
Foliar feeding vs Root feeding Illustration
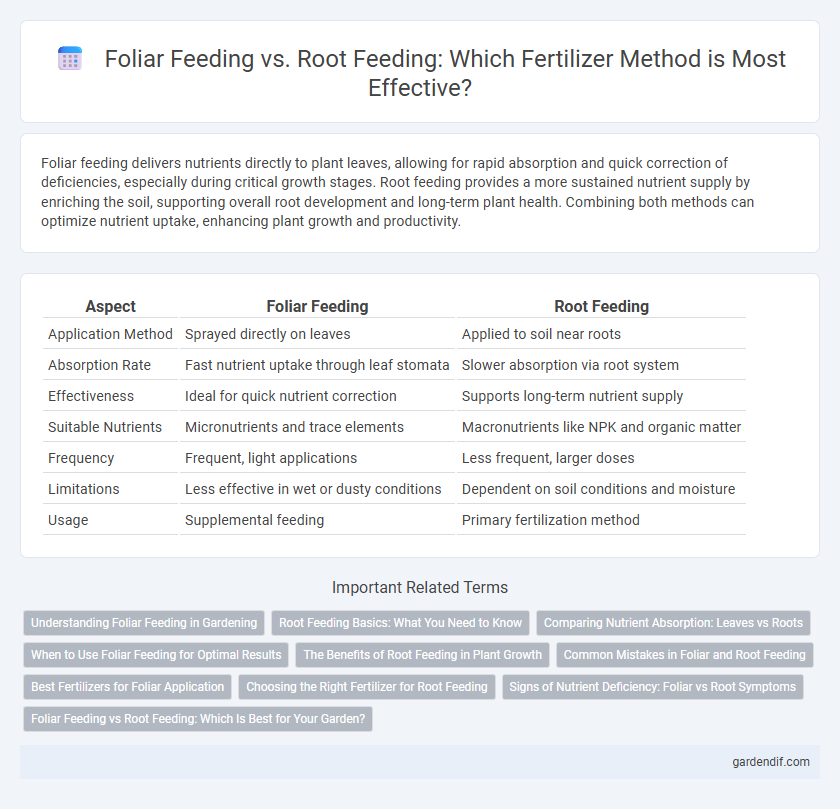
Foliar feeding delivers nutrients directly to plant leaves, allowing for rapid absorption and quick correction of deficiencies, especially during critical growth stages. Root feeding provides a more sustained nutrient supply by enriching the soil, supporting overall root development and long-term plant health. Combining both methods can optimize nutrient uptake, enhancing plant growth and productivity.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Foliar Feeding | Root Feeding |
|---|---|---|
| Application Method | Sprayed directly on leaves | Applied to soil near roots |
| Absorption Rate | Fast nutrient uptake through leaf stomata | Slower absorption via root system |
| Effectiveness | Ideal for quick nutrient correction | Supports long-term nutrient supply |
| Suitable Nutrients | Micronutrients and trace elements | Macronutrients like NPK and organic matter |
| Frequency | Frequent, light applications | Less frequent, larger doses |
| Limitations | Less effective in wet or dusty conditions | Dependent on soil conditions and moisture |
| Usage | Supplemental feeding | Primary fertilization method |
Understanding Foliar Feeding in Gardening
Foliar feeding delivers nutrients directly to plant leaves, enabling rapid absorption and immediate correction of nutrient deficiencies compared to root feeding, which relies on soil nutrient uptake. This method enhances nutrient efficiency, especially in conditions where root uptake is impaired by poor soil quality or environmental stresses. Optimal foliar feeding requires careful selection of nutrient formulations and application timing to maximize plant growth and yield.
Root Feeding Basics: What You Need to Know
Root feeding involves applying fertilizer directly to the soil, allowing nutrients to be absorbed by plant roots for sustained growth and development. This method enhances nutrient availability in the root zone, promoting robust root systems and improving water and nutrient uptake efficiency. Understanding soil composition and moisture levels is essential for optimizing root feeding effectiveness and preventing nutrient leaching.
Comparing Nutrient Absorption: Leaves vs Roots
Foliar feeding delivers nutrients directly to plant leaves, enabling rapid absorption through stomata and cuticles, which is particularly effective for micronutrients like zinc and iron. Root feeding relies on soil nutrient availability and root uptake mechanisms, often providing a sustained nutrient supply but may be limited by soil conditions such as pH and moisture. Nutrient absorption through leaves bypasses soil constraints, offering quick correction of deficiencies, while root feeding supports long-term plant growth by accessing a broader nutrient spectrum.
When to Use Foliar Feeding for Optimal Results
Foliar feeding is most effective during periods of rapid growth or stress when nutrient uptake through roots is limited, such as in drought conditions or nutrient-deficient soils. It delivers nutrients directly to the leaves, enabling quick absorption and immediate correction of deficiencies. Use foliar feeding for micronutrients like zinc, iron, and manganese to boost plant health and yield when root uptake is compromised.
The Benefits of Root Feeding in Plant Growth
Root feeding enhances nutrient absorption efficiency by delivering essential minerals directly to the root zone, promoting stronger root development and overall plant health. This method supports sustained nutrient uptake, improving water retention and increasing resistance to environmental stressors. Compared to foliar feeding, root feeding fosters long-term growth by enriching soil microbiome activity and ensuring a steady supply of macronutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium.
Common Mistakes in Foliar and Root Feeding
Common mistakes in foliar feeding include applying fertilizers during peak sunlight, which can cause leaf burn, and using incorrect concentrations that reduce nutrient uptake efficiency. Root feeding errors often involve overwatering that leads to nutrient leaching or poor soil aeration, impairing root nutrient absorption. Both methods require precise timing and dosage to optimize nutrient availability and avoid plant stress.
Best Fertilizers for Foliar Application
Foliar feeding delivers nutrients directly to plant leaves, enabling rapid absorption and quick correction of nutrient deficiencies, making it ideal for trace elements like zinc, iron, and manganese. Best fertilizers for foliar application include water-soluble compounds such as chelated micronutrients, urea, and potassium nitrate, which ensure efficient uptake and minimize leaf burn. Foliar feeding complements root feeding by providing targeted nutrition during critical growth stages or when soil conditions limit root nutrient availability.
Choosing the Right Fertilizer for Root Feeding
Selecting the right fertilizer for root feeding involves prioritizing nutrient absorption efficiency and soil compatibility. Fertilizers with balanced NPK ratios and micronutrients optimize root uptake and promote healthy plant growth. Slow-release formulations or organic options enhance nutrient availability and reduce leaching, making them ideal for sustained root nutrition.
Signs of Nutrient Deficiency: Foliar vs Root Symptoms
Foliar feeding often reveals nutrient deficiencies through discoloration, spotting, or chlorosis on leaves, indicating issues like nitrogen, magnesium, or iron imbalance. Root feeding deficiencies manifest more gradually with stunted growth, poor root development, and wilting due to insufficient uptake of potassium, phosphorus, or micronutrients from the soil. Early detection of foliar symptoms enables quicker corrective action compared to the slower visible signs associated with root nutrient shortages.
Foliar Feeding vs Root Feeding: Which Is Best for Your Garden?
Foliar feeding delivers nutrients directly to plant leaves, enabling rapid absorption and quick correction of deficiencies, especially for micronutrients like iron and zinc. Root feeding, meanwhile, provides a slow-release nutrient supply through soil application, supporting overall root development and long-term plant health. Choosing between foliar and root feeding depends on your garden's immediate nutrient needs and soil condition, with foliar feeding best for quick fixes and root feeding optimal for sustained nutrition.
Foliar feeding vs Root feeding Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com