
Urea fertilizer vs ammonium sulfate Illustration
Urea fertilizer contains 46% nitrogen, making it highly efficient for rapid plant growth, while ammonium sulfate provides both nitrogen and sulfur, essential for crops with sulfur deficiency. Urea releases nitrogen more quickly, requiring careful management to minimize volatilization losses, whereas ammonium sulfate has lower nitrogen content but improves soil acidification and sulfur availability. Choosing between urea and ammonium sulfate depends on specific crop needs, soil pH, and nutrient requirements for optimal yield.
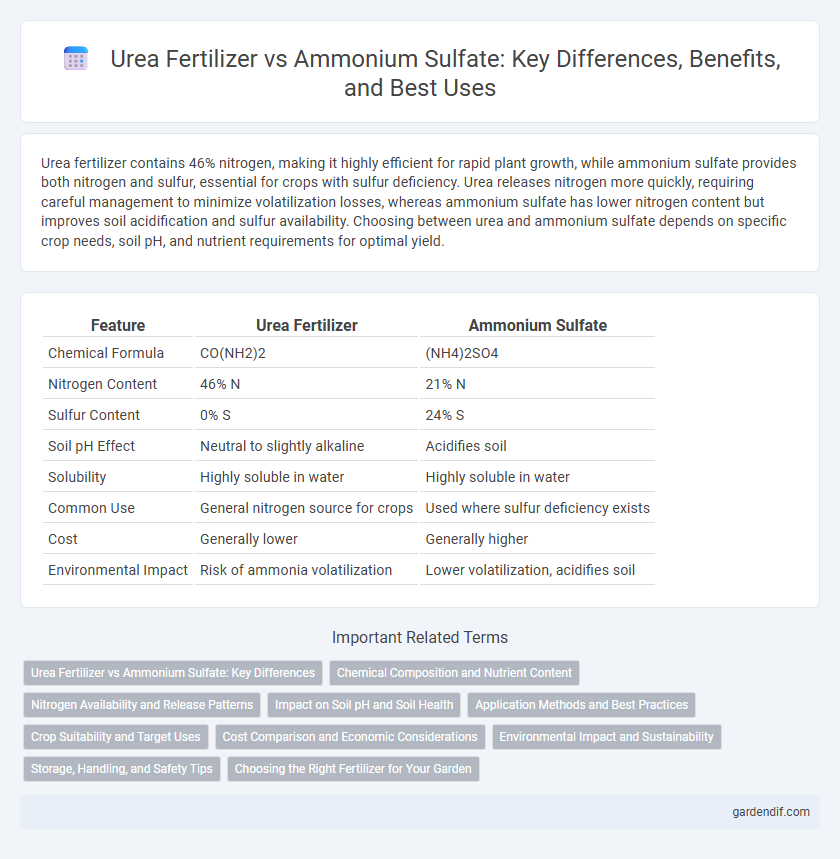
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Urea Fertilizer | Ammonium Sulfate |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Formula | CO(NH2)2 | (NH4)2SO4 |
| Nitrogen Content | 46% N | 21% N |
| Sulfur Content | 0% S | 24% S |
| Soil pH Effect | Neutral to slightly alkaline | Acidifies soil |
| Solubility | Highly soluble in water | Highly soluble in water |
| Common Use | General nitrogen source for crops | Used where sulfur deficiency exists |
| Cost | Generally lower | Generally higher |
| Environmental Impact | Risk of ammonia volatilization | Lower volatilization, acidifies soil |
Urea Fertilizer vs Ammonium Sulfate: Key Differences
Urea fertilizer contains about 46% nitrogen, making it the most concentrated nitrogen source commonly used in agriculture, whereas ammonium sulfate provides around 21% nitrogen plus 24% sulfur, essential for sulfur-deficient soils. Urea has a higher nitrogen content and is less acidic compared to ammonium sulfate, which is beneficial for crops needing both nitrogen and sulfur, but may lower soil pH over time. The choice between urea and ammonium sulfate depends on soil nutrient status, crop requirements, and environmental factors influencing nitrogen availability and retention.
Chemical Composition and Nutrient Content
Urea fertilizer contains 46% nitrogen in the form of ammonium carbonate, offering a high nitrogen concentration that promotes rapid plant growth. Ammonium sulfate provides 21% nitrogen and 24% sulfur, supplying essential sulfur for crops while improving soil acidity. Comparing nutrient content, urea is preferred for nitrogen-rich applications, whereas ammonium sulfate benefits sulfur-deficient soils with balanced nitrogen and sulfur availability.
Nitrogen Availability and Release Patterns
Urea fertilizer provides a high concentration of nitrogen in the form of ammonium carbonate, which quickly converts to available nitrate, offering rapid nitrogen availability for crop uptake. Ammonium sulfate releases nitrogen more gradually as ammonium ions, maintaining availability over a longer period and supplying sulfur as a secondary nutrient. The choice between urea and ammonium sulfate impacts nitrogen release patterns and timing, influencing nutrient efficiency and crop growth dynamics.
Impact on Soil pH and Soil Health
Urea fertilizer typically raises soil pH slightly due to the hydrolysis of urea releasing ammonia, which can increase alkalinity. In contrast, ammonium sulfate lowers soil pH by releasing sulfate ions that acidify the soil, making it suitable for acid-loving crops. Long-term use of ammonium sulfate can improve soil structure in acidic soils but may lead to soil acidification and nutrient imbalances if not managed properly.
Application Methods and Best Practices
Urea fertilizer is primarily applied using broadcasting, banding, or foliar spraying to maximize nitrogen efficiency, while ammonium sulfate is best used through soil incorporation or side-dressing to prevent nitrogen volatilization and acidify alkaline soils. Precision application techniques such as fertigation for urea enhance nutrient uptake and reduce losses, whereas ammonium sulfate's solubility allows for efficient use in both granular and liquid forms during crop growth stages needing sulfur. Best practices for both fertilizers include timing applications to crop nitrogen demand and avoiding over-application to minimize environmental impacts and optimize yield.
Crop Suitability and Target Uses
Urea fertilizer offers a high nitrogen content of 46%, making it ideal for promoting rapid vegetative growth in cereal crops like wheat, corn, and rice, which require substantial nitrogen uptake. Ammonium sulfate provides both nitrogen (21%) and sulfur (24%), essential for crops like legumes, oilseeds, and sulfur-deficient soils, enhancing protein synthesis and improving crop quality. The choice between urea and ammonium sulfate depends on specific crop nutritional needs and soil sulfur availability, optimizing yields and nutrient efficiency.
Cost Comparison and Economic Considerations
Urea fertilizer generally offers a lower cost per unit of nitrogen compared to ammonium sulfate, making it more economical for large-scale agricultural use. Ammonium sulfate, despite its higher price, provides additional sulfur nutrients beneficial for sulfur-deficient soils, potentially reducing the need for separate sulfur applications. Farmers must weigh the cost-per-nitrogen advantage of urea against the long-term soil health benefits and nutrient requirements that ammonium sulfate addresses.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Urea fertilizer releases more greenhouse gases like nitrous oxide compared to ammonium sulfate, contributing significantly to global warming. Ammonium sulfate improves soil pH and is less prone to volatilization, making it a more environmentally sustainable nitrogen source. Sustainable fertilization practices prioritize ammonium sulfate to reduce nutrient runoff and enhance long-term soil health.
Storage, Handling, and Safety Tips
Urea fertilizer requires storage in a cool, dry place to prevent caking and moisture absorption, while ammonium sulfate should be kept away from heat and moisture to avoid degradation and hardening. Handling urea involves minimizing dust exposure and using gloves to prevent skin irritation, whereas ammonium sulfate necessitates protective equipment to avoid inhalation hazards and skin contact due to its acidic nature. Ensuring proper ventilation, using sealed containers, and adhering to safety data sheet (SDS) guidelines are crucial for the safe storage and handling of both fertilizers.
Choosing the Right Fertilizer for Your Garden
Urea fertilizer contains 46% nitrogen, making it a highly concentrated source ideal for fast-growing plants needing a quick nitrogen boost. Ammonium sulfate provides both nitrogen (21%) and sulfur (24%), which is beneficial for sulfur-deficient soils and acid-loving plants. Selecting urea or ammonium sulfate depends on soil pH and nutrient requirements to optimize plant health and growth.
Urea fertilizer vs ammonium sulfate Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com