
Sun scorch vs sunburn Illustration
Sun scorch and sunburn both result from excessive exposure to sunlight but affect the skin differently. Sun scorch typically refers to damage caused by intense heat and UV radiation, leading to redness and irritation without deep tissue damage. Sunburn, a more severe condition, involves strong UV radiation causing painful, inflamed skin and increasing the risk of long-term damage such as peeling, blistering, and skin cancer.
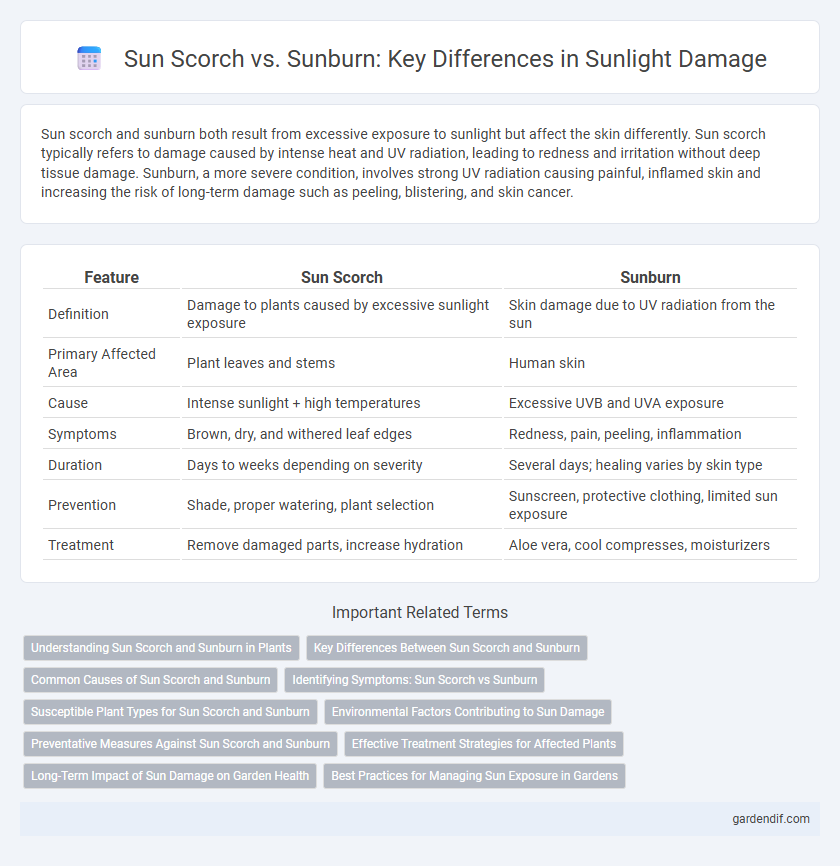
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Sun Scorch | Sunburn |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Damage to plants caused by excessive sunlight exposure | Skin damage due to UV radiation from the sun |
| Primary Affected Area | Plant leaves and stems | Human skin |
| Cause | Intense sunlight + high temperatures | Excessive UVB and UVA exposure |
| Symptoms | Brown, dry, and withered leaf edges | Redness, pain, peeling, inflammation |
| Duration | Days to weeks depending on severity | Several days; healing varies by skin type |
| Prevention | Shade, proper watering, plant selection | Sunscreen, protective clothing, limited sun exposure |
| Treatment | Remove damaged parts, increase hydration | Aloe vera, cool compresses, moisturizers |
Understanding Sun Scorch and Sunburn in Plants
Sun scorch and sunburn in plants both result from excessive exposure to sunlight, but they affect plants differently at the cellular level. Sun scorch typically causes browning and drying of leaf edges due to heat stress and dehydration, whereas sunburn damages the leaf tissues by causing cell death from intense ultraviolet radiation. Recognizing these distinct symptoms helps in implementing targeted protective measures, such as shading and proper irrigation, to maintain plant health under high sunlight conditions.
Key Differences Between Sun Scorch and Sunburn
Sun scorch primarily affects plants, causing wilting, browning, and leaf damage due to excessive solar radiation and heat stress, whereas sunburn refers to skin damage in humans characterized by redness, inflammation, and pain from ultraviolet (UV) radiation exposure. Sun scorch results from thermal injury and dehydration in plant tissues, while sunburn involves UV-induced skin cell damage and increased risk of long-term skin conditions like melanoma. Understanding these differences is crucial for appropriate prevention strategies: shading and watering for plants versus sunscreen and protective clothing for humans.
Common Causes of Sun Scorch and Sunburn
Sun scorch and sunburn commonly occur due to prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun, which damages skin cells and leads to inflammation. Sun scorch primarily affects plants, caused by intense sunlight combined with heat stress, dehydration, or insufficient watering. Human sunburn results from excessive UVB radiation exposure, often aggravated by fair skin, lack of protective clothing, and absence of sunscreen application.
Identifying Symptoms: Sun Scorch vs Sunburn
Sun scorch primarily affects plants, causing leaves to turn brown or crispy due to excessive ultraviolet radiation and heat exposure. Sunburn in humans manifests as red, inflamed skin with pain, blistering, and peeling caused by prolonged ultraviolet light exposure. Identifying symptoms relies on recognizing tissue damage in plants for sun scorch, while in humans, redness, swelling, and discomfort indicate sunburn.
Susceptible Plant Types for Sun Scorch and Sunburn
Sun scorch predominantly affects broadleaf plants such as maples, oaks, and rhododendrons, causing browning and damage to leaf edges due to intense sunlight and heat stress. Sunburn, on the other hand, is more common in fruit-bearing plants like tomatoes, apples, and grapes, where direct sunlight leads to tissue necrosis and fruit blemishes. Shade-sensitive species with thin epidermal layers are generally more vulnerable to both sun scorch and sunburn, requiring protective measures to prevent lasting damage.
Environmental Factors Contributing to Sun Damage
Sun scorch and sunburn both result from excessive exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, but environmental factors like altitude, reflective surfaces, and atmospheric conditions intensify their effects. Higher altitudes increase UV intensity, while surfaces such as water, sand, and snow reflect sunlight, amplifying skin damage risk. Hot, dry climates exacerbate sun scorch by dehydrating the skin, whereas humid conditions can make sunburn more severe due to prolonged sun exposure without adequate skin protection.
Preventative Measures Against Sun Scorch and Sunburn
Effective preventative measures against sun scorch and sunburn include applying broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher, wearing protective clothing such as wide-brimmed hats and UV-blocking sunglasses, and seeking shade during peak sunlight hours between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. Hydration is essential to maintain skin health, while gradual exposure to sunlight helps build natural tolerance and reduces the risk of severe skin damage. Regular reapplication of sunscreen every two hours, especially after swimming or sweating, is crucial for sustained protection.
Effective Treatment Strategies for Affected Plants
Sun scorch causes brown, dry patches on leaves due to excessive sunlight, while sunburn results in bleaching and tissue damage. Effective treatment strategies include providing shade during peak sunlight hours, increasing soil moisture to help plants recover, and applying anti-transpirants or foliar sprays to reduce water loss. Pruning damaged foliage promotes new growth and prevents further stress on affected plants.
Long-Term Impact of Sun Damage on Garden Health
Sun scorch causes localized damage to plant leaves and stems, leading to browning and wilting, while sunburn results in more severe tissue damage visible as blistering or necrosis. Long-term exposure to intense sunlight can weaken plants, reducing photosynthesis efficiency and increasing susceptibility to pests and diseases. Persistent sun damage ultimately diminishes overall garden health and productivity, necessitating protective measures like shading and proper hydration.
Best Practices for Managing Sun Exposure in Gardens
Sun scorch and sunburn affect plants differently; sun scorch damages leaves due to excessive heat and light, while sunburn causes tissue damage similar to human skin burns. To manage sun exposure effectively in gardens, provide shade through structures or plant taller species to shield vulnerable plants. Regular watering and using mulch help maintain soil moisture, reducing stress from intense sunlight and preventing damage.
Sun scorch vs sunburn Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com