
Sheet mulching vs Traditional amendment Illustration
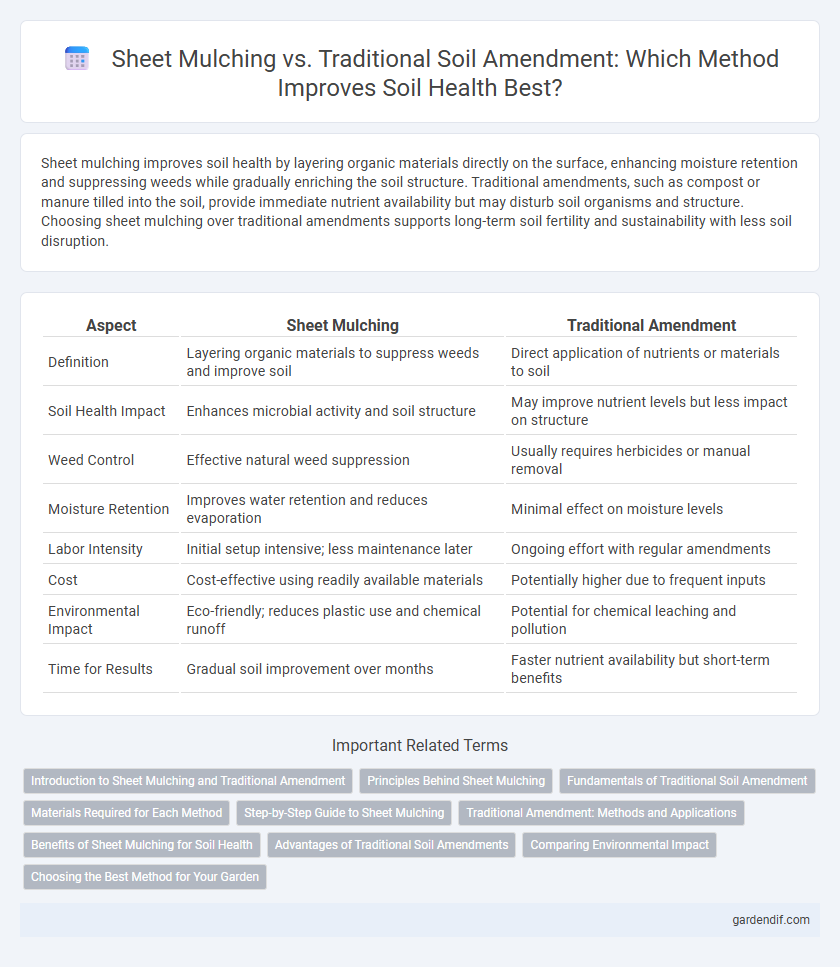
Sheet mulching improves soil health by layering organic materials directly on the surface, enhancing moisture retention and suppressing weeds while gradually enriching the soil structure. Traditional amendments, such as compost or manure tilled into the soil, provide immediate nutrient availability but may disturb soil organisms and structure. Choosing sheet mulching over traditional amendments supports long-term soil fertility and sustainability with less soil disruption.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Sheet Mulching | Traditional Amendment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Layering organic materials to suppress weeds and improve soil | Direct application of nutrients or materials to soil |
| Soil Health Impact | Enhances microbial activity and soil structure | May improve nutrient levels but less impact on structure |
| Weed Control | Effective natural weed suppression | Usually requires herbicides or manual removal |
| Moisture Retention | Improves water retention and reduces evaporation | Minimal effect on moisture levels |
| Labor Intensity | Initial setup intensive; less maintenance later | Ongoing effort with regular amendments |
| Cost | Cost-effective using readily available materials | Potentially higher due to frequent inputs |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly; reduces plastic use and chemical runoff | Potential for chemical leaching and pollution |
| Time for Results | Gradual soil improvement over months | Faster nutrient availability but short-term benefits |
Introduction to Sheet Mulching and Traditional Amendment
Sheet mulching is an organic gardening technique that involves layering biodegradable materials like cardboard, compost, and mulch directly on soil to suppress weeds, retain moisture, and enhance soil fertility. Traditional amendments typically consist of incorporating single nutrients or organic matter such as compost, manure, or lime into the soil to improve texture and nutrient content. While traditional amendments target specific soil deficiencies, sheet mulching creates a self-sustaining ecosystem that promotes long-term soil health and biodiversity.
Principles Behind Sheet Mulching
Sheet mulching relies on layering organic materials like cardboard, compost, and mulch to suppress weeds, retain soil moisture, and gradually improve soil structure through natural decomposition. This method enhances microbial activity and nutrient cycling by creating a habitat rich in organic matter, contrasting with traditional amendments that often involve direct soil mixing and chemical inputs. The principles behind sheet mulching emphasize soil health restoration and erosion control through a no-till, carbon-rich approach that mimics natural forest floor processes.
Fundamentals of Traditional Soil Amendment
Traditional soil amendment fundamentally enhances soil fertility by incorporating organic matter such as compost, manure, and natural minerals directly into the soil to improve nutrient availability, structure, and microbial activity. This method promotes long-term soil health by balancing pH levels and increasing cation exchange capacity, facilitating better water retention and root growth. Unlike sheet mulching, traditional amendments require periodic mixing and integration, ensuring nutrients are evenly distributed throughout the root zone.
Materials Required for Each Method
Sheet mulching requires layers of biodegradable materials such as cardboard or newspaper for weed suppression, followed by organic matter like compost, mulch, and wood chips to enhance soil fertility and moisture retention. Traditional amendment involves direct incorporation of compost, manure, lime, or chemical fertilizers into the soil to improve nutrient content and pH balance. Sheet mulching emphasizes natural decomposition through layering, while traditional methods rely on soil mixing and nutrient addition for immediate effects.
Step-by-Step Guide to Sheet Mulching
Sheet mulching involves layering organic materials such as cardboard, compost, and mulch directly on top of the soil to suppress weeds and improve soil fertility, avoiding soil disturbance common in traditional amendments like tilling. This method enhances soil structure by promoting microbial activity and moisture retention through gradual decomposition of layered materials, contrasting with traditional amendment where nutrients are often added through fertilizers or soil mixing. A step-by-step guide to sheet mulching includes clearing the area, laying down cardboard or newspaper to block weeds, adding a nutrient-rich compost layer, and finishing with a thick mulch layer, all of which create a living soil ecosystem and reduce erosion.
Traditional Amendment: Methods and Applications
Traditional soil amendments involve incorporating organic matter such as compost, manure, or green manure directly into the soil to enhance fertility and structure. These methods improve nutrient availability, water retention, and microbial activity by physically mixing amendments into the topsoil, often using tilling or digging techniques. Applications vary depending on crop requirements and soil conditions, with precise timing and amendment ratios critical for optimizing plant growth and soil health.
Benefits of Sheet Mulching for Soil Health
Sheet mulching improves soil health by enhancing organic matter content, promoting microbial activity, and reducing soil erosion compared to traditional amendments. It creates a protective mulch layer that conserves moisture, suppresses weeds, and gradually breaks down, enriching the soil structure. This method facilitates better nutrient cycling and supports sustainable soil fertility without the compaction risks associated with conventional tilling.
Advantages of Traditional Soil Amendments
Traditional soil amendments improve soil fertility by adding organic matter such as compost, manure, or lime, which enhances nutrient content and soil structure. These amendments promote microbial activity and water retention, leading to healthier plant growth and increased crop yields. Unlike sheet mulching, traditional methods allow more precise nutrient adjustments tailored to specific soil deficiencies.
Comparing Environmental Impact
Sheet mulching significantly reduces soil erosion and improves moisture retention by creating a protective organic layer, which enhances soil biodiversity and carbon sequestration. Traditional amendments like tilling and synthetic fertilizers often disrupt soil structure, increase greenhouse gas emissions, and contaminate waterways through runoff. Overall, sheet mulching offers a more sustainable and environmentally friendly approach compared to conventional soil amendment methods.
Choosing the Best Method for Your Garden
Sheet mulching improves soil structure by layering organic materials like cardboard and compost, fostering moisture retention and weed suppression, ideal for new garden beds. Traditional amendment involves incorporating compost or fertilizers directly into the soil, providing targeted nutrient boosts for established plants. Selecting the best method depends on soil health, garden goals, and maintenance preferences to optimize plant growth and soil fertility.
Sheet mulching vs Traditional amendment Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com