
Pelletized fertilizer vs Granular fertilizer Illustration
Pelletized fertilizer offers uniform size and shape, promoting even nutrient distribution and reducing dust during application compared to granular fertilizer. Granular fertilizer, while often more cost-effective, can vary in particle size, potentially leading to uneven nutrient release and application challenges. Choosing between pelletized and granular types depends on crop requirements, soil conditions, and application equipment compatibility.
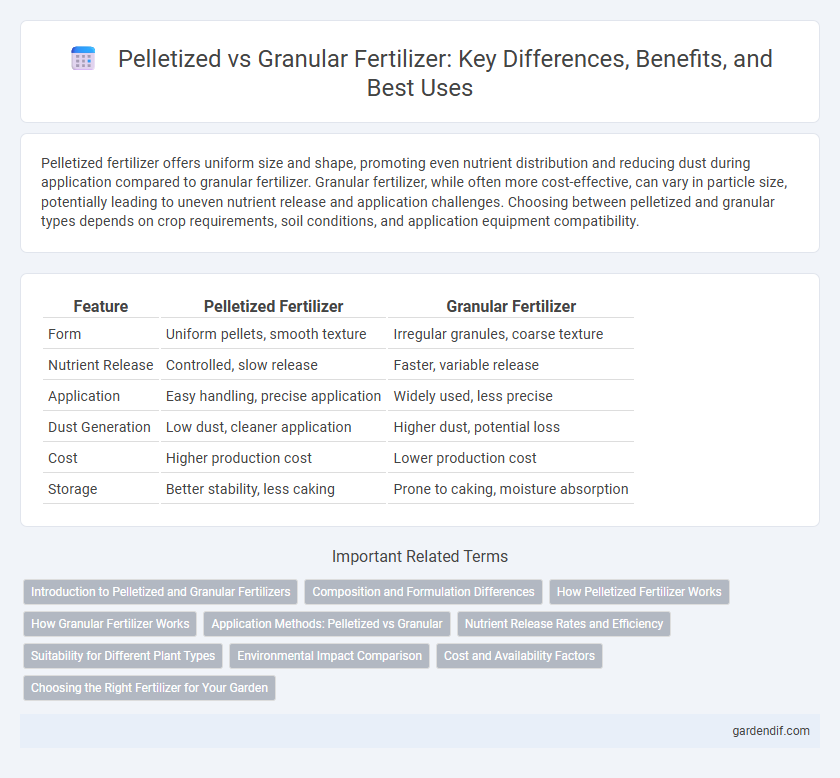
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Pelletized Fertilizer | Granular Fertilizer |
|---|---|---|
| Form | Uniform pellets, smooth texture | Irregular granules, coarse texture |
| Nutrient Release | Controlled, slow release | Faster, variable release |
| Application | Easy handling, precise application | Widely used, less precise |
| Dust Generation | Low dust, cleaner application | Higher dust, potential loss |
| Cost | Higher production cost | Lower production cost |
| Storage | Better stability, less caking | Prone to caking, moisture absorption |
Introduction to Pelletized and Granular Fertilizers
Pelletized fertilizers consist of finely ground nutrients compressed into uniform, spherical pellets that enhance nutrient release and reduce dust during application. Granular fertilizers are coarse particles varying in size and shape, providing slower nutrient dispersion suitable for long-term soil enrichment. Both forms offer targeted nutrient delivery but differ in application efficiency and nutrient availability based on crop requirements and soil conditions.
Composition and Formulation Differences
Pelletized fertilizer consists of uniformly sized, compressed particles that enhance nutrient release control and reduce dust compared to granular fertilizer, which contains irregularly sized crystals or particles. Pelletized formulations often incorporate binders and coating materials to improve handling and nutrient stability, while granular fertilizers rely on their natural crystalline structure. The composition of pelletized fertilizers is engineered for slow or controlled nutrient release, whereas granular types typically provide quicker nutrient availability due to their higher solubility and surface area variability.
How Pelletized Fertilizer Works
Pelletized fertilizer works by compressing nutrient-rich materials into dense, uniform pellets that dissolve slowly, providing a controlled release of essential nutrients to plants. This slow-release mechanism enhances nutrient uptake efficiency, minimizes leaching, and reduces environmental impact compared to traditional granular fertilizers. The consistent pellet size also improves application accuracy and ensures even distribution across soil surfaces.
How Granular Fertilizer Works
Granular fertilizer works by releasing nutrients slowly into the soil as the granules dissolve with moisture, providing a steady supply of essential elements such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium directly to plant roots. The physical form of granular fertilizer allows for uniform application and enhanced soil contact, improving nutrient absorption efficiency. This controlled nutrient release supports sustained plant growth and helps maintain soil fertility over time.
Application Methods: Pelletized vs Granular
Pelletized fertilizer offers uniform nutrient distribution and is ideal for precise application methods such as broadcasting or banding, ensuring better soil contact and reduced nutrient runoff. Granular fertilizer, with its coarser texture, is suited for spot application or side dressing, allowing targeted delivery to plant root zones for enhanced nutrient uptake. Choosing the appropriate application method depends on crop type, soil conditions, and desired nutrient release rates.
Nutrient Release Rates and Efficiency
Pelletized fertilizer offers a more controlled nutrient release rate, enhancing nutrient use efficiency by reducing losses through leaching and volatilization compared to granular fertilizer. Granular fertilizers typically release nutrients more rapidly, which can lead to quicker plant uptake but may increase the risk of nutrient runoff and reduced efficiency. Optimizing fertilizer choice based on crop needs and soil conditions ensures better nutrient availability and improved crop yield.
Suitability for Different Plant Types
Pelletized fertilizer offers uniform nutrient release ideal for slow-growing plants and turfgrass, promoting consistent root development. Granular fertilizer dissolves quickly, making it suitable for fast-growing crops such as vegetables and annual flowers requiring immediate nutrient uptake. Selecting the appropriate fertilizer type enhances nutrient efficiency tailored to specific plant growth cycles and soil conditions.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Pelletized fertilizer typically offers a more controlled nutrient release, reducing runoff and minimizing environmental pollution compared to granular fertilizer, which can dissolve quickly and increase the risk of leaching into waterways. Pelletized forms often have lower dust emissions during application, decreasing air quality concerns and soil contamination. Both types impact ecosystems differently, but pelletized fertilizers generally demonstrate a better environmental profile due to their slow-release properties and reduced application frequency.
Cost and Availability Factors
Pelletized fertilizer generally costs more than granular fertilizer due to its specialized manufacturing process, which enhances nutrient release efficiency and reduces dust. Availability of pelletized fertilizers can be limited in certain regions, primarily due to higher production costs and niche market demand, whereas granular fertilizers are widely accessible and produced at larger scales globally. Cost-effectiveness of granular fertilizers makes them a preferred choice for large-scale agricultural applications, while pelletized options are favored for precision farming despite a higher price point.
Choosing the Right Fertilizer for Your Garden
Pelletized fertilizer offers uniform nutrient distribution and easy application, making it ideal for small-scale gardens requiring precise feeding. Granular fertilizer provides broader coverage with slower nutrient release, suitable for large garden beds or lawns needing long-lasting nourishment. Selecting between pelletized and granular fertilizer depends on garden size, soil type, and desired nutrient delivery speed to optimize plant growth and health.
Pelletized fertilizer vs Granular fertilizer Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com