
Direct sunlight vs filtered sunlight Illustration
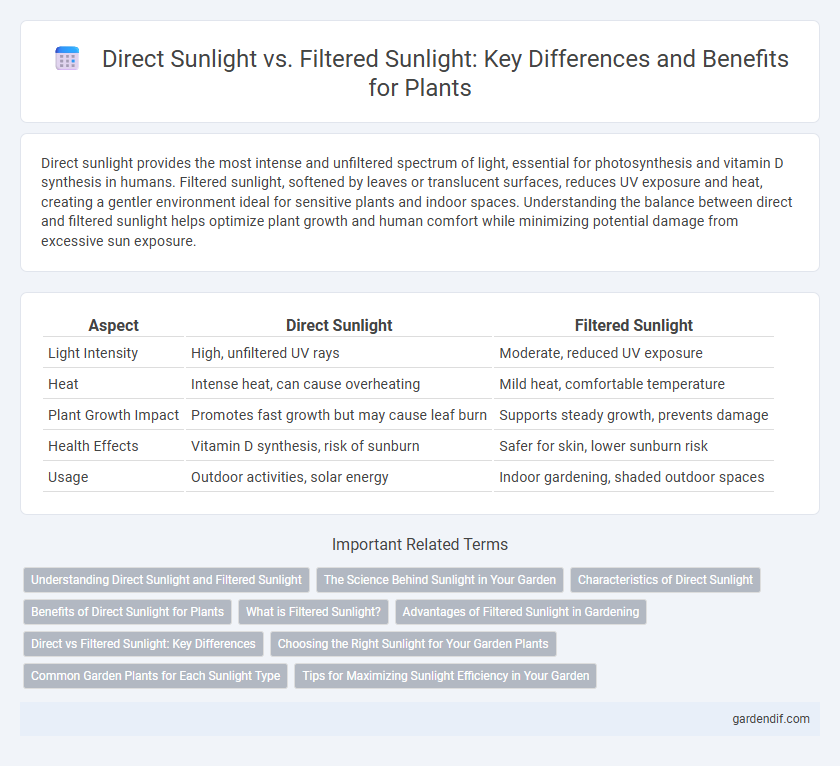
Direct sunlight provides the most intense and unfiltered spectrum of light, essential for photosynthesis and vitamin D synthesis in humans. Filtered sunlight, softened by leaves or translucent surfaces, reduces UV exposure and heat, creating a gentler environment ideal for sensitive plants and indoor spaces. Understanding the balance between direct and filtered sunlight helps optimize plant growth and human comfort while minimizing potential damage from excessive sun exposure.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Direct Sunlight | Filtered Sunlight |
|---|---|---|
| Light Intensity | High, unfiltered UV rays | Moderate, reduced UV exposure |
| Heat | Intense heat, can cause overheating | Mild heat, comfortable temperature |
| Plant Growth Impact | Promotes fast growth but may cause leaf burn | Supports steady growth, prevents damage |
| Health Effects | Vitamin D synthesis, risk of sunburn | Safer for skin, lower sunburn risk |
| Usage | Outdoor activities, solar energy | Indoor gardening, shaded outdoor spaces |
Understanding Direct Sunlight and Filtered Sunlight
Direct sunlight delivers intense, unfiltered rays that provide maximum energy for plants and essential vitamin D synthesis in humans, but it can cause leaf burn and overheating in sensitive species. Filtered sunlight passes through obstructions like foliage or curtains, reducing intensity and diffusing light to create a gentler environment, ideal for shade-loving plants and preventing UV-related damage. Recognizing the differences between direct and filtered sunlight helps optimize plant growth, enhance energy efficiency, and promote health benefits while minimizing risks from overexposure.
The Science Behind Sunlight in Your Garden
Direct sunlight delivers the full spectrum of solar radiation, including ultraviolet (UV), visible, and infrared light, which drives photosynthesis and influences plant growth cycles in your garden. Filtered sunlight, often occurring under tree canopies or shade cloth, reduces UV intensity and light saturation, modulating photosynthetic rates and preventing leaf scorch in shade-tolerant species. Understanding the photobiological responses to different light qualities helps optimize plant health and productivity by aligning species with their preferred sunlight exposure.
Characteristics of Direct Sunlight
Direct sunlight delivers intense, unfiltered solar rays that provide maximum light intensity and full-spectrum wavelengths essential for photosynthesis. This type of sunlight causes rapid heating and strong shadows, often reaching brightness levels above 100,000 lux. Plants exposed to direct sunlight typically exhibit robust growth, higher chlorophyll production, and enhanced vitamin D synthesis in humans.
Benefits of Direct Sunlight for Plants
Direct sunlight provides plants with the full spectrum of natural light, essential for photosynthesis and robust growth. Exposure to direct sunlight enhances chlorophyll production, improving energy conversion and plant health. This intense light source supports flowering, fruiting, and overall vitality better than filtered sunlight.
What is Filtered Sunlight?
Filtered sunlight refers to natural light that passes through a medium such as tree leaves, curtains, or blinds, diffusing its intensity and reducing direct exposure to harmful UV rays. This type of sunlight provides sufficient illumination while minimizing heat and glare, making it ideal for indoor plants and sensitive skin. Unlike direct sunlight, filtered sunlight balances brightness with protection, promoting healthier growth and comfort.
Advantages of Filtered Sunlight in Gardening
Filtered sunlight provides plants with a balanced spectrum of light that reduces the risk of leaf scorch and dehydration common in direct sunlight exposure. This moderated light intensity enhances photosynthesis without overwhelming delicate plants, promoting healthier growth and vibrant blooms. The gentle dappled light environment also helps maintain optimal soil moisture levels, minimizing water stress in garden plants.
Direct vs Filtered Sunlight: Key Differences
Direct sunlight delivers intense, unfiltered rays that boost photosynthesis but can cause leaf scorch or dehydration in sensitive plants. Filtered sunlight, passing through obstacles like leaves or curtains, reduces intensity and UV exposure, promoting gradual growth and reducing heat stress. Choosing between direct and filtered sunlight depends on plant species' light tolerance and desired growth outcomes.
Choosing the Right Sunlight for Your Garden Plants
Direct sunlight provides intense, unfiltered rays that boost photosynthesis and promote faster growth in sun-loving plants such as tomatoes and sunflowers. Filtered sunlight, softened by shade or plant cover, reduces the risk of leaf scorch and dehydration, making it ideal for shade-tolerant species like ferns and begonias. Selecting the appropriate sunlight exposure based on a plant's light requirements ensures optimal health, vibrant foliage, and robust flowering throughout the growing season.
Common Garden Plants for Each Sunlight Type
Common garden plants thriving in direct sunlight include tomatoes, lavender, and marigolds, which require at least six hours of unfiltered sun daily to maximize photosynthesis and bloom production. Filtered sunlight benefits shade-tolerant plants like ferns, hostas, and impatiens, protecting them from leaf scorch while providing sufficient light for growth. Selecting plants based on sunlight preferences enhances garden health, optimizing chlorophyll synthesis and overall plant vigor.
Tips for Maximizing Sunlight Efficiency in Your Garden
Direct sunlight provides intense, uninterrupted light ideal for sun-loving plants like tomatoes and sunflowers, while filtered sunlight suits shade-tolerant species such as ferns and impatiens. Position plants according to their light requirements, using structures like pergolas or shade cloths to modulate sunlight exposure effectively. Optimize garden layout by analyzing sun patterns to maximize daily light absorption and improve photosynthesis efficiency.
Direct sunlight vs filtered sunlight Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com