
Mulching vs Top-dressing Illustration
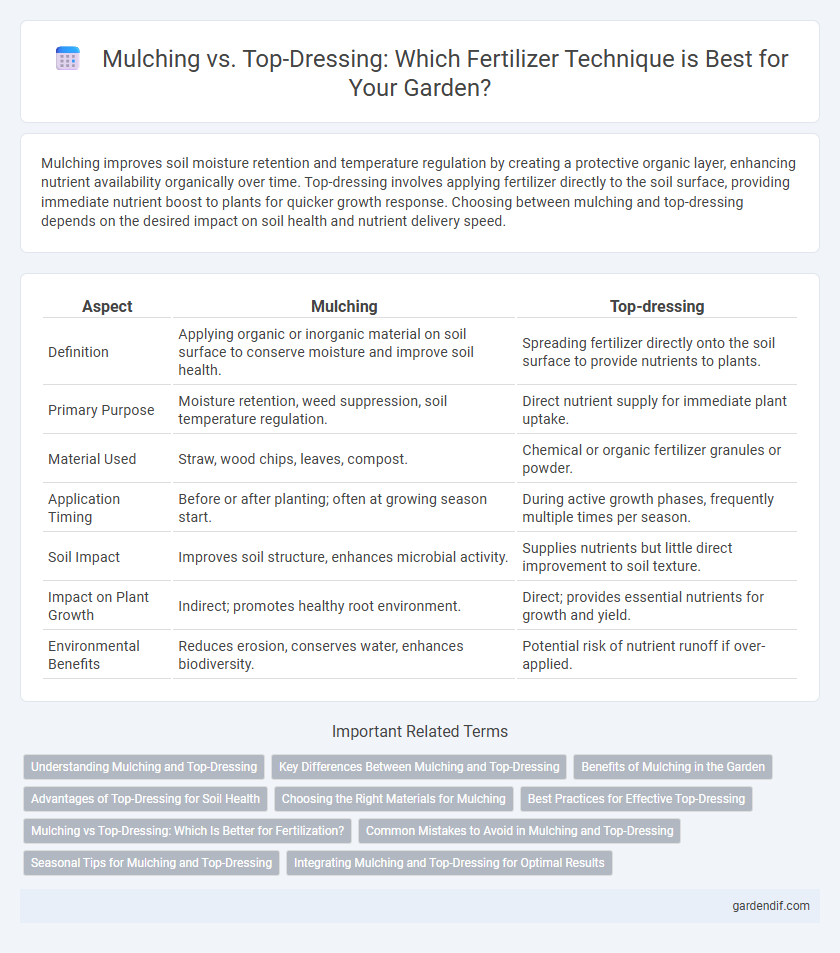
Mulching improves soil moisture retention and temperature regulation by creating a protective organic layer, enhancing nutrient availability organically over time. Top-dressing involves applying fertilizer directly to the soil surface, providing immediate nutrient boost to plants for quicker growth response. Choosing between mulching and top-dressing depends on the desired impact on soil health and nutrient delivery speed.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Mulching | Top-dressing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Applying organic or inorganic material on soil surface to conserve moisture and improve soil health. | Spreading fertilizer directly onto the soil surface to provide nutrients to plants. |
| Primary Purpose | Moisture retention, weed suppression, soil temperature regulation. | Direct nutrient supply for immediate plant uptake. |
| Material Used | Straw, wood chips, leaves, compost. | Chemical or organic fertilizer granules or powder. |
| Application Timing | Before or after planting; often at growing season start. | During active growth phases, frequently multiple times per season. |
| Soil Impact | Improves soil structure, enhances microbial activity. | Supplies nutrients but little direct improvement to soil texture. |
| Impact on Plant Growth | Indirect; promotes healthy root environment. | Direct; provides essential nutrients for growth and yield. |
| Environmental Benefits | Reduces erosion, conserves water, enhances biodiversity. | Potential risk of nutrient runoff if over-applied. |
Understanding Mulching and Top-Dressing
Mulching involves covering the soil with organic materials like straw, leaves, or compost to retain moisture, regulate temperature, and suppress weeds, promoting healthier plant growth. Top-dressing refers to the application of a thin layer of fertilizer or soil amendment directly onto the surface of the soil to enhance nutrient availability and improve soil structure. Understanding the specific benefits and appropriate use of mulching and top-dressing helps optimize soil health and plant productivity in sustainable gardening and agriculture.
Key Differences Between Mulching and Top-Dressing
Mulching involves applying a protective organic or inorganic layer on the soil surface to retain moisture, regulate temperature, and suppress weeds, while top-dressing refers to spreading a thin layer of fertilizer or soil amendments directly onto the soil or turf to enhance nutrient availability. Mulching primarily improves soil structure and water retention, whereas top-dressing focuses on nutrient supplementation and soil pH adjustment. The key difference lies in mulching's role in soil protection versus top-dressing's function in targeted nutrient delivery.
Benefits of Mulching in the Garden
Mulching improves soil moisture retention by reducing evaporation, leading to healthier plant roots and less frequent watering. It suppresses weed growth, minimizing competition for nutrients and enhancing plant development. Mulch also enriches soil structure as it decomposes, providing essential nutrients that promote sustainable garden fertility.
Advantages of Top-Dressing for Soil Health
Top-dressing enhances soil health by gradually supplying nutrients, promoting sustained microbial activity and improving nutrient retention in the root zone. This method minimizes nutrient runoff and leaching compared to other fertilization techniques, leading to better soil structure and increased organic matter content. Frequent application of top-dressing supports consistent plant growth and soil vitality throughout the growing season.
Choosing the Right Materials for Mulching
Selecting the right materials for mulching is crucial to maximize soil moisture retention and nutrient supply. Organic options like straw, wood chips, and composted leaves enhance soil fertility by gradually releasing nutrients, while inorganic mulches such as plastic or gravel primarily control weeds and temperature without enriching the soil. Choosing mulch materials that complement crop needs and local climate optimizes growth and boosts fertilizer efficiency.
Best Practices for Effective Top-Dressing
Effective top-dressing involves evenly applying a thin layer of fertilizer or organic material over the soil surface to enhance nutrient availability and improve soil structure. Best practices include using slow-release fertilizers to minimize nutrient runoff, timing applications prior to rainfall to aid nutrient absorption, and avoiding over-application to prevent grass burn or water contamination. Regular soil testing guides precise nutrient management, optimizing plant growth and sustainability compared to mulching, which primarily aids moisture retention and weed suppression.
Mulching vs Top-Dressing: Which Is Better for Fertilization?
Mulching provides a protective layer that retains soil moisture, suppresses weeds, and gradually releases nutrients, enhancing soil health over time. Top-dressing involves applying fertilizer directly to the soil surface, allowing for quick nutrient availability but with higher risks of nutrient runoff and volatilization. For sustainable fertilization, mulching is generally better as it improves soil structure and nutrient retention, while top-dressing suits situations needing immediate nutrient supply.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Mulching and Top-Dressing
Applying mulch too thickly can suffocate plant roots and promote fungal growth, while uneven top-dressing leads to nutrient imbalances in soil layers. Using non-organic or chemical-laden materials in mulching often causes soil contamination and inhibits microbial activity essential for plant health. Avoiding these errors ensures effective moisture retention and nutrient delivery, optimizing fertilizer efficiency and promoting sustainable soil fertility.
Seasonal Tips for Mulching and Top-Dressing
Seasonal tips for mulching emphasize applying organic mulch like straw or wood chips in spring to retain moisture and regulate soil temperature during growing seasons. Top-dressing with nutrient-rich compost or balanced fertilizers is most effective in early fall, enhancing soil fertility before winter dormancy. Both practices improve soil health and plant growth when timed according to crop requirements and local climate conditions.
Integrating Mulching and Top-Dressing for Optimal Results
Integrating mulching and top-dressing techniques enhances soil fertility and moisture retention by combining organic matter from mulch with nutrient-rich fertilizers applied on the soil surface. Mulching improves soil structure and temperature regulation while top-dressing supplies essential nutrients directly to plant roots, maximizing nutrient uptake efficiency. This combined approach promotes sustainable crop growth, reduces nutrient leaching, and supports long-term soil health.
Mulching vs Top-dressing Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com