
Raised Bed Soil vs Ground Soil Illustration
Raised bed soil offers improved drainage, enhanced nutrient retention, and better aeration compared to ground soil, promoting healthier root development and higher crop yields. Ground soil often suffers from compaction and variable texture, which can hinder root growth and limit water infiltration. Optimizing soil mix in raised beds with organic matter and balanced nutrients creates an ideal growing environment unmatched by traditional ground soil.
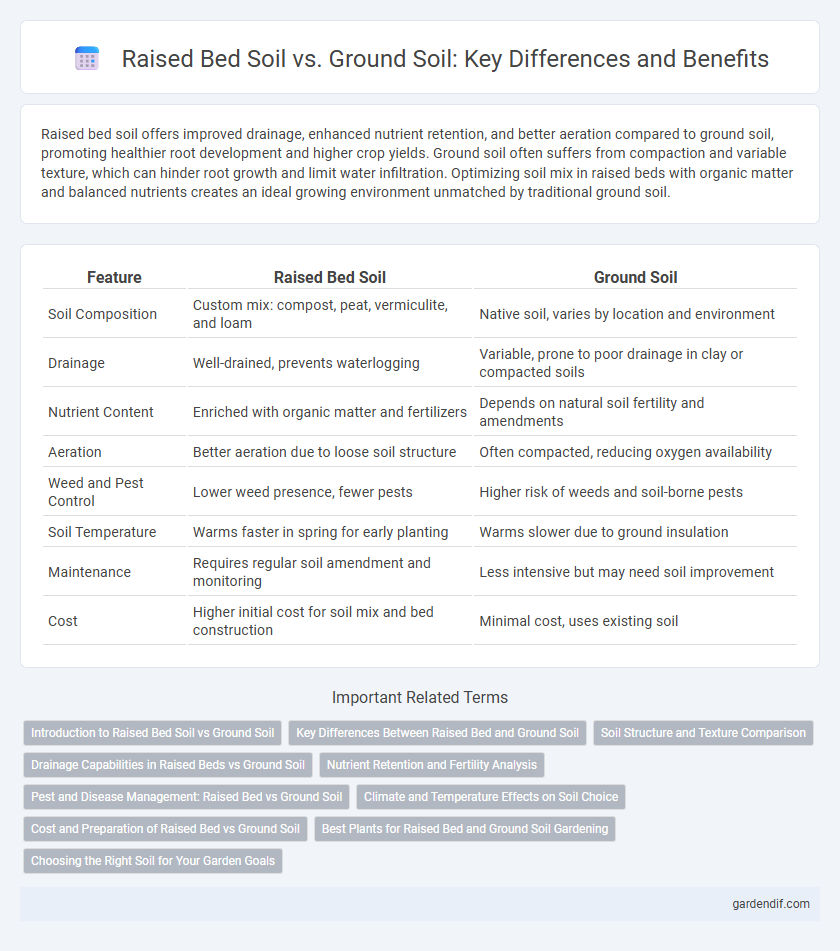
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Raised Bed Soil | Ground Soil |
|---|---|---|
| Soil Composition | Custom mix: compost, peat, vermiculite, and loam | Native soil, varies by location and environment |
| Drainage | Well-drained, prevents waterlogging | Variable, prone to poor drainage in clay or compacted soils |
| Nutrient Content | Enriched with organic matter and fertilizers | Depends on natural soil fertility and amendments |
| Aeration | Better aeration due to loose soil structure | Often compacted, reducing oxygen availability |
| Weed and Pest Control | Lower weed presence, fewer pests | Higher risk of weeds and soil-borne pests |
| Soil Temperature | Warms faster in spring for early planting | Warms slower due to ground insulation |
| Maintenance | Requires regular soil amendment and monitoring | Less intensive but may need soil improvement |
| Cost | Higher initial cost for soil mix and bed construction | Minimal cost, uses existing soil |
Introduction to Raised Bed Soil vs Ground Soil
Raised bed soil typically consists of a carefully balanced mixture of organic matter, sand, and compost that ensures superior drainage and nutrient availability compared to ground soil. Ground soil varies widely in texture and composition, often containing more clay or compacted particles, which can impede root growth and water movement. Choosing raised bed soil enhances plant health by providing an optimized environment tailored for specific crops.
Key Differences Between Raised Bed and Ground Soil
Raised bed soil typically offers improved drainage, higher nutrient content, and better root aeration compared to ground soil, which can be denser and prone to compaction. Raised beds enable precise control over soil composition, pH balance, and organic matter levels, fostering optimal conditions for plant growth. Ground soil varies widely depending on local conditions and often requires amendment to match the tailored benefits provided by raised bed soil.
Soil Structure and Texture Comparison
Raised bed soil typically features a lighter, well-aerated structure with a balanced texture of sand, silt, and clay, promoting optimal root growth and water drainage. Ground soil often contains denser particles and varying organic matter content, which can lead to compaction and poor drainage affecting plant health. Comparing soil structure and texture, raised beds offer improved porosity and nutrient availability, enhancing plant development compared to traditional ground soil.
Drainage Capabilities in Raised Beds vs Ground Soil
Raised bed soil typically offers superior drainage capabilities compared to ground soil due to its elevated structure and controlled soil composition, which often includes a mix of organic matter, sand, and compost. This enhanced drainage prevents waterlogging and promotes root health by allowing excess water to flow away more efficiently. In contrast, ground soil, especially in compacted or clay-heavy areas, tends to retain water longer, increasing the risk of poor aeration and root rot.
Nutrient Retention and Fertility Analysis
Raised bed soil typically offers superior nutrient retention compared to ground soil due to its enhanced drainage and aeration, which supports healthy microbial activity essential for fertility. Fertility analysis frequently reveals higher organic matter content and balanced nutrient profiles in raised beds, promoting robust plant growth and sustained soil health. In contrast, ground soil often suffers from compaction and nutrient leaching, reducing its overall fertility and long-term productivity.
Pest and Disease Management: Raised Bed vs Ground Soil
Raised bed soil offers improved drainage and aeration, reducing conditions that favor soil-borne pests and diseases compared to ground soil. Elevated soil temperature in raised beds inhibits the proliferation of fungal pathogens, while ground soil often retains moisture, creating a breeding ground for root rot and nematodes. Incorporating organic matter and crop rotation in raised beds further enhances pest resistance by promoting beneficial microorganisms and disrupting pest life cycles more effectively than traditional ground planting.
Climate and Temperature Effects on Soil Choice
Raised bed soil offers better drainage and warms up faster in cooler climates, promoting early plant growth compared to ground soil. Ground soil retains more moisture, which can be advantageous in hot, dry regions but may slow warming in colder temperatures. Gardeners should consider local climate and temperature fluctuations when choosing between raised bed and ground soil to optimize plant health and yield.
Cost and Preparation of Raised Bed vs Ground Soil
Raised bed soil typically incurs higher initial costs due to the need for constructing bed frames and purchasing quality soil mixes, whereas ground soil requires minimal upfront investment as it utilizes existing earth. Preparation of raised bed soil involves thorough soil amendment and mixing for optimal drainage and nutrient content, while ground soil often demands extensive tilling, weed removal, and conditioning to improve fertility. Over time, raised beds offer better control over soil quality and reduce maintenance efforts compared to ground soil, which may need periodic rejuvenation.
Best Plants for Raised Bed and Ground Soil Gardening
Raised bed soil offers superior drainage and nutrient control, making it ideal for plants like tomatoes, lettuce, carrots, and herbs that thrive in well-aerated, rich soil. Ground soil supports deep-rooted plants such as potatoes, beans, and perennials due to its natural ecosystem and volume. Choosing the right plants for each soil type maximizes growth potential and yield, enhancing garden productivity and health.
Choosing the Right Soil for Your Garden Goals
Raised bed soil offers enhanced drainage, aeration, and nutrient control compared to traditional ground soil, making it ideal for gardeners seeking higher yields and reduced soil compaction. Ground soil varies widely based on local conditions, often requiring amendment to improve texture, fertility, and pH balance for specific plant needs. Selecting the right soil depends on your garden goals, such as maximizing growth, improving root health, or simplifying maintenance, with raised bed soil providing a customizable medium versus the natural variability of ground soil.
Raised Bed Soil vs Ground Soil Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com