
Peat moss vs Coco coir Illustration
Peat moss and coco coir are popular growing mediums with distinct properties: peat moss is acidic and rich in organic matter, making it ideal for acid-loving plants, while coco coir offers excellent water retention and aeration with a neutral pH, suitable for a wide range of crops. Peat moss is a non-renewable resource harvested from peat bogs, raising environmental concerns, whereas coco coir is an eco-friendly alternative derived from coconut husks. Choosing between peat moss and coco coir depends on plant requirements, sustainability preferences, and soil amendment goals.
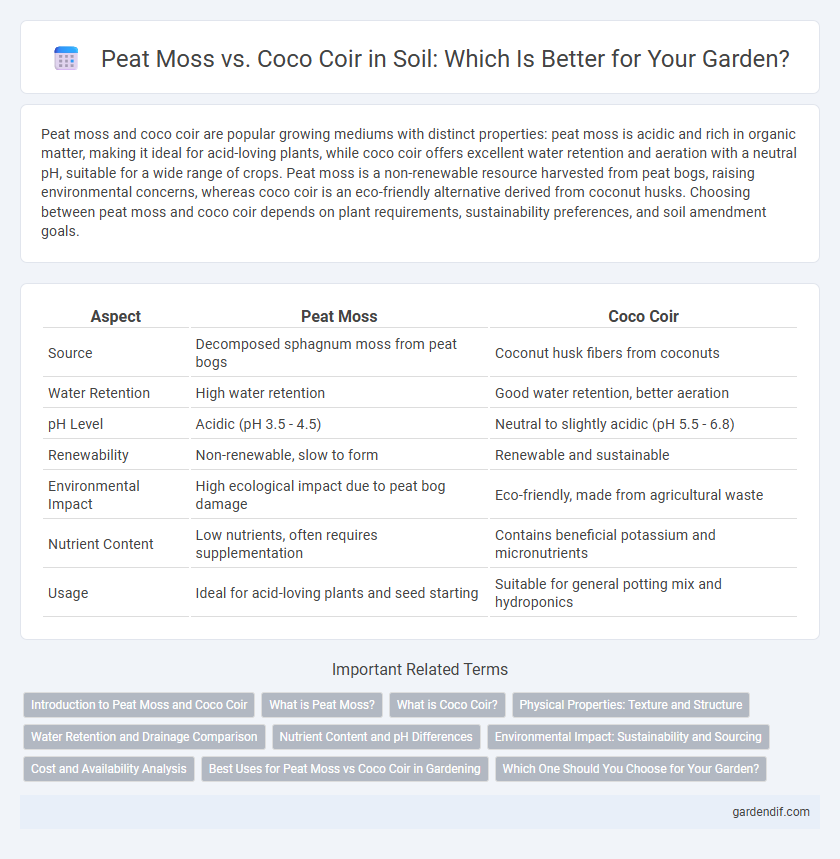
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Peat Moss | Coco Coir |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Decomposed sphagnum moss from peat bogs | Coconut husk fibers from coconuts |
| Water Retention | High water retention | Good water retention, better aeration |
| pH Level | Acidic (pH 3.5 - 4.5) | Neutral to slightly acidic (pH 5.5 - 6.8) |
| Renewability | Non-renewable, slow to form | Renewable and sustainable |
| Environmental Impact | High ecological impact due to peat bog damage | Eco-friendly, made from agricultural waste |
| Nutrient Content | Low nutrients, often requires supplementation | Contains beneficial potassium and micronutrients |
| Usage | Ideal for acid-loving plants and seed starting | Suitable for general potting mix and hydroponics |
Introduction to Peat Moss and Coco Coir
Peat moss is an organic material derived from decomposed sphagnum moss, known for its excellent water retention and acidic pH, making it ideal for acid-loving plants and improving soil aeration. Coco coir, sourced from coconut husks, offers a sustainable alternative with high water retention, good aeration, and a near-neutral pH suitable for various plants. Both substrates enhance soil structure but differ in environmental impact and pH levels, influencing their choice for specific gardening needs.
What is Peat Moss?
Peat moss is a natural, organic material harvested from decomposed sphagnum moss in peat bogs, known for its excellent water retention and aeration properties. It is acidic, with a pH typically between 3.5 and 4.5, making it ideal for acid-loving plants like blueberries and azaleas. Peat moss improves soil structure by increasing porosity and moisture-holding capacity but is non-renewable due to its slow formation rate.
What is Coco Coir?
Coco coir is a natural fiber extracted from the outer husk of coconut shells, commonly used as an environmentally friendly soil amendment in gardening and horticulture. It offers excellent water retention, aeration, and root support, making it ideal for hydroponic systems and potted plants. Unlike peat moss, coco coir is renewable and biodegradable, reducing environmental impact while enhancing soil structure.
Physical Properties: Texture and Structure
Peat moss features a fine, spongy texture that retains moisture effectively, promoting aeration and water retention in soil mixes. Coco coir has a coarse, fibrous structure, providing excellent drainage and air circulation while resisting compaction over time. Both materials improve soil texture differently, with peat moss enhancing water-holding capacity and coco coir offering superior durability and aeration.
Water Retention and Drainage Comparison
Peat moss has superior water retention capabilities, absorbing up to 20 times its weight in water, making it ideal for moisture-loving plants. Coco coir offers better drainage and aeration due to its fibrous structure, preventing root rot in plants that require well-drained soil. Both substrates contribute to soil health, but peat moss retains moisture longer while coco coir ensures optimal air flow and prevents waterlogging.
Nutrient Content and pH Differences
Peat moss typically has a low nutrient content and a naturally acidic pH ranging from 3.5 to 4.5, requiring supplementation for most plants. Coco coir contains more inherent potassium and other trace minerals, with a near-neutral pH around 5.5 to 6.8, making it more suitable for a broader range of crops without extensive pH adjustments. Both substrates offer excellent water retention but differ significantly in their nutrient profiles and pH levels, influencing plant growth and soil management practices.
Environmental Impact: Sustainability and Sourcing
Peat moss extraction significantly contributes to the degradation of sensitive peatland ecosystems, releasing stored carbon and reducing biodiversity, whereas coco coir is a renewable byproduct of coconut husks, making it a more sustainable choice. Peatlands take thousands of years to form, while coco coir is rapidly renewable, helping reduce environmental footprint. Sustainable sourcing of coco coir often involves responsible harvesting and minimizing transportation emissions, which enhances its eco-friendly profile compared to peat moss.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Peat moss typically costs more due to its limited renewable supply and environmental regulations, while coco coir offers a more affordable and sustainable alternative derived from coconut husks, which are widely available as agricultural waste. In terms of availability, coco coir is increasingly accessible in global markets, especially in regions near coconut-producing countries, whereas peat moss extraction is restricted in many areas to preserve peatlands. This difference in cost and availability makes coco coir a preferred choice for large-scale horticultural and gardening applications seeking cost-efficiency and sustainability.
Best Uses for Peat Moss vs Coco Coir in Gardening
Peat moss excels in acid-loving plants like blueberries and azaleas due to its low pH and high moisture retention, making it ideal for seed starting and improving soil aeration. Coco coir is preferred for hydroponic systems and container gardening because of its superior water drainage, neutral pH, and sustainable renewable nature. Both mediums enhance soil structure, but peat moss is better suited for long-term soil acidification while coco coir supports faster root growth and oxygen exchange.
Which One Should You Choose for Your Garden?
Peat moss and coco coir offer distinct benefits for soil improvement, with peat moss providing excellent water retention and acidity suitable for acid-loving plants, while coco coir offers superior aeration, sustainable sourcing, and neutral pH ideal for a wider variety of plants. Coco coir's renewable nature and ability to retain moisture without compaction make it a preferred choice for environmentally conscious gardeners seeking long-term soil health. For acidic soil requirements and moisture retention, peat moss remains valuable, but coco coir's versatility and eco-friendliness often make it the better overall amendment for most gardens.
Peat moss vs Coco coir Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com