
Sheet composting vs Trench composting Illustration
Sheet composting involves spreading organic waste in a thin layer over the soil surface, promoting gradual decomposition and enhancing soil fertility without disturbing plant roots. Trench composting requires burying organic matter in trenches, accelerating decomposition by maintaining moisture and warmth, and reducing pest issues. Both methods improve soil structure and nutrient content but differ in application depth and speed of compost integration.
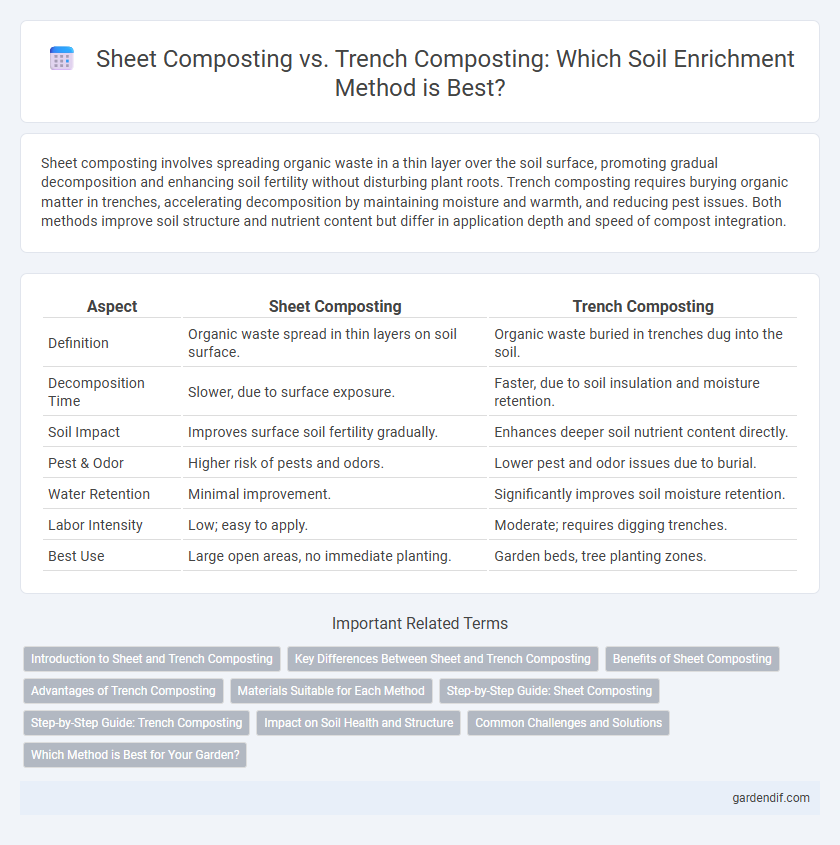
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Sheet Composting | Trench Composting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Organic waste spread in thin layers on soil surface. | Organic waste buried in trenches dug into the soil. |
| Decomposition Time | Slower, due to surface exposure. | Faster, due to soil insulation and moisture retention. |
| Soil Impact | Improves surface soil fertility gradually. | Enhances deeper soil nutrient content directly. |
| Pest & Odor | Higher risk of pests and odors. | Lower pest and odor issues due to burial. |
| Water Retention | Minimal improvement. | Significantly improves soil moisture retention. |
| Labor Intensity | Low; easy to apply. | Moderate; requires digging trenches. |
| Best Use | Large open areas, no immediate planting. | Garden beds, tree planting zones. |
Introduction to Sheet and Trench Composting
Sheet composting involves spreading organic matter like leaves, grass clippings, and kitchen scraps directly onto the soil surface to decompose naturally, enriching the topsoil with nutrients and improving soil structure. Trench composting requires digging trenches 6 to 12 inches deep and burying organic waste, which accelerates decomposition by providing a protected environment and minimizing nutrient loss. Both methods enhance soil fertility and promote healthy microbial activity essential for plant growth.
Key Differences Between Sheet and Trench Composting
Sheet composting involves spreading organic materials in a thin layer over the soil surface, promoting nutrient absorption and improving soil structure gradually. Trench composting requires digging a trench where kitchen scraps and organic waste are buried directly, enhancing decomposition through insulated below-ground conditions and reducing pest attraction. The key differences lie in the method of application, depth of composting, and the speed and containment of nutrient release into the soil.
Benefits of Sheet Composting
Sheet composting enhances soil fertility by evenly distributing organic matter across the surface, promoting gradual nutrient release and improving soil structure. This method minimizes labor while maintaining moisture retention and suppressing weed growth, leading to healthier plant development. Its simplicity and efficiency make it ideal for gardeners seeking sustainable soil enrichment with minimal disturbance.
Advantages of Trench Composting
Trench composting enhances soil fertility by directly enriching the root zone, promoting faster nutrient absorption and plant growth. It minimizes pest and odor issues by burying organic waste deeper into the soil, reducing exposure to surface pests. This method conserves moisture effectively and improves soil aeration, leading to healthier microbial activity and enhanced soil structure.
Materials Suitable for Each Method
Sheet composting is ideal for organic materials such as kitchen scraps, grass clippings, shredded leaves, and manure, which decompose efficiently on the soil surface. Trench composting works best with kitchen waste, small plant trimmings, and soft garden waste buried directly in trenches to accelerate decomposition and reduce pests. Both methods benefit from balanced nitrogen-rich and carbon-rich materials to enhance microbial activity and soil fertility.
Step-by-Step Guide: Sheet Composting
Sheet composting involves spreading organic materials such as leaves, grass clippings, and kitchen scraps in thin layers directly over the soil surface, enriching the soil as they decompose. Begin by clearing the ground of weeds, then apply alternating layers of green and brown materials to maintain a balanced carbon-to-nitrogen ratio for optimal microbial activity. Water each layer lightly to promote decomposition, and allow the layers to break down naturally, improving soil structure and fertility over time.
Step-by-Step Guide: Trench Composting
Trench composting involves digging a trench or hole 12 to 18 inches deep where organic waste such as kitchen scraps, garden clippings, and leaves are deposited and then covered with soil. This method accelerates decomposition by limiting oxygen exposure, reducing pests, and improving soil fertility directly at the application site. Regularly rotating trench locations promotes healthy soil structure and nutrient distribution, making it ideal for sustainable garden maintenance.
Impact on Soil Health and Structure
Sheet composting enhances soil health by providing a continuous layer of organic matter that improves moisture retention and encourages microbial activity at the surface. Trench composting enriches deeper soil layers, promoting better aeration and nutrient distribution, which strengthens soil structure and root development. Both methods increase organic content, but trench composting has a more substantial impact on subsoil fertility and long-term soil stability.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Sheet composting often faces challenges such as uneven decomposition and pest attraction due to exposed organic material, which can be mitigated by layering carbon-rich materials and covering with soil or mulch. Trench composting may struggle with proper aeration and slow breakdown, requiring periodic loosening of soil and addition of nitrogen-rich scraps to enhance microbial activity. Both methods benefit from regular moisture monitoring and balancing green and brown materials to optimize composting efficiency and soil health.
Which Method is Best for Your Garden?
Sheet composting spreads organic materials like leaves, grass clippings, and kitchen scraps directly over the soil surface, enhancing nutrient availability and moisture retention with minimal labor. Trench composting involves burying compostable materials deeper in the soil, accelerating decomposition and improving soil aeration while reducing surface pests. Garden size, soil type, and time availability determine the best method: sheet composting suits large areas and gradual nutrient release, whereas trench composting works well for smaller gardens requiring rapid soil enrichment.
Sheet composting vs Trench composting Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com