
Organic fertilizer vs Synthetic fertilizer Illustration
Organic fertilizer enriches soil by improving its structure and increasing microbial activity, enhancing long-term fertility sustainably. Synthetic fertilizer provides targeted nutrient supply for rapid plant growth but may lead to soil degradation and nutrient imbalances over time. Choosing organic fertilizer promotes healthier soil ecosystems, while synthetic options offer immediate nutrient availability.
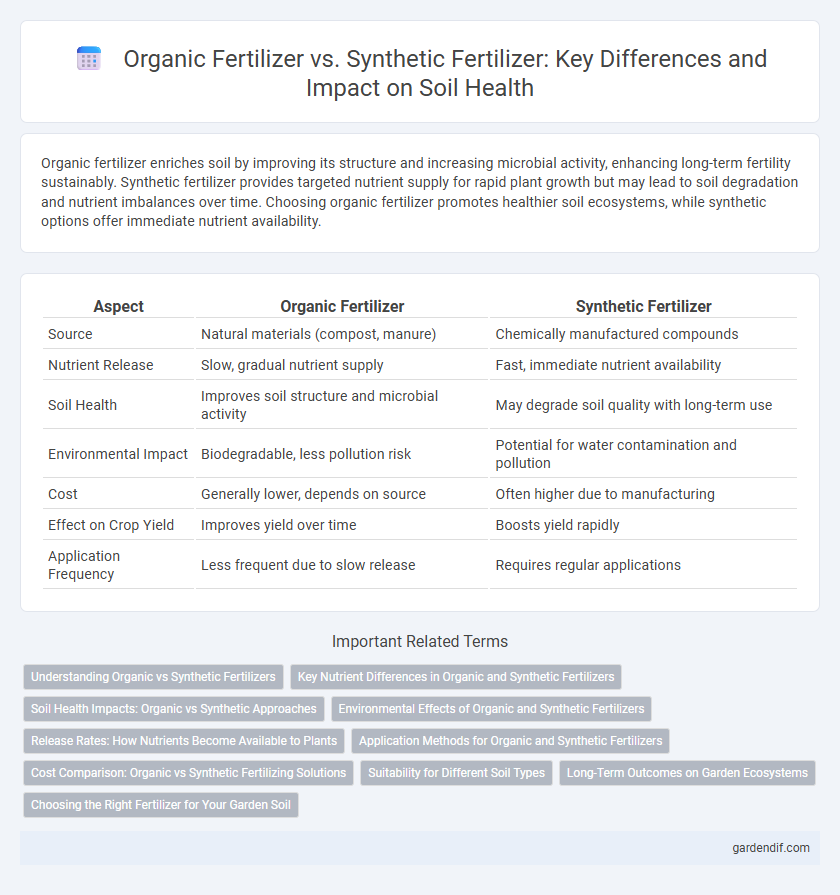
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Organic Fertilizer | Synthetic Fertilizer |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Natural materials (compost, manure) | Chemically manufactured compounds |
| Nutrient Release | Slow, gradual nutrient supply | Fast, immediate nutrient availability |
| Soil Health | Improves soil structure and microbial activity | May degrade soil quality with long-term use |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, less pollution risk | Potential for water contamination and pollution |
| Cost | Generally lower, depends on source | Often higher due to manufacturing |
| Effect on Crop Yield | Improves yield over time | Boosts yield rapidly |
| Application Frequency | Less frequent due to slow release | Requires regular applications |
Understanding Organic vs Synthetic Fertilizers
Organic fertilizers release nutrients slowly through natural processes, improving soil structure and microbial activity, which enhances long-term soil fertility. Synthetic fertilizers provide readily available nutrients for rapid plant growth but may lead to nutrient imbalances and soil degradation over time. Understanding the nutrient release patterns and environmental impact of each fertilizer type is crucial for sustainable soil management.
Key Nutrient Differences in Organic and Synthetic Fertilizers
Organic fertilizers release nutrients slowly through natural decomposition, supplying essential elements such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium in complex forms that promote long-term soil health. Synthetic fertilizers provide concentrated, readily available nutrients in specific ratios, allowing precise nutrient management but often lacking micronutrients and organic matter. The key difference lies in organic fertilizers enhancing soil microbial activity and structure, while synthetic options focus on immediate nutrient availability and targeted fertilization.
Soil Health Impacts: Organic vs Synthetic Approaches
Organic fertilizers enhance soil health by improving microbial activity, increasing nutrient retention, and boosting soil structure through natural decomposition processes. Synthetic fertilizers often provide immediate nutrient availability but can lead to soil acidification, diminished microbial diversity, and long-term nutrient imbalances. Sustainable soil management favors organic inputs to promote resilience, biodiversity, and long-term fertility, contrasting with the short-term, impact-prone benefits of synthetic counterparts.
Environmental Effects of Organic and Synthetic Fertilizers
Organic fertilizers enhance soil biodiversity and structure by promoting microbial activity and reducing chemical runoff, thus minimizing water pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. In contrast, synthetic fertilizers often lead to nutrient leaching, soil acidification, and increased nitrous oxide emissions, contributing to environmental degradation and climate change. Sustainable soil management benefits from prioritizing organic inputs to maintain ecosystem health and long-term agricultural productivity.
Release Rates: How Nutrients Become Available to Plants
Organic fertilizers release nutrients slowly through microbial activity and decomposition, providing a steady nutrient supply that matches plant uptake. Synthetic fertilizers dissolve quickly, making nutrients immediately available but increasing the risk of leaching and nutrient runoff. Understanding these release rates helps optimize fertilization strategies for sustained soil fertility and plant health.
Application Methods for Organic and Synthetic Fertilizers
Organic fertilizers are typically applied through methods such as compost incorporation, mulching, or side-dressing to improve soil structure and microbial activity. Synthetic fertilizers are often applied using precise techniques like broadcasting, fertigation, or foliar spraying to deliver specific nutrient ratios quickly and efficiently. These application methods directly impact nutrient availability, soil health, and crop yield outcomes.
Cost Comparison: Organic vs Synthetic Fertilizing Solutions
Organic fertilizers typically incur higher upfront costs due to the labor-intensive production processes and slower nutrient release rates, requiring larger application volumes for effective soil enrichment. Synthetic fertilizers offer a cost-effective solution with precise nutrient formulations and faster availability, reducing frequency of application and immediate crop response. However, long-term soil health benefits and reduced environmental impacts of organic options may offset initial expenses, presenting a strategic investment in sustainable agriculture.
Suitability for Different Soil Types
Organic fertilizers enhance soil structure and water retention, making them ideal for sandy and loamy soils that benefit from improved nutrient-holding capacity. Synthetic fertilizers provide precise nutrient formulations suitable for clay and nutrient-deficient soils, allowing targeted correction of imbalances. Selecting the appropriate fertilizer depends on soil texture, pH, and nutrient profile to maximize plant growth and soil health.
Long-Term Outcomes on Garden Ecosystems
Organic fertilizer enhances soil health by promoting microbial diversity and improving soil structure, leading to sustained nutrient availability and increased plant resilience over time. Synthetic fertilizer provides immediate nutrient supply but may disrupt soil microbial balance and cause nutrient runoff, resulting in long-term soil degradation and reduced ecosystem stability. Gardens managed with organic fertilizers typically exhibit higher biodiversity, better water retention, and greater resistance to pests and diseases compared to those relying on synthetic inputs.
Choosing the Right Fertilizer for Your Garden Soil
Organic fertilizer improves soil structure and microbial activity by adding natural nutrients and enhancing water retention. Synthetic fertilizer provides precise nutrient control and faster plant growth but may risk soil degradation and nutrient imbalance over time. Selecting the right fertilizer depends on soil health, crop needs, and long-term sustainability goals for your garden.
Organic fertilizer vs Synthetic fertilizer Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com