
Sheet Mulching vs Lasagna Gardening Illustration
Sheet mulching creates a weed-suppressing, nutrient-rich soil layer by layering organic materials such as cardboard, compost, and mulch directly on the ground, enhancing soil structure and moisture retention. Lasagna gardening involves building raised garden beds using alternating layers of compostable materials, which decompose to form fertile soil ideal for planting vegetables and flowers. Both methods improve soil health and reduce erosion, but sheet mulching is typically used for large areas, while lasagna gardening suits smaller, manageable beds.
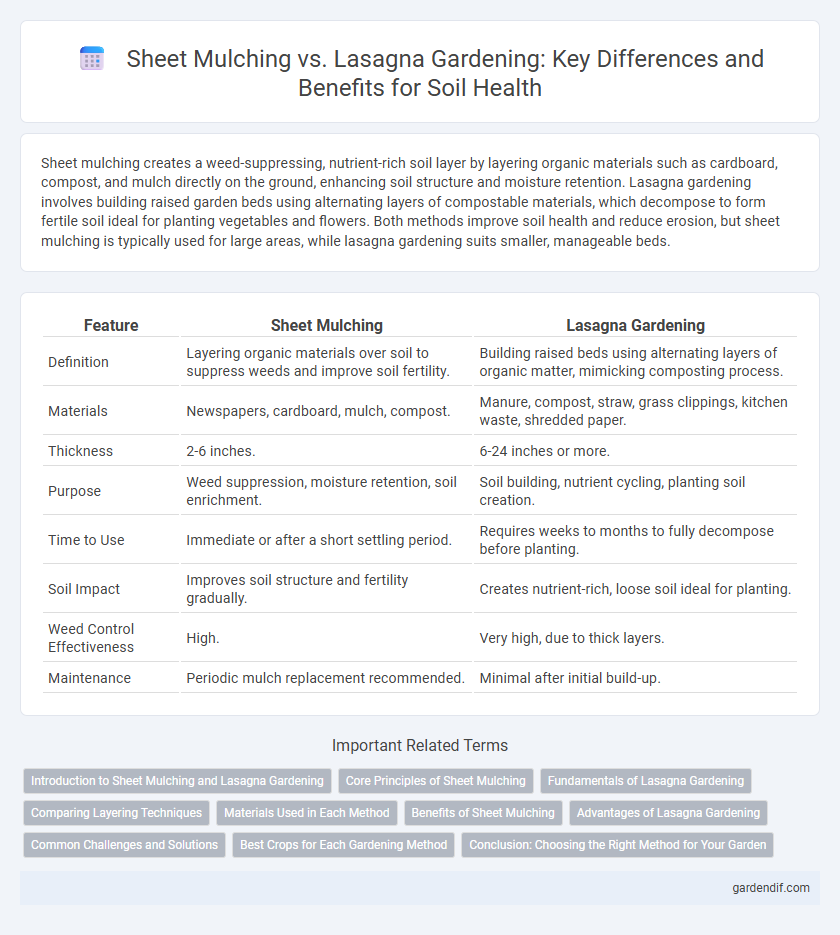
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Sheet Mulching | Lasagna Gardening |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Layering organic materials over soil to suppress weeds and improve soil fertility. | Building raised beds using alternating layers of organic matter, mimicking composting process. |
| Materials | Newspapers, cardboard, mulch, compost. | Manure, compost, straw, grass clippings, kitchen waste, shredded paper. |
| Thickness | 2-6 inches. | 6-24 inches or more. |
| Purpose | Weed suppression, moisture retention, soil enrichment. | Soil building, nutrient cycling, planting soil creation. |
| Time to Use | Immediate or after a short settling period. | Requires weeks to months to fully decompose before planting. |
| Soil Impact | Improves soil structure and fertility gradually. | Creates nutrient-rich, loose soil ideal for planting. |
| Weed Control Effectiveness | High. | Very high, due to thick layers. |
| Maintenance | Periodic mulch replacement recommended. | Minimal after initial build-up. |
Introduction to Sheet Mulching and Lasagna Gardening
Sheet mulching is a sustainable gardening technique that improves soil health by layering organic materials such as cardboard, compost, and mulch directly on the soil surface, suppressing weeds and enhancing moisture retention. Lasagna gardening, also known as lasagna composting, builds fertile soil by layering nitrogen-rich and carbon-rich materials, mimicking natural composting processes without tilling. Both methods promote soil fertility and structure while reducing waste and erosion, making them effective for improving garden productivity.
Core Principles of Sheet Mulching
Sheet mulching core principles include creating a nutrient-rich, weed-suppressing base by layering organic materials such as cardboard, compost, and mulch directly onto soil. This process enhances soil structure, moisture retention, and microbial activity, promoting healthy plant growth without disturbing existing earth layers. Unlike lasagna gardening, which involves building raised beds through sequential layering, sheet mulching typically occurs in situ, leveraging natural decomposition to improve soil fertility over time.
Fundamentals of Lasagna Gardening
Lasagna gardening is a no-dig, layered composting technique that builds fertile soil by alternating organic materials such as carbon-rich leaves and nitrogen-rich grass clippings. It promotes soil structure, moisture retention, and microbial activity, enhancing plant growth without mechanical disturbance. This method contrasts with sheet mulching by focusing more extensively on decomposing layers that transform into rich humus over time.
Comparing Layering Techniques
Sheet mulching employs a dense layering of cardboard or newspaper topped with organic materials to suppress weeds and improve soil structure, emphasizing a weed-free base. Lasagna gardening utilizes alternating layers of nitrogen-rich greens and carbon-rich browns, creating a nutrient-rich compost layer that enhances soil fertility over time. Both techniques focus on layering organic matter but differ in composition and primary function, with sheet mulching prioritizing weed control and lasagna gardening optimizing nutrient cycling.
Materials Used in Each Method
Sheet mulching primarily utilizes layers of cardboard, newspaper, compost, and organic mulch such as straw or leaves, creating a weed-blocking, moisture-retentive barrier. Lasagna gardening involves alternating layers of green (nitrogen-rich) materials like grass clippings or kitchen scraps with brown (carbon-rich) materials such as dried leaves, paper, or cardboard, enhancing soil fertility through decomposition. Both methods prioritize organic inputs but differ in their layering approach and material composition to improve soil structure and nutrient content.
Benefits of Sheet Mulching
Sheet mulching improves soil health by enhancing moisture retention, suppressing weeds, and adding organic matter that fosters beneficial microbial activity. This method reduces soil erosion and compaction, promoting better root growth and nutrient availability. Its layered approach accelerates decomposition, enriching the soil structure and fertility more effectively than conventional mulching techniques.
Advantages of Lasagna Gardening
Lasagna gardening enhances soil fertility by layering organic materials that decompose, enriching the soil structure and moisture retention significantly better than traditional sheet mulching. This method fosters diverse microbial activity and earthworm populations, promoting healthier root development and nutrient cycling. It also reduces weed growth naturally by creating a dense, nutrient-rich barrier that improves plant resilience and growth rates.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Sheet mulching and lasagna gardening both face challenges such as weed suppression, moisture retention, and soil nutrient balance. Common issues include slow decomposition of materials and potential nitrogen depletion, which can be mitigated by using nitrogen-rich compost layers and regularly monitoring soil health. Proper layering of organic materials in sheet mulching and the strategic placement of green and brown layers in lasagna gardening optimize microbial activity and improve soil fertility.
Best Crops for Each Gardening Method
Leafy greens and root vegetables thrive in sheet mulching due to its thick organic layers that retain moisture and suppress weeds, creating ideal conditions for spinach, lettuce, carrots, and beets. Lasagna gardening's nutrient-rich, layered composting system best supports fruiting crops such as tomatoes, peppers, and eggplants, which benefit from the enhanced soil fertility and aeration. Both methods improve soil structure but selecting crops that match each technique maximizes yield and plant health.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Method for Your Garden
Sheet mulching offers a faster, more intensive soil-building approach by layering organic materials to smother weeds and improve fertility, ideal for creating new garden beds quickly. Lasagna gardening focuses on a gradual decomposition process, layering diverse materials that enrich soil structure and microbial activity over time, perfect for nurturing long-term soil health. Selecting the right method depends on garden goals, available materials, and desired timeline for soil improvement.
Sheet Mulching vs Lasagna Gardening Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com