
Mulching vs Sheet mulching Illustration
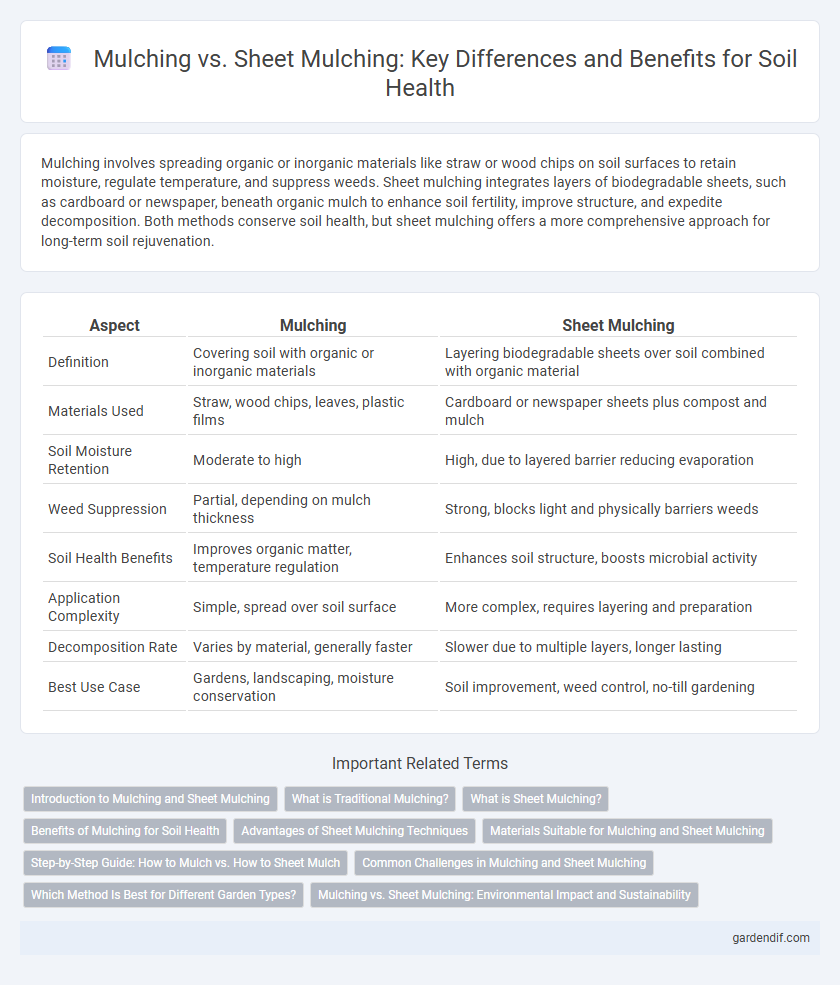
Mulching involves spreading organic or inorganic materials like straw or wood chips on soil surfaces to retain moisture, regulate temperature, and suppress weeds. Sheet mulching integrates layers of biodegradable sheets, such as cardboard or newspaper, beneath organic mulch to enhance soil fertility, improve structure, and expedite decomposition. Both methods conserve soil health, but sheet mulching offers a more comprehensive approach for long-term soil rejuvenation.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Mulching | Sheet Mulching |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Covering soil with organic or inorganic materials | Layering biodegradable sheets over soil combined with organic material |
| Materials Used | Straw, wood chips, leaves, plastic films | Cardboard or newspaper sheets plus compost and mulch |
| Soil Moisture Retention | Moderate to high | High, due to layered barrier reducing evaporation |
| Weed Suppression | Partial, depending on mulch thickness | Strong, blocks light and physically barriers weeds |
| Soil Health Benefits | Improves organic matter, temperature regulation | Enhances soil structure, boosts microbial activity |
| Application Complexity | Simple, spread over soil surface | More complex, requires layering and preparation |
| Decomposition Rate | Varies by material, generally faster | Slower due to multiple layers, longer lasting |
| Best Use Case | Gardens, landscaping, moisture conservation | Soil improvement, weed control, no-till gardening |
Introduction to Mulching and Sheet Mulching
Mulching involves covering soil with organic or inorganic materials to conserve moisture, suppress weeds, and improve soil quality. Sheet mulching, a specific mulching method, uses layers of biodegradable materials like cardboard and compost to mimic natural soil-building processes and enhance fertility. Both techniques significantly boost soil health by promoting microbial activity and preventing erosion.
What is Traditional Mulching?
Traditional mulching involves spreading organic materials such as straw, wood chips, or leaves directly over the soil surface to conserve moisture, regulate temperature, and suppress weeds. This method enhances soil fertility by decomposing and enriching the soil with nutrients, improving microbial activity and structure. Unlike sheet mulching, traditional mulching is simpler and does not typically involve layering with cardboard or newspaper as a weed barrier.
What is Sheet Mulching?
Sheet mulching is an organic gardening technique that layers materials such as cardboard, newspaper, compost, and mulch directly on top of the soil to improve fertility, moisture retention, and weed suppression. This method mimics natural decomposition processes, enriching soil structure and microbial life while minimizing erosion. Compared to traditional mulching, sheet mulching provides a more sustainable, long-term soil amendment by gradually breaking down and integrating into the soil ecosystem.
Benefits of Mulching for Soil Health
Mulching improves soil health by conserving moisture, regulating temperature, and suppressing weed growth, which enhances root development and microbial activity. Sheet mulching, a layered technique combining cardboard or newspaper with organic materials, accelerates soil fertility by breaking down into nutrient-rich compost while preventing erosion. Both methods increase organic matter content, promoting soil structure and long-term sustainability.
Advantages of Sheet Mulching Techniques
Sheet mulching significantly improves soil structure by enhancing water retention and reducing erosion, promoting healthier plant growth. This technique effectively suppresses weeds without the need for chemical herbicides, supporting organic gardening practices. The decomposition of layers in sheet mulching enriches the soil with vital nutrients, fostering a sustainable and fertile growing environment.
Materials Suitable for Mulching and Sheet Mulching
Organic materials such as straw, wood chips, and compost are ideal for traditional mulching, providing moisture retention and weed suppression while enriching soil nutrients. Sheet mulching typically involves layers of newspaper or cardboard topped with organic mulch, effectively blocking sunlight to prevent weed growth and promoting soil health through gradual decomposition. Both methods benefit from using biodegradable, nutrient-rich materials to enhance soil structure and fertility.
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Mulch vs. How to Sheet Mulch
Mulching involves spreading organic materials such as wood chips or straw evenly over soil to retain moisture, regulate temperature, and suppress weeds, typically applied by first clearing debris, then layering mulch around plants to a depth of 2-4 inches. Sheet mulching begins with laying down a layer of cardboard or newspaper on cleared soil to block weeds, followed by adding alternating layers of compost, mulch, and organic matter, creating a nutrient-rich, moisture-retentive environment that improves soil structure over time. Both techniques enhance soil health but sheet mulching provides a more comprehensive soil-building method through layered decomposition.
Common Challenges in Mulching and Sheet Mulching
Common challenges in mulching include uneven moisture retention, pest attraction, and nutrient imbalances that can affect soil health and plant growth. Sheet mulching specifically faces difficulties with proper layering to prevent weed growth while ensuring adequate aeration and decomposition of organic materials. Both methods require careful selection of mulch types and maintenance to optimize soil structure and fertility.
Which Method Is Best for Different Garden Types?
Mulching with organic materials like straw or wood chips is ideal for vegetable gardens and flower beds, promoting moisture retention and nutrient enrichment while allowing soil aeration. Sheet mulching, involving layers of cardboard or newspaper topped with compost, works best for transforming lawns or heavily compacted areas into new garden beds by suppressing weeds and improving soil structure over time. Choosing the right method depends on garden type, soil condition, and desired long-term soil health outcomes.
Mulching vs. Sheet Mulching: Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Mulching helps conserve soil moisture, reduce erosion, and improve nutrient cycling by adding organic material directly to the soil surface, promoting a healthier soil ecosystem. Sheet mulching combines traditional mulching with layers of cardboard or newspaper that suppress weeds and enhance soil structure while reducing the need for chemical herbicides. Both methods support sustainable gardening practices by improving soil health and reducing water usage, but sheet mulching offers a more comprehensive approach to soil regeneration and waste reduction.
Mulching vs Sheet mulching Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com