
Full sun vs partial sun Illustration
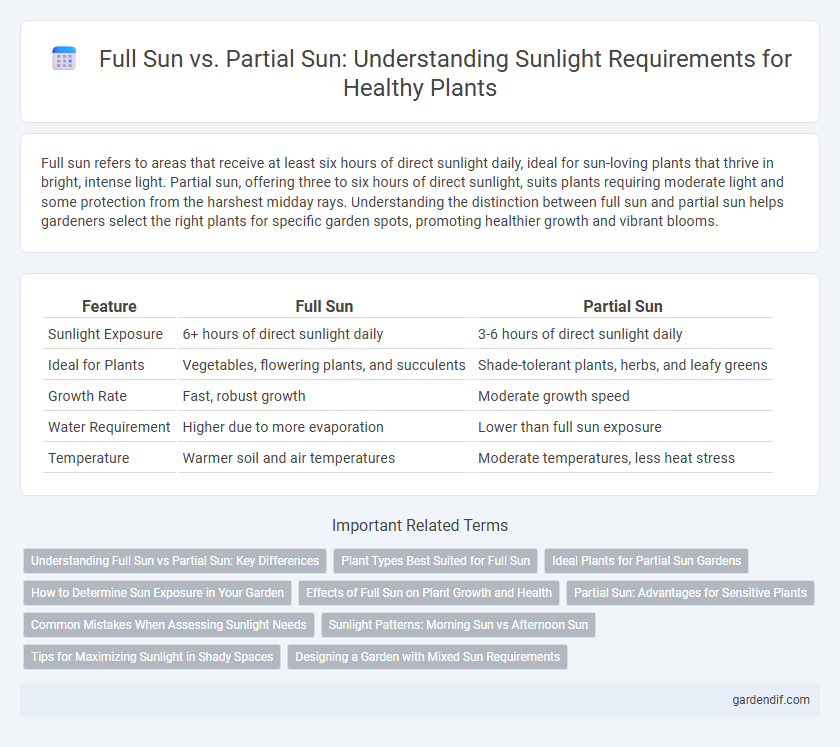
Full sun refers to areas that receive at least six hours of direct sunlight daily, ideal for sun-loving plants that thrive in bright, intense light. Partial sun, offering three to six hours of direct sunlight, suits plants requiring moderate light and some protection from the harshest midday rays. Understanding the distinction between full sun and partial sun helps gardeners select the right plants for specific garden spots, promoting healthier growth and vibrant blooms.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Full Sun | Partial Sun |
|---|---|---|
| Sunlight Exposure | 6+ hours of direct sunlight daily | 3-6 hours of direct sunlight daily |
| Ideal for Plants | Vegetables, flowering plants, and succulents | Shade-tolerant plants, herbs, and leafy greens |
| Growth Rate | Fast, robust growth | Moderate growth speed |
| Water Requirement | Higher due to more evaporation | Lower than full sun exposure |
| Temperature | Warmer soil and air temperatures | Moderate temperatures, less heat stress |
Understanding Full Sun vs Partial Sun: Key Differences
Full sun refers to areas receiving at least six hours of direct sunlight daily, essential for sun-loving plants like tomatoes and sunflowers to thrive and produce optimal growth and blooms. Partial sun typically means 3 to 6 hours of direct sunlight, offering a balance that suits plants such as impatiens and ferns, which require moderate light without intense heat exposure. Understanding these distinctions helps gardeners select appropriate plant species for garden zones, ensuring healthy development and maximizing photosynthesis efficiency.
Plant Types Best Suited for Full Sun
Plants best suited for full sun include heat-loving vegetables like tomatoes, peppers, and cucumbers that thrive with at least six hours of direct sunlight daily. Sunflowers, lavender, and most succulents also flourish in full sun conditions, maximizing photosynthesis and growth. Full sun promotes vibrant blooms and robust foliage in these species, essential for optimal plant health and yield.
Ideal Plants for Partial Sun Gardens
Partial sun gardens thrive with plants such as azaleas, hydrangeas, and ferns, which require approximately 3 to 6 hours of direct sunlight daily. These plants benefit from morning sun exposure combined with afternoon shade to prevent leaf scorch and maintain vibrant blooms. Choosing shade-tolerant yet light-loving species ensures optimal growth and prolonged flowering in partially sunny environments.
How to Determine Sun Exposure in Your Garden
Determine sun exposure in your garden by observing sunlight patterns throughout the day, noting areas that receive at least six hours of direct sunlight qualify as full sun, while those with three to six hours fall under partial sun. Use tools like a sunlight meter or simply mark spots where shadows shift, tracking sunlight intensity during peak hours between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. Understanding the precise sun exposure helps select suitable plants that thrive under full sun or partial sun conditions, optimizing growth and garden health.
Effects of Full Sun on Plant Growth and Health
Full sun exposure, typically defined as six or more hours of direct sunlight daily, significantly boosts photosynthesis, enhancing plant growth, flowering, and fruit production. Plants adapted to full sun conditions develop stronger stems and thicker leaves, improving overall health and resilience against pests and diseases. However, excessive exposure can cause stress in shade-loving species, leading to wilting, leaf scorch, and reduced growth efficiency.
Partial Sun: Advantages for Sensitive Plants
Partial sun provides 3 to 6 hours of direct sunlight daily, offering an ideal environment for sensitive plants that may wilt or scorch under full sun exposure. This moderate light intensity reduces the risk of leaf burn and dehydration while still supporting photosynthesis for healthy growth. Gardeners benefit from using partial sun locations to cultivate shade-tolerant species such as ferns, begonias, and impatiens, which thrive without the stress of intense sunlight.
Common Mistakes When Assessing Sunlight Needs
Common mistakes when assessing sunlight needs often include confusing full sun with partial sun, leading to improper plant placement and growth issues. Full sun requires at least six hours of direct sunlight daily, while partial sun typically means three to six hours, often with some afternoon shade to prevent leaf scorch. Misjudging these conditions can cause stress to plants, reduce flowering, and increase vulnerability to pests and diseases.
Sunlight Patterns: Morning Sun vs Afternoon Sun
Full sun provides at least six hours of direct sunlight daily, ideal for sun-loving plants, while partial sun offers three to six hours, often benefiting species sensitive to intense light. Morning sun is cooler and less intense, reducing the risk of leaf scorch and promoting steady growth, whereas afternoon sun delivers stronger, hotter rays that can increase heat stress on foliage. Understanding these sunlight patterns helps optimize plant placement for health and productivity in gardens and landscapes.
Tips for Maximizing Sunlight in Shady Spaces
Maximizing sunlight in shady spaces involves strategic placement of reflective surfaces such as mirrors or light-colored walls to redirect available sunlight onto plants. Selecting shade-tolerant plant species like hostas, ferns, or impatiens ensures better growth under partial sun conditions, which typically means 3 to 6 hours of direct sunlight daily. Using pruning techniques to thin overhanging branches increases light penetration, enhancing photosynthesis and overall plant health in areas with limited full sun exposure.
Designing a Garden with Mixed Sun Requirements
Designing a garden with mixed sun requirements involves strategic placement of plants based on their sunlight needs. Full sun plants require a minimum of six hours of direct sunlight, thriving best in open, unobstructed areas, while partial sun plants need between three to six hours of direct sunlight, often benefiting from dappled shade during the hottest parts of the day. Incorporating raised beds, carefully positioned shading structures, and utilizing plant height variations helps optimize light exposure, ensuring healthy growth for both full sun and partial sun species.
Full sun vs partial sun Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com