
Sun requirements vs shade tolerance Illustration
Sunlight requirements vary greatly among plants, with some species thriving in full sun while others prefer partial to full shade. Understanding the specific light needs is crucial for plant health, as inadequate sun exposure can inhibit growth and flowering, whereas too much direct sunlight may cause leaf scorch or dehydration. Selecting plants suited to the available light conditions ensures optimal photosynthesis and overall garden vitality.
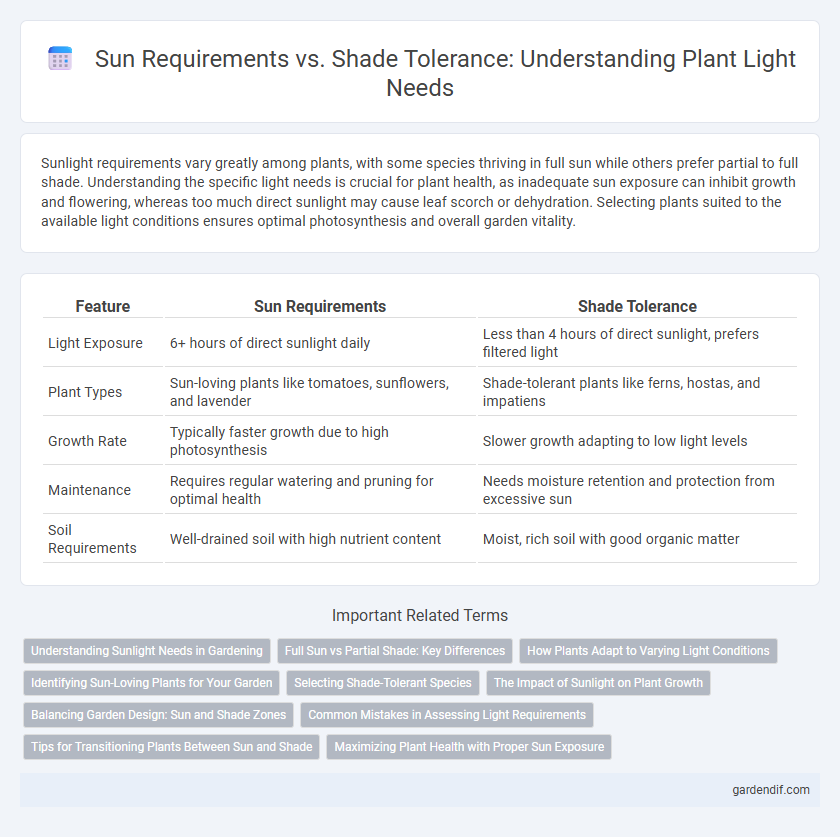
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Sun Requirements | Shade Tolerance |
|---|---|---|
| Light Exposure | 6+ hours of direct sunlight daily | Less than 4 hours of direct sunlight, prefers filtered light |
| Plant Types | Sun-loving plants like tomatoes, sunflowers, and lavender | Shade-tolerant plants like ferns, hostas, and impatiens |
| Growth Rate | Typically faster growth due to high photosynthesis | Slower growth adapting to low light levels |
| Maintenance | Requires regular watering and pruning for optimal health | Needs moisture retention and protection from excessive sun |
| Soil Requirements | Well-drained soil with high nutrient content | Moist, rich soil with good organic matter |
Understanding Sunlight Needs in Gardening
Sunlight requirements vary significantly among plants, with some species thriving in full sun exposure of at least six hours daily, while others prefer partial to full shade to avoid stress and ensure optimal growth. Understanding the specific light needs of each plant is crucial for successful gardening, helping to prevent issues like leaf scorch or poor flowering. Gardeners must assess their garden's sunlight patterns and match plants accordingly to promote healthy, vigorous development.
Full Sun vs Partial Shade: Key Differences
Full sun plants require at least six hours of direct sunlight daily, promoting maximum photosynthesis and robust growth, while partial shade plants thrive with three to six hours of filtered or indirect sunlight, avoiding leaf scorch and moisture loss. Understanding the specific light needs ensures optimal plant health, flowering, and fruit production in diverse garden environments. Selecting plants based on their sun requirements versus shade tolerance is crucial for maintaining a balanced ecosystem and achieving aesthetic garden design.
How Plants Adapt to Varying Light Conditions
Plants adapt to varying light conditions through specialized mechanisms such as chlorophyll concentration adjustments and leaf morphology changes to optimize photosynthesis in both sunlit and shaded environments. Sun-loving plants typically possess thicker leaves with higher photosynthetic capacities to withstand intense light and minimize water loss, whereas shade-tolerant species develop broader, thinner leaves with increased chlorophyll content to capture limited sunlight efficiently. These adaptations enable plants to thrive across diverse habitats by maximizing energy absorption while minimizing stress from excessive or insufficient light exposure.
Identifying Sun-Loving Plants for Your Garden
Sun-loving plants thrive in environments with at least six hours of direct sunlight daily, making them ideal for bright, open gardens. Species such as lavender, sunflowers, and tomatoes require full sun to maximize photosynthesis and promote robust growth. Selecting plants based on their sun requirements versus shade tolerance ensures optimal health, vibrant blooms, and higher yields in your garden landscape.
Selecting Shade-Tolerant Species
Selecting shade-tolerant species is crucial for optimizing plant growth in low-light environments, as these plants have adapted to thrive with limited sunlight by efficiently using available light for photosynthesis. Species such as ferns, hostas, and certain types of ivy exhibit high shade tolerance, making them ideal choices for densely shaded areas where sun requirements cannot be met. Understanding the specific light requirements and physiological adaptations of these shade-tolerant plants ensures successful landscaping and garden planning in shaded locations.
The Impact of Sunlight on Plant Growth
Sunlight intensity directly influences photosynthesis rates, with full sun plants requiring at least six hours of direct light daily to optimize growth and flowering. Shade-tolerant plants have adapted to lower light conditions, often thriving with filtered or indirect sunlight due to their efficient chlorophyll utilization. Understanding the specific sunlight needs of plant species is crucial for maximizing biomass production and overall plant health.
Balancing Garden Design: Sun and Shade Zones
Balancing garden design requires understanding plant sun requirements versus shade tolerance to create thriving sun and shade zones. Sun-loving plants such as tomatoes and lavender need at least six hours of direct sunlight, while shade-tolerant species like hostas and ferns flourish in partial to full shade conditions. Strategically positioning these plants based on their light preferences ensures optimal growth and visual harmony in diverse garden environments.
Common Mistakes in Assessing Light Requirements
Many gardeners mistakenly assume that plants requiring full sunlight can thrive with partial shade, leading to stunted growth or poor blooms. Shade tolerance varies significantly among species, with some plants only surviving in dappled sunlight rather than deep shade or full sun. Accurately assessing a plant's specific light needs by consulting horticultural guides or observing its natural habitat prevents common errors in sun exposure management.
Tips for Transitioning Plants Between Sun and Shade
Gradually introduce plants to their new light environment by increasing or decreasing sun exposure over 7 to 10 days to minimize stress and sunburn. Monitor soil moisture closely since sun-exposed areas dry out faster, requiring more frequent watering. Select plant varieties known for their shade tolerance or sun adaptability to ensure a successful transition between light conditions.
Maximizing Plant Health with Proper Sun Exposure
Maximizing plant health requires balancing sun requirements and shade tolerance to ensure optimal growth conditions. Plants with high sun requirements perform best under 6 or more hours of direct sunlight daily, which boosts photosynthesis and nutrient uptake. Shade-tolerant species thrive in reduced light environments, typically needing less than 4 hours of direct sun, preventing leaf scorch and promoting robust foliage development.
Sun requirements vs shade tolerance Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com