
Compost amendment vs Peat amendment Illustration
Compost amendment improves soil structure by enhancing microbial activity and nutrient content, leading to better plant growth and soil fertility. Peat amendment primarily increases soil water retention and aeration but has limited nutrient value and raises environmental concerns due to peat extraction. Choosing between compost and peat depends on the desired soil benefits, with compost being a more sustainable and nutrient-rich option.
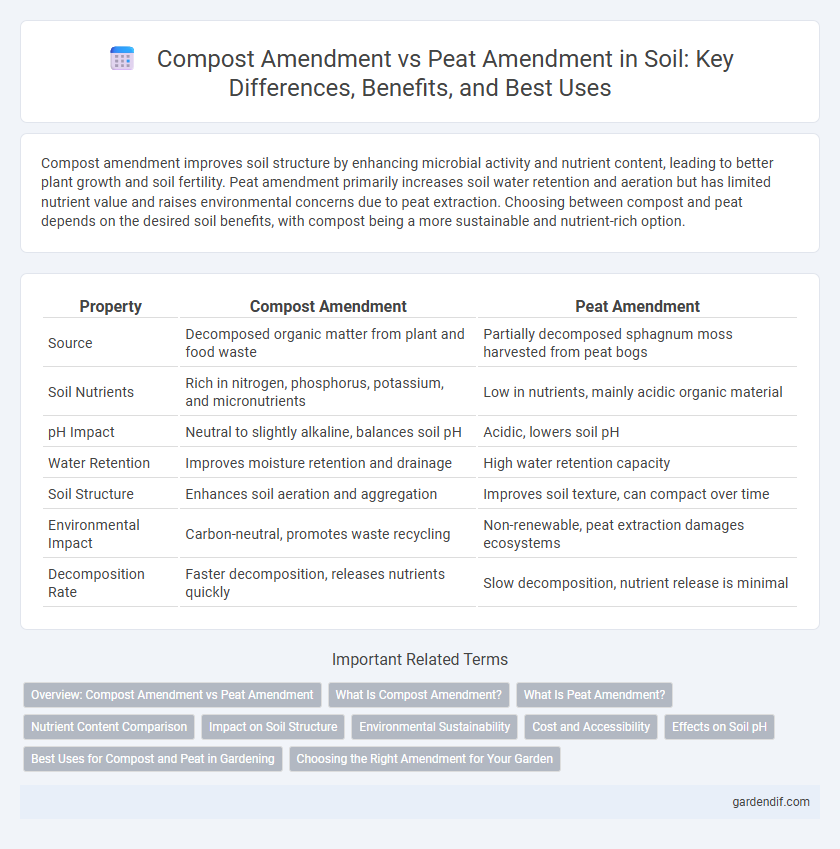
Table of Comparison
| Property | Compost Amendment | Peat Amendment |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Decomposed organic matter from plant and food waste | Partially decomposed sphagnum moss harvested from peat bogs |
| Soil Nutrients | Rich in nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and micronutrients | Low in nutrients, mainly acidic organic material |
| pH Impact | Neutral to slightly alkaline, balances soil pH | Acidic, lowers soil pH |
| Water Retention | Improves moisture retention and drainage | High water retention capacity |
| Soil Structure | Enhances soil aeration and aggregation | Improves soil texture, can compact over time |
| Environmental Impact | Carbon-neutral, promotes waste recycling | Non-renewable, peat extraction damages ecosystems |
| Decomposition Rate | Faster decomposition, releases nutrients quickly | Slow decomposition, nutrient release is minimal |
Overview: Compost Amendment vs Peat Amendment
Compost amendments enhance soil fertility by increasing organic matter, improving microbial activity, and boosting nutrient availability, making it ideal for sustainable gardening and agriculture. Peat amendments primarily improve soil structure and water retention but have limited nutrient content and raise environmental concerns due to peatland degradation. Choosing between compost and peat depends on soil needs, with compost favored for nutrient enrichment and peat selected for moisture management.
What Is Compost Amendment?
Compost amendment is an organic soil enhancer made from decomposed plant and animal materials that improves soil structure, nutrient content, and microbial activity. It increases water retention, aeration, and promotes healthy root development, making soil more fertile and sustainable for plant growth. Unlike peat amendment, compost supports soil biodiversity and reduces the need for chemical fertilizers by supplying essential nutrients naturally.
What Is Peat Amendment?
Peat amendment refers to the use of partially decomposed organic material harvested from peat bogs to improve soil structure and water retention. It enhances soil aeration and nutrient availability, making it popular in horticulture and agriculture. However, peat is a non-renewable resource and its extraction raises environmental concerns related to habitat destruction and carbon emissions.
Nutrient Content Comparison
Compost amendment typically contains higher levels of essential nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium compared to peat amendment, making it more effective for enhancing soil fertility. Peat amendment primarily improves soil structure and water retention but has low inherent nutrient content, often requiring supplementary fertilization. The nutrient-rich profile of compost supports robust plant growth and microbial activity, whereas peat serves mainly as a soil conditioner with minimal direct nutrient contribution.
Impact on Soil Structure
Compost amendment improves soil structure by increasing organic matter content, enhancing soil aggregation, and boosting microbial activity, which promotes better aeration and water retention. Peat amendment, while improving soil water holding capacity, tends to compact over time, potentially reducing soil porosity and aeration. Compost's balanced nutrient profile further supports the development of stable soil aggregates compared to the more acidic and less nutrient-rich nature of peat.
Environmental Sustainability
Compost amendment enhances soil fertility by recycling organic waste, reducing landfill use, and lowering greenhouse gas emissions compared to peat amendment. Peat extraction depletes carbon-rich wetlands, releasing stored carbon and harming biodiversity, which undermines environmental sustainability. Utilizing compost supports regenerative agriculture and promotes carbon sequestration, making it a more eco-friendly soil amendment choice.
Cost and Accessibility
Compost amendments are generally more cost-effective than peat amendments due to their organic waste origins and local availability, which reduces transportation expenses. Peat amendments often involve higher costs linked to extraction, processing, and environmental regulations limiting peat harvesting. Accessibility favors compost, as it can be produced from various organic materials worldwide, while peat sources are geographically limited and subject to sustainability concerns.
Effects on Soil pH
Compost amendment typically raises soil pH by adding alkaline organic matter, improving nutrient availability and microbial activity. In contrast, peat amendment tends to lower soil pH due to its acidic nature, making it suitable for acid-loving plants but potentially limiting nutrient uptake for others. Selecting between compost and peat amendments depends on the desired soil pH adjustment and specific crop requirements.
Best Uses for Compost and Peat in Gardening
Compost amendment is ideal for enhancing soil structure, increasing nutrient content, and promoting microbial activity, making it best suited for vegetable gardens, flower beds, and container plants requiring rich, well-drained soil. Peat amendment excels in improving soil acidity and water retention, which benefits acid-loving plants like blueberries, azaleas, and rhododendrons. Using compost supports sustainable gardening by recycling organic waste, while peat is preferred for maintaining moisture in potting mixes and sandy soils.
Choosing the Right Amendment for Your Garden
Compost amendment enhances soil fertility by adding organic matter and beneficial microbes, improving water retention and nutrient availability for plants, while peat amendment increases soil acidity and aeration but offers limited nutrients. Choosing the right amendment depends on soil type and plant requirements; compost suits nutrient-poor, heavy soils, whereas peat benefits acidic-loving plants or sandy soils needing improved structure. Evaluating soil pH, texture, and nutrient levels optimizes amendment selection for sustainable garden growth.
Compost amendment vs Peat amendment Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com