
Dappled sunlight vs direct sunlight Illustration
Dappled sunlight filters through leaves, creating soft, scattered light that reduces harsh shadows and glare, making it ideal for delicate plants and shaded outdoor spaces. In contrast, direct sunlight delivers intense, unfiltered rays that promote robust growth in sun-loving species but can cause stress or damage to shade-preferring flora. Understanding the differences between these sunlight types helps gardeners optimize plant health and landscape aesthetics.
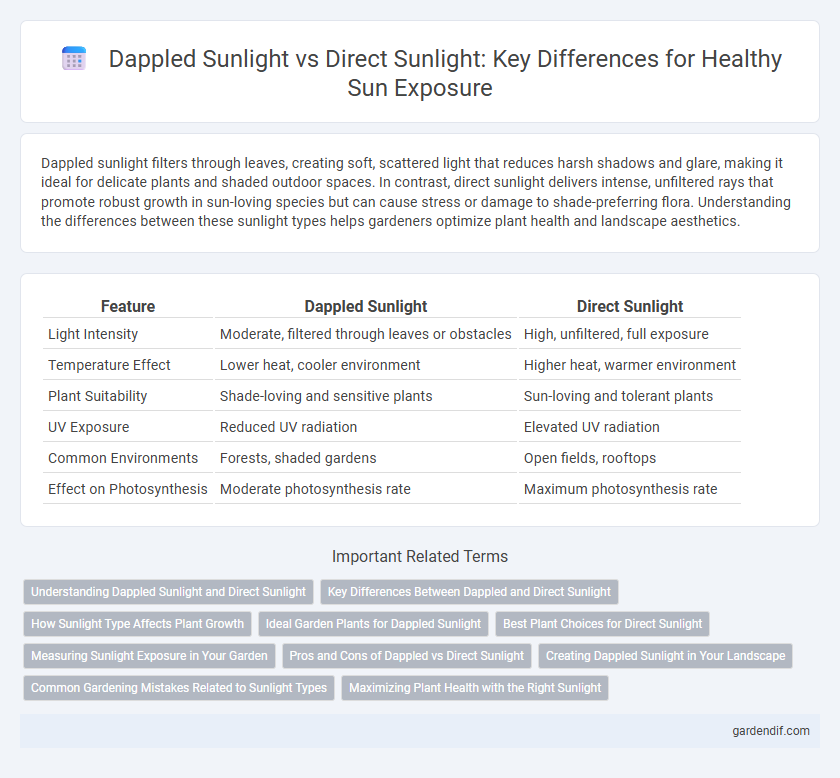
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Dappled Sunlight | Direct Sunlight |
|---|---|---|
| Light Intensity | Moderate, filtered through leaves or obstacles | High, unfiltered, full exposure |
| Temperature Effect | Lower heat, cooler environment | Higher heat, warmer environment |
| Plant Suitability | Shade-loving and sensitive plants | Sun-loving and tolerant plants |
| UV Exposure | Reduced UV radiation | Elevated UV radiation |
| Common Environments | Forests, shaded gardens | Open fields, rooftops |
| Effect on Photosynthesis | Moderate photosynthesis rate | Maximum photosynthesis rate |
Understanding Dappled Sunlight and Direct Sunlight
Dappled sunlight occurs when sunlight filters through gaps in tree leaves, creating a pattern of light and shadow that provides moderate intensity and reduces glare. Direct sunlight delivers full, unfiltered rays that offer maximum brightness and heat, intensifying exposure to UV radiation. Understanding these light types helps optimize plant growth, skin protection, and outdoor activity planning.
Key Differences Between Dappled and Direct Sunlight
Dappled sunlight occurs when light filters through leaves or other objects, creating a pattern of light and shadow, while direct sunlight shines unobstructed and evenly on surfaces. Plants exposed to dappled sunlight often experience cooler temperatures and reduced UV exposure compared to those under direct sunlight, which can cause higher heat stress and increased photosynthesis rates. The intensity and duration of light exposure in these conditions significantly influence plant growth, hydration, and overall health.
How Sunlight Type Affects Plant Growth
Dappled sunlight, characterized by filtered light through leaves, provides plants with moderate light intensity ideal for shade-tolerant species, promoting steady photosynthesis and preventing leaf scorch. In contrast, direct sunlight delivers high light intensity essential for sun-loving plants, enhancing chlorophyll production and accelerating growth but potentially causing stress or dehydration if exposure is excessive. Understanding these sunlight types helps optimize plant placement and care for maximizing growth and health.
Ideal Garden Plants for Dappled Sunlight
Dappled sunlight provides plants with intermittent exposure to sunlight filtered through foliage, creating a unique light environment ideal for shade-loving garden species. Plants such as hostas, ferns, astilbes, and hydrangeas thrive in dappled sunlight, benefiting from balanced light that prevents leaf scorch while promoting healthy growth. This light condition supports moisture retention in soil, making it favorable for temperate, shade-tolerant perennials and understory shrubs essential for vibrant garden diversity.
Best Plant Choices for Direct Sunlight
Succulents, cacti, and lavender thrive in direct sunlight due to their high tolerance for intense UV rays and heat. These plants have adapted to conserve water and withstand prolonged exposure to full sun, making them ideal for south-facing windows or outdoor spaces with unfiltered sunlight. Choosing sun-loving species like rosemary and bougainvillea ensures vibrant growth and minimal leaf scorch in bright, direct light conditions.
Measuring Sunlight Exposure in Your Garden
Measuring sunlight exposure in your garden requires distinguishing between dappled sunlight and direct sunlight to optimize plant growth. Dappled sunlight provides intermittent light filtered through tree canopies, ideal for shade-tolerant plants, while direct sunlight delivers continuous, intense rays necessary for sun-loving species. Using light meters or sunlight tracking apps allows precise quantification of exposure, ensuring proper placement and health of various garden plants.
Pros and Cons of Dappled vs Direct Sunlight
Dappled sunlight provides filtered light that reduces the risk of leaf scorch and water loss, making it ideal for shade-loving plants and promoting a cooler microclimate. Direct sunlight delivers full-intensity light essential for photosynthesis in sun-loving species but can increase heat stress and dehydration in sensitive plants. Choosing between dappled and direct sunlight depends on the specific light and temperature requirements of the plant species to optimize growth and health.
Creating Dappled Sunlight in Your Landscape
Creating dappled sunlight in your landscape involves strategically planting deciduous trees or shrubs with open canopies that filter sunlight, allowing soft, scattered light to reach the ground. Incorporating structures such as pergolas with climbing vines enhances shade patterns, producing a comfortable and visually appealing environment. Dappled sunlight benefits shade-loving plants by reducing harsh exposure while maintaining adequate light for photosynthesis and growth.
Common Gardening Mistakes Related to Sunlight Types
Dappled sunlight, characterized by filtered light through tree leaves, is often mistaken for insufficient light, leading gardeners to overcompensate with excessive watering or fertilizer application. Direct sunlight, which exposes plants to intense, unfiltered rays, commonly results in leaf burn or wilting when gardeners fail to select sun-tolerant species or neglect shading techniques. Understanding the distinctions between these sunlight types helps prevent typical gardening errors such as improper plant placement and inadequate light management.
Maximizing Plant Health with the Right Sunlight
Dappled sunlight provides plants with filtered light that reduces the risk of leaf scorch while supporting photosynthesis, making it ideal for shade-loving and understory plants. Direct sunlight delivers intense, unfiltered rays that boost growth for sun-loving species but can cause stress or dehydration in sensitive plants. Maximizing plant health involves matching the sunlight type to the specific light tolerance and water needs of each plant species to optimize photosynthetic efficiency and overall vitality.
Dappled sunlight vs direct sunlight Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com