
Raised beds vs In-ground beds Illustration
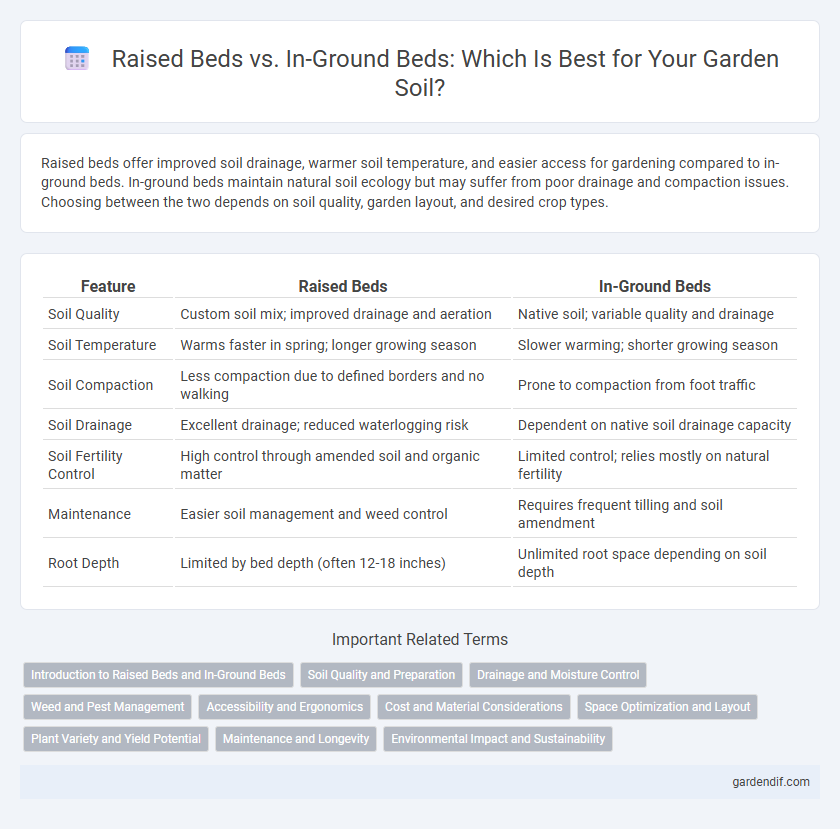
Raised beds offer improved soil drainage, warmer soil temperature, and easier access for gardening compared to in-ground beds. In-ground beds maintain natural soil ecology but may suffer from poor drainage and compaction issues. Choosing between the two depends on soil quality, garden layout, and desired crop types.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Raised Beds | In-Ground Beds |
|---|---|---|
| Soil Quality | Custom soil mix; improved drainage and aeration | Native soil; variable quality and drainage |
| Soil Temperature | Warms faster in spring; longer growing season | Slower warming; shorter growing season |
| Soil Compaction | Less compaction due to defined borders and no walking | Prone to compaction from foot traffic |
| Soil Drainage | Excellent drainage; reduced waterlogging risk | Dependent on native soil drainage capacity |
| Soil Fertility Control | High control through amended soil and organic matter | Limited control; relies mostly on natural fertility |
| Maintenance | Easier soil management and weed control | Requires frequent tilling and soil amendment |
| Root Depth | Limited by bed depth (often 12-18 inches) | Unlimited root space depending on soil depth |
Introduction to Raised Beds and In-Ground Beds
Raised beds offer improved soil drainage, better root growth, and easier weed control compared to in-ground beds. In-ground beds rely on existing soil conditions, which can vary in texture, fertility, and drainage, affecting plant health and yield. Both bed types influence soil temperature and moisture retention, crucial factors for successful gardening.
Soil Quality and Preparation
Raised beds offer enhanced soil quality by allowing gardeners to control soil composition, drainage, and nutrient levels more effectively than in-ground beds. Soil in raised beds warms faster in spring and is less prone to compaction, promoting healthier root growth and higher yields. In contrast, in-ground beds depend on the existing native soil conditions, requiring more intensive amendment and preparation to achieve optimal fertility and structure.
Drainage and Moisture Control
Raised beds offer superior drainage compared to in-ground beds, preventing waterlogging and promoting healthier root systems by allowing excess water to escape more easily. In-ground beds tend to retain more moisture due to soil compaction and poor drainage, which can increase the risk of root rot and other moisture-related issues. Effective moisture control in raised beds can be further enhanced by using well-amended soil mixes and adding organic matter to maintain optimal water retention without saturation.
Weed and Pest Management
Raised beds improve weed and pest management by providing better soil drainage and aeration, which inhibits weed seed germination and reduces pest habitat. The elevated structure allows for easier application of mulch and physical barriers, limiting weed growth and pest access. In-ground beds often face increased weed pressure and pest infestations due to direct soil contact and denser planting conditions.
Accessibility and Ergonomics
Raised beds provide improved accessibility by elevating the soil surface, reducing the need for bending and kneeling, which benefits individuals with mobility challenges and minimizes strain on joints. In-ground beds require more physical effort to access and maintain, increasing discomfort and fatigue during planting, weeding, and harvesting. Ergonomically designed raised beds can be tailored to ideal heights, promoting better posture and reducing the risk of musculoskeletal injuries.
Cost and Material Considerations
Raised beds generally require more upfront investment due to the need for framing materials such as wood, metal, or composite, which can increase initial costs compared to in-ground beds. In-ground beds utilize existing soil, minimizing material expenses but may require soil amendments to enhance fertility and drainage, which adds to ongoing costs. Maintenance costs for raised beds tend to be lower over time since they offer better soil control and reduced compaction, potentially increasing overall cost-effectiveness despite higher initial expenditure.
Space Optimization and Layout
Raised beds maximize space efficiency by enabling intensive planting and vertical gardening, making them ideal for small or irregularly shaped areas. In-ground beds offer more flexible layout options and can accommodate larger plant varieties but may require more spacing to prevent soil compaction and optimize root growth. Strategic arrangement of raised beds can enhance airflow and sunlight exposure, further improving crop yield per square foot.
Plant Variety and Yield Potential
Raised beds offer improved soil drainage and temperature control, supporting a wider variety of plants that require specific growing conditions compared to in-ground beds. The enhanced soil quality in raised beds often results in higher yields due to better root aeration and nutrient availability. In-ground beds may limit plant diversity and yield potential due to soil compaction and variable moisture retention.
Maintenance and Longevity
Raised beds typically require more initial construction effort but offer easier access for maintenance tasks like weeding, watering, and soil amendments, extending the lifespan of the soil quality. In-ground beds may demand more consistent weed control and can suffer from soil compaction over time, reducing long-term productivity. Properly maintained raised beds often retain nutrients and moisture better, promoting sustainable plant growth and reducing soil degradation.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Raised beds reduce soil erosion and compaction by providing controlled growing environments and better drainage, which decreases the need for chemical inputs. In-ground beds preserve natural soil ecosystems but may require more water and fertilizers, potentially increasing environmental strain. Utilizing organic mulch and sustainable practices in either method enhances soil health and supports long-term environmental sustainability.
Raised beds vs In-ground beds Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com