
Direct sunlight vs indirect sunlight Illustration
Direct sunlight delivers intense, focused rays that provide maximum brightness and warmth, ideal for sun-loving plants and outdoor activities. Indirect sunlight offers a softer, diffused light that reduces glare and prevents overheating, making it perfect for indoor plants and delicate environments. Understanding the difference between direct and indirect sunlight is crucial for optimizing plant growth and maintaining comfort in living spaces.
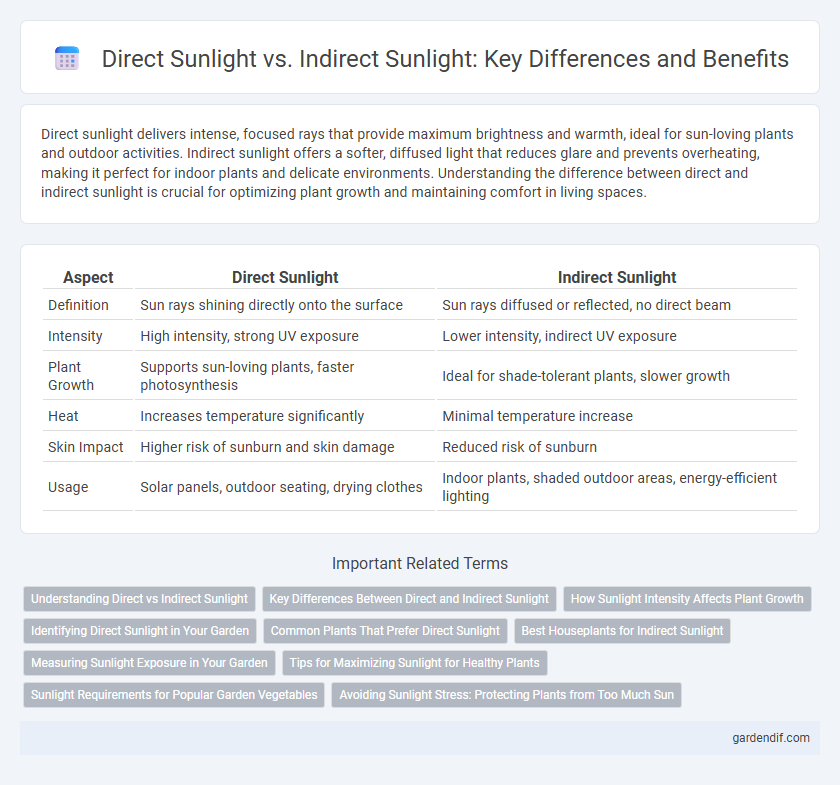
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Direct Sunlight | Indirect Sunlight |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Sun rays shining directly onto the surface | Sun rays diffused or reflected, no direct beam |
| Intensity | High intensity, strong UV exposure | Lower intensity, indirect UV exposure |
| Plant Growth | Supports sun-loving plants, faster photosynthesis | Ideal for shade-tolerant plants, slower growth |
| Heat | Increases temperature significantly | Minimal temperature increase |
| Skin Impact | Higher risk of sunburn and skin damage | Reduced risk of sunburn |
| Usage | Solar panels, outdoor seating, drying clothes | Indoor plants, shaded outdoor areas, energy-efficient lighting |
Understanding Direct vs Indirect Sunlight
Direct sunlight provides intense and focused rays that deliver maximum light energy, ideal for sun-loving plants like succulents and tomatoes. Indirect sunlight occurs when light is diffused or reflected, offering softer illumination beneficial for shade-tolerant species such as ferns and peace lilies. Understanding the difference between direct and indirect sunlight is crucial for optimizing plant growth, as varying light intensities influence photosynthesis and overall plant health.
Key Differences Between Direct and Indirect Sunlight
Direct sunlight delivers intense, unfiltered rays that provide higher UV exposure and increased heat, essential for sun-loving plants and vitamin D synthesis. Indirect sunlight offers diffused light through barriers like curtains or reflected surfaces, fostering gentle illumination suitable for shade-tolerant plants and sensitive skin. Key differences include light intensity, heat levels, and potential for UV damage, influencing their respective uses in gardening and health contexts.
How Sunlight Intensity Affects Plant Growth
Direct sunlight provides high-intensity light that promotes robust photosynthesis, resulting in faster plant growth and healthier foliage. Indirect sunlight offers lower light intensity, which may slow down photosynthesis but helps prevent leaf scorching and dehydration in shade-tolerant plants. Understanding sunlight intensity allows gardeners to optimize plant placement for species-specific growth requirements and maximize photosynthetic efficiency.
Identifying Direct Sunlight in Your Garden
Direct sunlight in your garden is characterized by unfiltered light rays that cast distinct, sharp shadows and typically occur when the sun's position is overhead or unobstructed by objects like trees or buildings. Plants receiving direct sunlight generally thrive in areas exposed for at least six hours a day, essential for sun-loving species such as tomatoes, peppers, and sunflowers. Identifying zones of direct sunlight ensures optimized plant placement, boosting photosynthesis and overall garden productivity.
Common Plants That Prefer Direct Sunlight
Common plants that prefer direct sunlight include succulents like aloe vera and cacti, which thrive under intense, unfiltered light for at least six hours a day. Tomatoes and peppers also require direct sunlight to produce optimal fruit yield and maintain robust growth. These plants develop stronger stems and vibrant foliage when exposed to consistent direct sunlight, avoiding the weaker growth associated with indirect light conditions.
Best Houseplants for Indirect Sunlight
Best houseplants for indirect sunlight thrive in filtered or shaded light conditions, making them ideal for rooms without direct sun exposure. Popular options include the snake plant (Sansevieria), pothos (Epipremnum aureum), and ZZ plant (Zamioculcas zamiifolia), all known for their low light tolerance and air-purifying qualities. These plants maintain vibrant foliage and growth in indirect sunlight, enhancing indoor environments where direct sunlight is limited.
Measuring Sunlight Exposure in Your Garden
Measuring sunlight exposure in your garden involves assessing both direct and indirect sunlight to optimize plant growth and health. Direct sunlight delivers the most intense energy, typically exceeding 1,000 lumens per square foot, essential for sun-loving plants like tomatoes and roses. Indirect sunlight, often filtered through clouds or foliage, provides lower intensity light around 500 lumens, suitable for shade-tolerant plants such as ferns and begonias.
Tips for Maximizing Sunlight for Healthy Plants
Place plants requiring direct sunlight near south-facing windows where they receive at least six hours of uninterrupted bright light daily, essential for photosynthesis and growth. For plants preferring indirect sunlight, position them in areas with filtered light, such as behind sheer curtains or near east- or west-facing windows to prevent leaf scorch while ensuring adequate illumination. Rotate plants regularly to expose all sides evenly, promoting balanced growth and optimizing chlorophyll absorption.
Sunlight Requirements for Popular Garden Vegetables
Most popular garden vegetables such as tomatoes, peppers, and cucumbers require direct sunlight for at least 6 to 8 hours daily to ensure optimal growth and fruit production. Leafy greens like lettuce, spinach, and kale thrive well in indirect sunlight or partial shade, needing around 4 to 6 hours of filtered light to avoid leaf burn and bolting. Understanding specific sunlight requirements helps maximize vegetable yield and maintain plant health in various garden settings.
Avoiding Sunlight Stress: Protecting Plants from Too Much Sun
Direct sunlight provides intense light essential for photosynthesis but can cause sunlight stress, leading to leaf scorch and dehydration in sensitive plants. Indirect sunlight offers a gentler light intensity, reducing the risk of heat damage while still supporting healthy growth. Implementing shade cloths or relocating plants can prevent excessive sun exposure, optimizing plant health and minimizing stress-related decline.
Direct sunlight vs indirect sunlight Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com