
Peak Sun Hours vs Diffused Light Illustration
Peak sun hours refer to the period when sunlight is most intense and direct, providing optimal energy for solar panels and plant growth. Diffused light consists of sunlight scattered by clouds or atmospheric particles, delivering lower intensity but more evenly distributed illumination. Understanding the difference between peak sun hours and diffused light is crucial for maximizing efficiency in solar energy systems and horticulture.
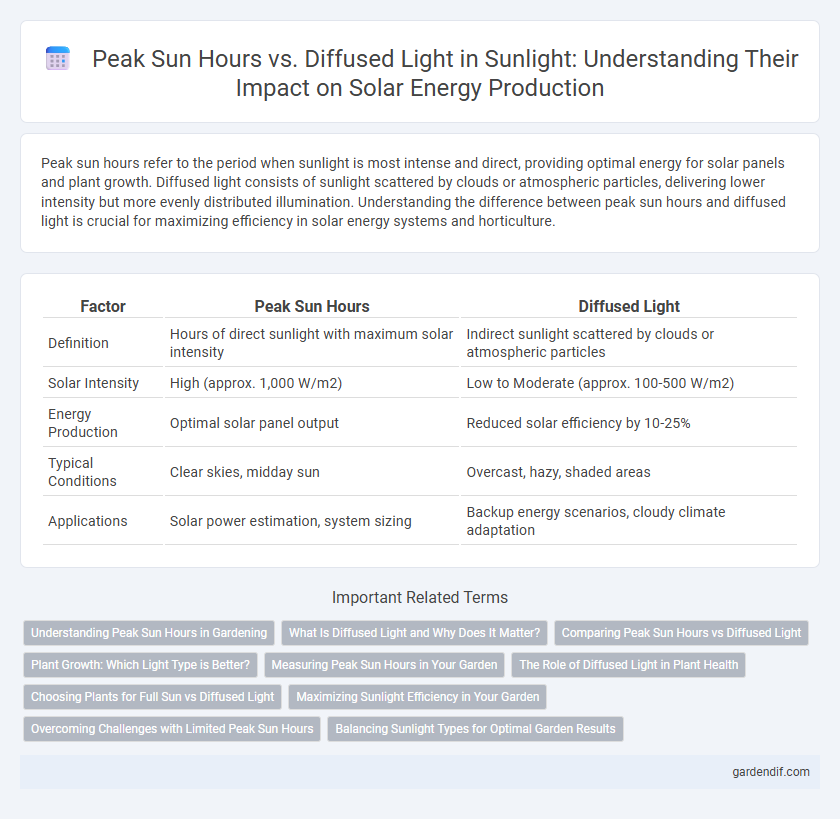
Table of Comparison
| Factor | Peak Sun Hours | Diffused Light |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Hours of direct sunlight with maximum solar intensity | Indirect sunlight scattered by clouds or atmospheric particles |
| Solar Intensity | High (approx. 1,000 W/m2) | Low to Moderate (approx. 100-500 W/m2) |
| Energy Production | Optimal solar panel output | Reduced solar efficiency by 10-25% |
| Typical Conditions | Clear skies, midday sun | Overcast, hazy, shaded areas |
| Applications | Solar power estimation, system sizing | Backup energy scenarios, cloudy climate adaptation |
Understanding Peak Sun Hours in Gardening
Peak sun hours represent the amount of solar energy received during the brightest part of the day, typically between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m., providing the essential light intensity for optimal photosynthesis in plants. Unlike diffused light, which is scattered and less intense due to cloud cover or shading, peak sun hours deliver concentrated sunlight critical for growth, flowering, and fruit production in gardens. Measuring peak sun hours helps gardeners select appropriate plant species and optimize their placement to maximize photosynthetic efficiency and crop yields.
What Is Diffused Light and Why Does It Matter?
Diffused light is sunlight scattered by particles and clouds in the atmosphere, resulting in softer, more evenly distributed illumination without harsh shadows. This type of light is crucial for plants and solar panels because it penetrates shaded areas and improves photosynthesis and energy absorption compared to direct peak sun hours. Understanding the balance between peak sun hours and diffused light helps optimize agricultural yields and solar energy efficiency by maximizing light utilization throughout the day.
Comparing Peak Sun Hours vs Diffused Light
Peak sun hours refer to the period when sunlight intensity is strong enough to provide maximum solar energy, typically measured as equivalent full sun hours per day. Diffused light, scattered by clouds or atmospheric particles, offers lower intensity and less energy for solar panels but can still contribute to overall solar generation during overcast conditions. Comparing peak sun hours versus diffused light reveals that while peak sun hours deliver optimal energy output, diffused light maintains a baseline solar input important for energy consistency in less-than-ideal weather.
Plant Growth: Which Light Type is Better?
Peak sun hours deliver intense, direct sunlight that provides plants with the maximum amount of photosynthetically active radiation (PAR), essential for optimal growth and flowering. In contrast, diffused light, scattered through clouds or shade, reduces light intensity but increases light uniformity, which can benefit understory plants and reduce heat stress. Understanding a plant's light saturation point is crucial, as some species thrive under peak sun hours while others prefer diffused light for healthier growth and efficient photosynthesis.
Measuring Peak Sun Hours in Your Garden
Measuring peak sun hours in your garden involves tracking the duration when sunlight intensity reaches at least 1,000 watts per square meter, essential for optimizing plant growth and solar panel performance. Diffused light, scattered through clouds or foliage, provides lower intensity illumination that supports shade-tolerant plants but does not count as peak sun hours. Using a sunlight meter or solar pathfinder during midday offers the most accurate assessment of peak sun exposure throughout the growing season.
The Role of Diffused Light in Plant Health
Diffused light, scattered through clouds or plant canopies, provides essential illumination that reduces plant stress by preventing leaf scorch and promoting even photosynthesis. Unlike peak sun hours, which deliver intense direct sunlight for limited periods, diffused light supports sustained energy absorption throughout the day. This balanced light exposure enhances chlorophyll production and improves overall plant health by maintaining consistent photosynthetic activity.
Choosing Plants for Full Sun vs Diffused Light
Peak sun hours provide intense, direct sunlight essential for sun-loving plants such as tomatoes, peppers, and sunflowers that require 6 to 8 hours of full sun daily for optimal growth and fruit production. Diffused light, characterized by indirect or filtered sunlight, benefits shade-tolerant plants like ferns, begonias, and impatiens, which thrive with less intense light and reduced risk of leaf scorch. Understanding the local peak sun hours and distinguishing between full sun and diffused light environments ensures successful plant selection tailored to light requirements, enhancing garden health and productivity.
Maximizing Sunlight Efficiency in Your Garden
Peak sun hours describe the time when sunlight intensity reaches its maximum, delivering optimal energy for plant photosynthesis, while diffused light consists of sunlight scattered by clouds or foliage, offering less intense but more evenly distributed illumination. Maximizing sunlight efficiency in your garden involves positioning sun-loving plants in areas receiving peak sun hours to promote robust growth and placing shade-tolerant species where diffused light predominates. Utilizing tools like light meters and selecting plant varieties suited for specific light conditions ensures balanced photosynthetic activity and healthier garden yields.
Overcoming Challenges with Limited Peak Sun Hours
Limited peak sun hours reduce the intensity of direct sunlight essential for solar energy generation, posing challenges for maximizing output. Diffused light, scattered by clouds or atmospheric conditions, offers lower energy density but still contributes to solar panel efficiency, especially during overcast periods. Employing advanced solar technologies like bifacial panels and energy storage systems enhances performance by optimizing capture and utilization of both peak sun hours and diffused light.
Balancing Sunlight Types for Optimal Garden Results
Peak sun hours deliver intense, direct sunlight essential for photosynthesis and maximizing plant growth, while diffused light provides a gentler, evenly distributed illumination that reduces stress and prevents leaf burn. Balancing these sunlight types ensures plants receive sufficient energy without the risk of overheating or moisture loss, promoting healthier development and blooming. Integrating periods of full sun with shaded or filtered light creates an optimal microenvironment that enhances overall garden productivity and resilience.
Peak Sun Hours vs Diffused Light Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com