
Solarization vs shading Illustration
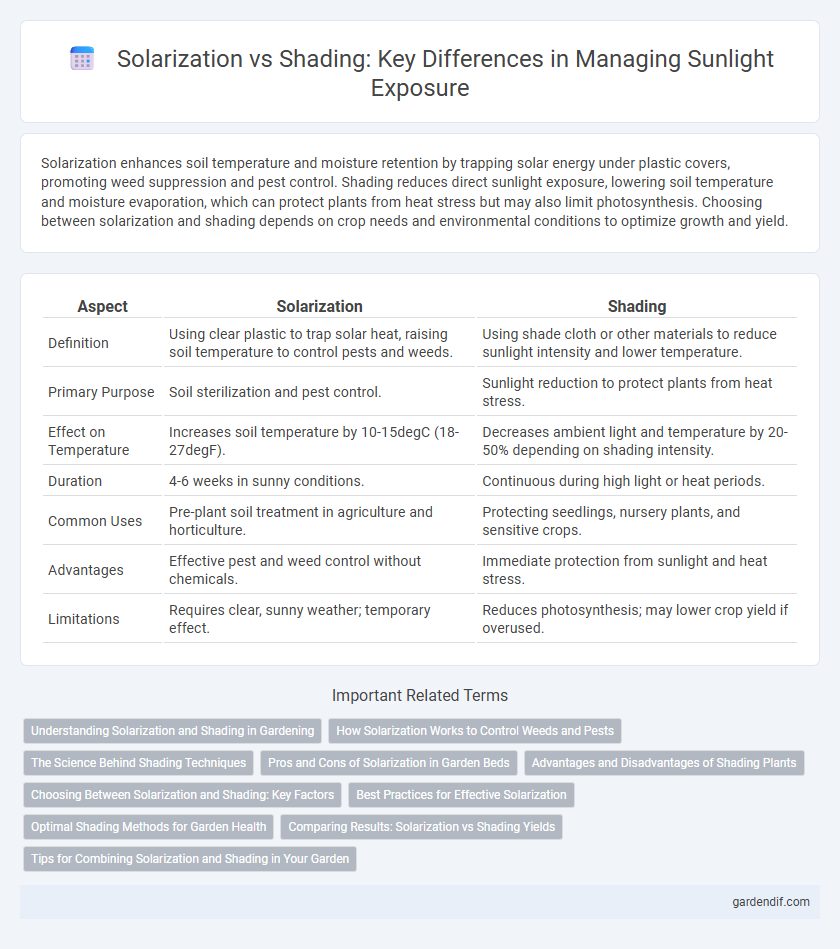
Solarization enhances soil temperature and moisture retention by trapping solar energy under plastic covers, promoting weed suppression and pest control. Shading reduces direct sunlight exposure, lowering soil temperature and moisture evaporation, which can protect plants from heat stress but may also limit photosynthesis. Choosing between solarization and shading depends on crop needs and environmental conditions to optimize growth and yield.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Solarization | Shading |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Using clear plastic to trap solar heat, raising soil temperature to control pests and weeds. | Using shade cloth or other materials to reduce sunlight intensity and lower temperature. |
| Primary Purpose | Soil sterilization and pest control. | Sunlight reduction to protect plants from heat stress. |
| Effect on Temperature | Increases soil temperature by 10-15degC (18-27degF). | Decreases ambient light and temperature by 20-50% depending on shading intensity. |
| Duration | 4-6 weeks in sunny conditions. | Continuous during high light or heat periods. |
| Common Uses | Pre-plant soil treatment in agriculture and horticulture. | Protecting seedlings, nursery plants, and sensitive crops. |
| Advantages | Effective pest and weed control without chemicals. | Immediate protection from sunlight and heat stress. |
| Limitations | Requires clear, sunny weather; temporary effect. | Reduces photosynthesis; may lower crop yield if overused. |
Understanding Solarization and Shading in Gardening
Solarization uses transparent plastic to trap solar energy, raising soil temperature to eliminate pests and weeds effectively. Shading employs materials like shade cloth to reduce sunlight intensity, protecting plants from heat stress and preventing moisture loss. Understanding these techniques helps gardeners optimize plant growth by managing light and temperature based on specific crop needs.
How Solarization Works to Control Weeds and Pests
Solarization controls weeds and pests by trapping solar energy under a clear plastic sheet, raising soil temperatures to 45-60degC (113-140degF) for several weeks, which effectively kills weed seeds, larvae, and soil-borne pathogens. This thermal treatment disrupts the life cycle of pests and suppresses weed germination without chemical use. The method relies on strong sunlight exposure and proper soil moisture to maximize efficacy in sustainable agriculture and gardening.
The Science Behind Shading Techniques
Shading techniques regulate sunlight intensity by blocking or diffusing solar radiation, reducing heat absorption and UV exposure on surfaces. Solarization involves covering soil with transparent or semi-transparent films to trap solar heat, accelerating pest and weed control through elevated temperatures. These methods manipulate light wavelength and intensity to optimize plant growth and protection, leveraging photosynthesis and thermal dynamics principles.
Pros and Cons of Solarization in Garden Beds
Solarization uses clear plastic to trap solar energy, raising soil temperatures to 113-140degF and effectively killing pathogens, weeds, and nematodes, which improves soil health and crop yield. This method is cost-effective and environmentally friendly but requires long exposure times of 4-6 weeks and depends heavily on strong, consistent sunlight, making it less effective in shaded or cloudy areas. Solarization may reduce beneficial soil microorganisms temporarily and is not suitable for all crops due to heat sensitivity.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Shading Plants
Shading plants reduces excessive solar radiation, preventing leaf scorch and water loss while improving growth in high-temperature environments. However, shading can limit photosynthesis by reducing light intensity, potentially slowing plant development and lowering yield in species requiring full sunlight. Balancing light exposure with appropriate shading techniques is crucial for optimizing plant health and productivity.
Choosing Between Solarization and Shading: Key Factors
Choosing between solarization and shading depends on factors such as crop type, climate, and pest pressure. Solarization effectively controls soilborne pathogens and weeds by using transparent plastic to trap solar heat, best suited for warm, sunny areas. Shading reduces heat stress and protects plants from excessive sunlight, making it ideal for sensitive crops in hot, high-radiation environments.
Best Practices for Effective Solarization
Solarization effectively controls soil-borne pathogens by covering moist soil with transparent plastic mulch during peak sunlight, reaching soil temperatures above 45degC (113degF) for 4 to 6 weeks. Optimal practices include selecting high-quality UV-stable polyethylene film, ensuring close soil contact to prevent heat loss, and scheduling treatment during the hottest months for maximum solar intensity. Proper solarization minimizes pest populations, improves soil health, and enhances subsequent crop yields without chemical inputs.
Optimal Shading Methods for Garden Health
Optimal shading methods for garden health balance sunlight exposure to prevent solarization, which can damage soil nutrients and harm plant roots by overheating the soil surface. Techniques like using shade cloths, strategically planting shade trees, and applying organic mulches reduce excessive heat while maintaining sufficient light for photosynthesis. These methods promote soil moisture retention and temperature regulation, enhancing plant growth and overall garden vitality.
Comparing Results: Solarization vs Shading Yields
Solarization typically improves crop yields by increasing soil temperature and reducing pathogens, resulting in healthier plant growth compared to traditional shading. Shading lowers light intensity, which can lead to reduced photosynthesis and subsequently lower yields in most sun-loving crops. Studies show solarized fields often yield 15-30% higher output than shaded fields due to enhanced nutrient availability and pest suppression.
Tips for Combining Solarization and Shading in Your Garden
Combining solarization and shading in your garden requires balancing sunlight exposure to optimize soil health and plant growth. Use clear plastic sheets for solarization in fully sunlit areas to effectively eliminate pests and weed seeds, then incorporate shade cloths to protect sensitive plants from excessive heat. Monitoring temperature and soil moisture ensures that the benefits of solarization complement shading techniques, promoting a thriving garden ecosystem.
Solarization vs shading Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com