
Foliar feeding vs Soil amendment Illustration
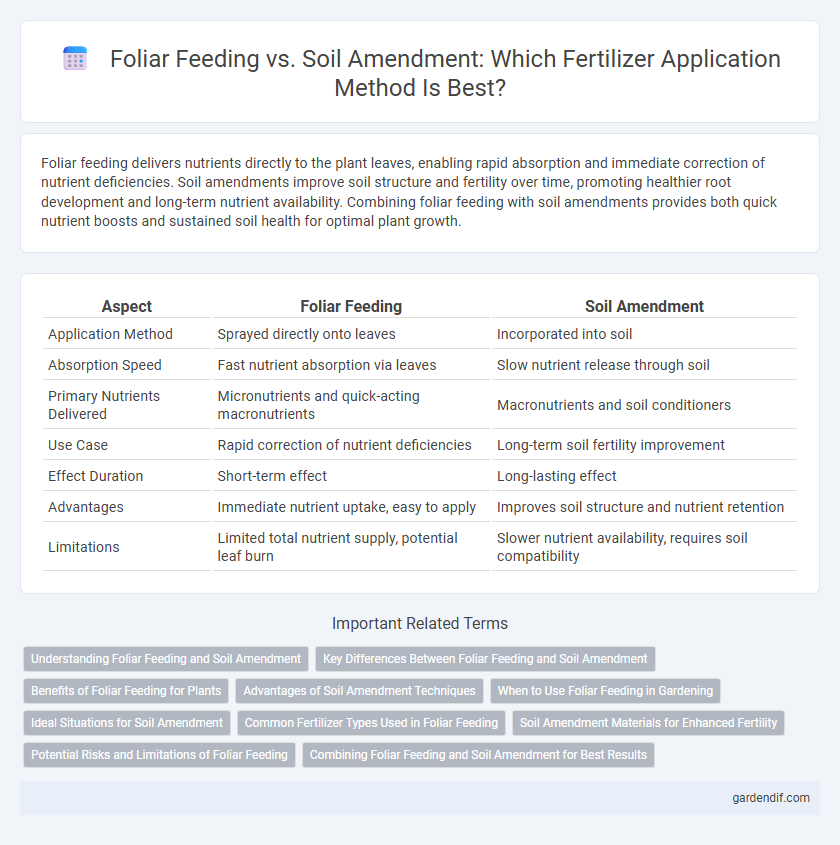
Foliar feeding delivers nutrients directly to the plant leaves, enabling rapid absorption and immediate correction of nutrient deficiencies. Soil amendments improve soil structure and fertility over time, promoting healthier root development and long-term nutrient availability. Combining foliar feeding with soil amendments provides both quick nutrient boosts and sustained soil health for optimal plant growth.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Foliar Feeding | Soil Amendment |
|---|---|---|
| Application Method | Sprayed directly onto leaves | Incorporated into soil |
| Absorption Speed | Fast nutrient absorption via leaves | Slow nutrient release through soil |
| Primary Nutrients Delivered | Micronutrients and quick-acting macronutrients | Macronutrients and soil conditioners |
| Use Case | Rapid correction of nutrient deficiencies | Long-term soil fertility improvement |
| Effect Duration | Short-term effect | Long-lasting effect |
| Advantages | Immediate nutrient uptake, easy to apply | Improves soil structure and nutrient retention |
| Limitations | Limited total nutrient supply, potential leaf burn | Slower nutrient availability, requires soil compatibility |
Understanding Foliar Feeding and Soil Amendment
Foliar feeding delivers essential nutrients directly to plant leaves, enabling rapid absorption and addressing micronutrient deficiencies more efficiently than soil application. Soil amendments improve soil structure, nutrient content, and microbial activity, fostering long-term plant health and root development. Integrating both techniques enhances nutrient availability while optimizing plant growth and crop yield.
Key Differences Between Foliar Feeding and Soil Amendment
Foliar feeding delivers nutrients directly to plant leaves, enabling rapid absorption and quick correction of nutrient deficiencies compared to soil amendments, which gradually improve soil fertility by enhancing nutrient availability and structure. Foliar feeding is ideal for immediate response to plant stress or deficiencies, while soil amendments provide long-term benefits by improving soil health, moisture retention, and microbial activity. The choice between foliar feeding and soil amendment depends on the urgency of nutrient needs versus sustainable soil management goals.
Benefits of Foliar Feeding for Plants
Foliar feeding delivers essential nutrients directly to plant leaves, enabling rapid absorption and immediate correction of nutrient deficiencies. This method enhances photosynthesis efficiency and boosts plant growth by supplying micronutrients that may be unavailable in the soil due to pH or environmental factors. Foliar applications reduce nutrient loss from leaching and volatilization, optimizing fertilizer use and promoting healthier, more resilient crops.
Advantages of Soil Amendment Techniques
Soil amendment techniques improve soil structure, enhance nutrient retention, and increase microbial activity, leading to sustained crop growth and higher yields. Unlike foliar feeding, which provides immediate but short-term nutrient supply, soil amendments create a long-lasting nutrient reservoir and improve overall soil health. These methods reduce nutrient leaching and promote better root development, optimizing plant nutrient uptake throughout the growing season.
When to Use Foliar Feeding in Gardening
Foliar feeding is most effective during periods of rapid plant growth or when nutrient deficiencies are quickly identified, as it allows for rapid absorption of nutrients through the leaves. It is ideal for correcting micronutrient deficits such as iron, zinc, or magnesium that soil amendments may not address promptly. Using foliar sprays during early morning or late afternoon enhances nutrient uptake while minimizing leaf burn.
Ideal Situations for Soil Amendment
Soil amendment is ideal for improving soil structure and nutrient retention in garden beds, especially in clay or sandy soils that require long-term fertility enhancement. It provides a stable supply of essential nutrients by enriching the root zone, promoting healthy root development and water retention. This method is best suited for crops or plants needing consistent nutrient access throughout the growing season.
Common Fertilizer Types Used in Foliar Feeding
Common fertilizer types used in foliar feeding include water-soluble nutrients such as urea, potassium nitrate, and calcium nitrate, which enable rapid absorption through leaf stomata. Micronutrients like zinc, iron, manganese, and magnesium are also frequently applied via foliar sprays to quickly correct specific nutrient deficiencies. Compared to soil amendments, foliar feeding provides a targeted, immediate nutrient boost, enhancing plant growth and productivity without altering soil composition.
Soil Amendment Materials for Enhanced Fertility
Soil amendment materials such as compost, biochar, and gypsum improve soil structure, nutrient retention, and microbial activity, leading to enhanced fertility. These materials increase the cation exchange capacity (CEC), promoting better nutrient availability and reducing leaching losses compared to foliar feeding. Incorporating organic matter through soil amendments supports long-term soil health and sustainability, making it a preferred method for boosting crop yields.
Potential Risks and Limitations of Foliar Feeding
Foliar feeding allows rapid nutrient absorption through leaves, but excessive application can cause leaf burn and toxicity due to nutrient imbalances. It is limited by environmental factors such as rain, high temperatures, and humidity, which reduce nutrient uptake efficiency. Reliance solely on foliar feeding may neglect root development and soil health, limiting long-term crop productivity.
Combining Foliar Feeding and Soil Amendment for Best Results
Combining foliar feeding and soil amendment enhances nutrient uptake by addressing both immediate plant nutritional needs and long-term soil fertility. Foliar feeding delivers micronutrients directly to leaves for rapid absorption, while soil amendments improve soil structure, moisture retention, and microbial activity essential for root development. Integrating these methods optimizes fertilizer efficiency, promotes balanced growth, and maximizes crop yield and quality.
Foliar feeding vs Soil amendment Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com