
NPK fertilizer vs Single-nutrient fertilizer Illustration
NPK fertilizer combines nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium to provide balanced nutrition essential for plant growth, improving crop yield and soil fertility simultaneously. Single-nutrient fertilizers supply only one specific nutrient, such as nitrogen or potassium, targeting specific deficiencies in the soil. Using NPK fertilizer ensures comprehensive nutrient availability, while single-nutrient fertilizers are ideal for correcting particular nutrient imbalances.
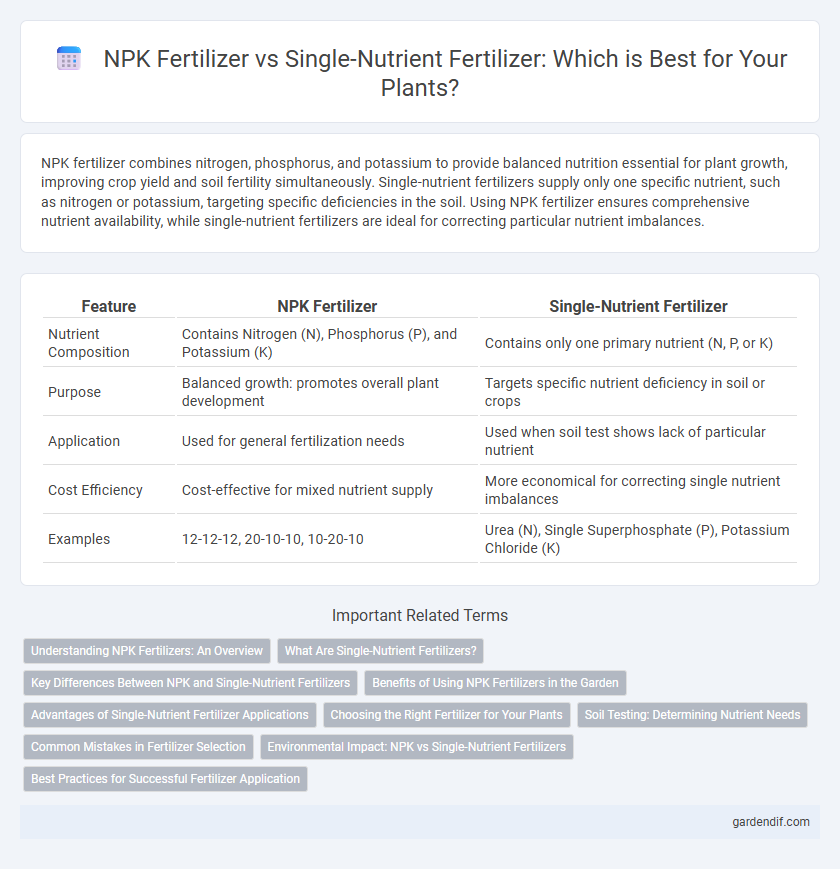
Table of Comparison
| Feature | NPK Fertilizer | Single-Nutrient Fertilizer |
|---|---|---|
| Nutrient Composition | Contains Nitrogen (N), Phosphorus (P), and Potassium (K) | Contains only one primary nutrient (N, P, or K) |
| Purpose | Balanced growth: promotes overall plant development | Targets specific nutrient deficiency in soil or crops |
| Application | Used for general fertilization needs | Used when soil test shows lack of particular nutrient |
| Cost Efficiency | Cost-effective for mixed nutrient supply | More economical for correcting single nutrient imbalances |
| Examples | 12-12-12, 20-10-10, 10-20-10 | Urea (N), Single Superphosphate (P), Potassium Chloride (K) |
Understanding NPK Fertilizers: An Overview
NPK fertilizers combine nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) in precise ratios to support balanced plant growth, enhance root development, and improve crop yields. Unlike single-nutrient fertilizers, which supply only one essential element, NPK formulations address multiple nutrient deficiencies simultaneously, optimizing soil fertility and nutrient availability. The strategic use of NPK fertilizers boosts photosynthesis efficiency, strengthens plants against disease, and increases overall agricultural productivity.
What Are Single-Nutrient Fertilizers?
Single-nutrient fertilizers contain only one primary nutrient, such as nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), or potassium (K), essential for specific plant growth requirements. These fertilizers allow for precise nutrient management, addressing particular soil deficiencies without overloading plants with unwanted elements. Common examples include urea for nitrogen, superphosphate for phosphorus, and potassium chloride for potassium, which are used to target specific crop needs effectively.
Key Differences Between NPK and Single-Nutrient Fertilizers
NPK fertilizers supply a balanced combination of nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K), promoting comprehensive plant growth and development. Single-nutrient fertilizers target specific nutrient deficiencies, providing only one essential element such as nitrogen, phosphorus, or potassium. The key difference lies in NPK fertilizers offering a multi-nutrient solution for overall soil fertility, whereas single-nutrient fertilizers address particular nutrient gaps based on soil and crop requirements.
Benefits of Using NPK Fertilizers in the Garden
NPK fertilizers provide a balanced combination of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, essential for promoting healthy plant growth, root development, and fruit production. Using NPK fertilizer in the garden ensures consistent nutrient availability, reducing the risk of nutrient deficiencies common with single-nutrient fertilizers. This balanced nutrient supply enhances soil fertility and improves overall crop yield and quality.
Advantages of Single-Nutrient Fertilizer Applications
Single-nutrient fertilizers offer precise nutrient management by delivering targeted amounts of nitrogen, phosphorus, or potassium, reducing the risk of nutrient imbalances in soil. These fertilizers enhance crop-specific nutrient uptake efficiency and allow farmers to adjust applications based on detailed soil test results. Using single-nutrient fertilizers can optimize plant growth and yield, particularly in soils with known nutrient deficiencies requiring focused correction.
Choosing the Right Fertilizer for Your Plants
NPK fertilizers provide a balanced blend of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, essential for overall plant growth, root development, and fruit production, making them ideal for varied soil nutrient needs. Single-nutrient fertilizers target specific nutrient deficiencies, allowing precise correction for plants with particular requirements or in soils tested to lack one key element. Selecting the right fertilizer depends on soil tests and plant type, ensuring optimal nutrient availability for healthy, vigorous growth and yield.
Soil Testing: Determining Nutrient Needs
Soil testing is crucial for determining the specific nutrient requirements before choosing between NPK fertilizer and single-nutrient fertilizer. NPK fertilizers provide a balanced mix of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, making them ideal when soil tests indicate multiple nutrient deficiencies. Single-nutrient fertilizers target a particular mineral deficiency identified through soil analysis, optimizing nutrient management and crop yield.
Common Mistakes in Fertilizer Selection
Choosing NPK fertilizer without soil testing often leads to nutrient imbalances, causing deficiencies or toxicities that reduce crop yield. Relying solely on single-nutrient fertilizers like nitrogen or phosphorus ignores the essential synergy of balanced nutrient combinations critical for plant growth. Misapplication rates and ignoring specific crop nutrient requirements further exacerbate inefficiencies in fertilizer use and environmental harm.
Environmental Impact: NPK vs Single-Nutrient Fertilizers
NPK fertilizers combine nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, providing balanced nutrient supply but posing risks of nutrient runoff and groundwater contamination if misapplied. Single-nutrient fertilizers target specific deficiencies, minimizing excess nutrient leaching and reducing environmental pollution when used precisely. Optimizing application rates and timing for both types is critical to mitigate negative ecological effects and promote sustainable agricultural practices.
Best Practices for Successful Fertilizer Application
NPK fertilizers provide balanced nutrition by delivering nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium in one compound, optimizing crop growth and yield. Single-nutrient fertilizers allow targeted nutrient management, essential when soil tests reveal specific deficiencies. For successful fertilizer application, calibrate equipment accurately, apply at recommended rates based on soil analysis, and time applications to align with crop nutrient uptake patterns.
NPK fertilizer vs Single-nutrient fertilizer Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com