms despite the harsher afternoon sunlight.
Sunlight Intensity: Morning vs Afternoon
Morning sun delivers lower sunlight intensity, producing softer and less harmful UV rays ideal for skin exposure and photosynthesis in plants. Afternoon sun exhibits higher sunlight intensity due to the sun's position near its zenith, resulting in stronger UV radiation and increased heat. This intensity difference significantly impacts outdoor activities, plant growth, and the potential for skin damage during various times of the day.
Garden Layout Tips for Optimal Sunlight
Plants in the morning sun benefit from gentle, cooler light that promotes healthy growth and reduces leaf burn, making east-facing garden beds ideal for delicate flowers and vegetables. Afternoon sun delivers stronger, more intense light ideal for drought-tolerant and sun-loving plants, so placing heat-resistant species on west or south-facing sides maximizes their thriving potential. Designing your garden layout to harness morning and afternoon sun patterns enhances plant health and optimizes photosynthesis throughout the day.
Protecting Plants from Harsh Afternoon Sun
Morning sun provides gentle, indirect light ideal for most plants, promoting healthy photosynthesis without causing stress. Afternoon sun, often intense and harsh, can lead to leaf scorch, dehydration, and slowed growth in sensitive plants. Shielding plants with shade cloths, relocating them to shaded areas, or using protective covers helps mitigate damage from strong afternoon sunlight, ensuring optimal health and growth.
Maximizing Garden Health with Proper Sun Orientation
Morning sun provides gentle, nutrient-rich light that supports photosynthesis and encourages strong plant growth, making it ideal for delicate flowers and leafy vegetables. Afternoon sun, often more intense and hotter, suits sun-loving plants like tomatoes and peppers, which thrive in higher light and heat. Maximizing garden health requires aligning plant selection with sun orientation, ensuring shade-tolerant species benefit from morning sun while sun-drenched areas host heat-tolerant varieties.
Morning sun vs afternoon sun Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com