
Synthetic vs Organic Illustration
Synthetic fertilizers provide immediate nutrient availability, promoting rapid plant growth through precise chemical formulations. Organic fertilizers improve soil health long-term by enhancing microbial activity and supplying nutrients through natural decomposition. Choosing between synthetic and organic options depends on balancing quick results with sustainable soil enrichment.
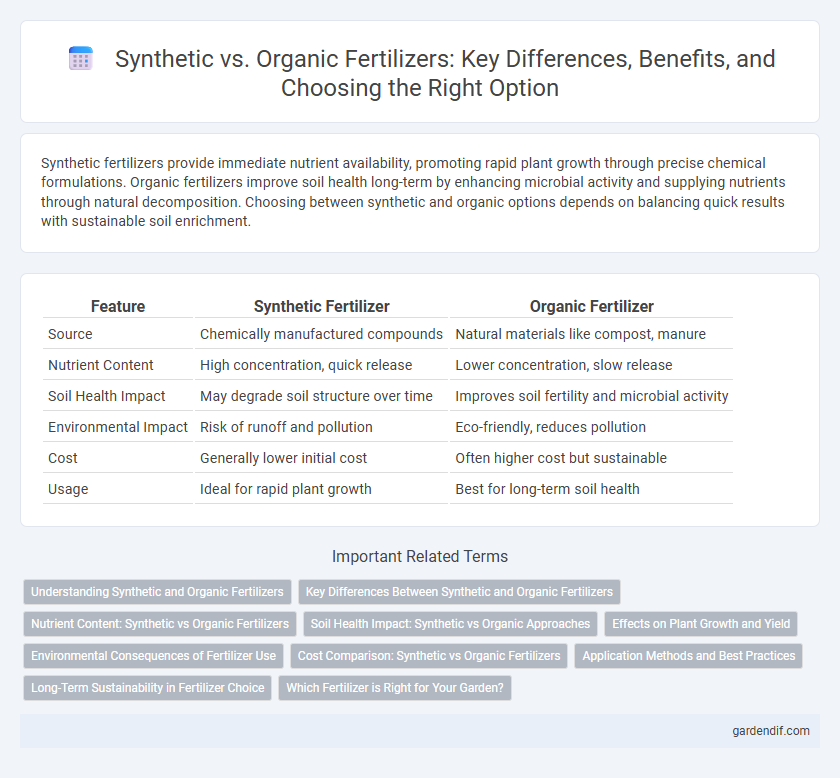
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Synthetic Fertilizer | Organic Fertilizer |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Chemically manufactured compounds | Natural materials like compost, manure |
| Nutrient Content | High concentration, quick release | Lower concentration, slow release |
| Soil Health Impact | May degrade soil structure over time | Improves soil fertility and microbial activity |
| Environmental Impact | Risk of runoff and pollution | Eco-friendly, reduces pollution |
| Cost | Generally lower initial cost | Often higher cost but sustainable |
| Usage | Ideal for rapid plant growth | Best for long-term soil health |
Understanding Synthetic and Organic Fertilizers
Synthetic fertilizers are chemically formulated products designed to provide specific nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium in precise, readily available forms to promote rapid plant growth. Organic fertilizers consist of natural materials such as compost, manure, or bone meal, releasing nutrients more slowly and improving soil structure and microbial activity over time. Understanding the differences in nutrient release, environmental impact, and soil health benefits is essential for choosing the appropriate fertilizer type for sustainable agricultural practices.
Key Differences Between Synthetic and Organic Fertilizers
Synthetic fertilizers contain concentrated nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium in precise ratios, enabling rapid nutrient availability and targeted plant growth. Organic fertilizers are derived from natural sources such as compost, manure, and bone meal, releasing nutrients slowly while improving soil structure and microbial activity. Unlike synthetic options, organic fertilizers enhance long-term soil health but may require larger application amounts and more time for nutrient absorption.
Nutrient Content: Synthetic vs Organic Fertilizers
Synthetic fertilizers contain concentrated, readily available nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, enabling quick plant absorption and rapid growth. Organic fertilizers provide nutrients through natural processes, releasing them slowly and improving soil health by enhancing microbial activity. Balancing nutrient content and release rates is crucial for optimizing crop yield and sustainability in agriculture.
Soil Health Impact: Synthetic vs Organic Approaches
Synthetic fertilizers provide immediate nutrient availability but can disrupt soil microbial balance and reduce long-term soil fertility due to chemical buildup. Organic fertilizers improve soil structure, enhance microbial activity, and increase nutrient retention, promoting sustainable soil health over time. Choosing organic amendments supports biodiversity and helps maintain the natural nutrient cycling essential for healthy crop growth.
Effects on Plant Growth and Yield
Synthetic fertilizers provide plants with readily available nutrients, promoting rapid growth and higher initial yields due to their precise nutrient formulation. Organic fertilizers improve soil structure and microbiome health, resulting in sustainable nutrient release and enhanced long-term plant growth and yield stability. Studies show that combining both fertilizer types can optimize nutrient availability, improve plant resilience, and maximize crop productivity.
Environmental Consequences of Fertilizer Use
Synthetic fertilizers often lead to nutrient runoff, causing water pollution and harmful algal blooms that disrupt aquatic ecosystems. Organic fertilizers improve soil health by enhancing microbial activity and reducing chemical residues, but they may release nutrients more slowly, necessitating careful management. Both types impact greenhouse gas emissions, with synthetic options typically associated with higher nitrous oxide release, a potent contributor to climate change.
Cost Comparison: Synthetic vs Organic Fertilizers
Synthetic fertilizers generally offer a lower upfront cost compared to organic fertilizers due to their concentrated nutrient content and mass production. Organic fertilizers, derived from natural sources like compost and manure, often incur higher costs related to sourcing, processing, and transportation. Long-term soil health benefits of organic fertilizers can offset initial expenses by reducing the need for frequent applications and improving soil fertility.
Application Methods and Best Practices
Synthetic fertilizers offer precise nutrient delivery through methods like foliar spraying and fertigation, enabling rapid plant absorption and efficient nutrient management. Organic fertilizers require incorporation into the soil to promote microbial activity and improve soil structure, with best practices including composting and timing applications to coincide with active root growth. Combining both types through integrated nutrient management maximizes crop yield and sustainability by balancing immediate nutrient availability and long-term soil health.
Long-Term Sustainability in Fertilizer Choice
Synthetic fertilizers deliver rapid nutrient availability but may lead to soil degradation and reduced microbial diversity over time, impacting long-term soil health. Organic fertilizers enhance soil structure, promote beneficial microbial activity, and improve water retention, supporting sustainable crop production through nutrient cycling. Choosing fertilizers with a focus on long-term soil fertility and ecosystem balance is critical for sustainable agriculture.
Which Fertilizer is Right for Your Garden?
Choosing between synthetic and organic fertilizers depends on soil health, plant needs, and environmental impact. Synthetic fertilizers provide rapid nutrient release and precise nutrient ratios, ideal for immediate growth boosts but may harm soil microbes over time. Organic fertilizers improve soil structure and promote long-term fertility by supplying slow-release nutrients and enhancing microbial activity, suitable for sustainable gardening practices.
Synthetic vs Organic Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com