
Claybreaker vs Gypsum Illustration
Claybreaker enhances soil structure by breaking down heavy clay particles, improving aeration and water infiltration, while gypsum primarily adds calcium and sulfur to soil, helping to reduce soil compaction and improve nutrient availability. Claybreaker is especially effective for loosening dense, sticky clay soils, whereas gypsum is ideal for soils with high sodium content that need reclamation. Combining both can synergistically enhance overall soil health by balancing physical texture and chemical properties.
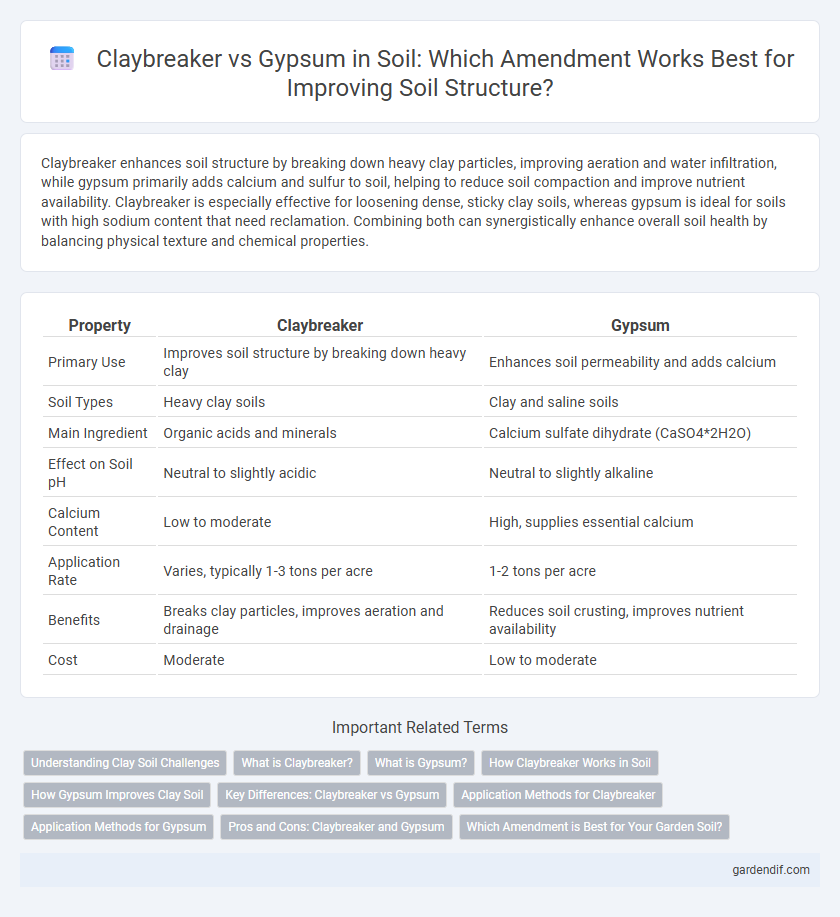
Table of Comparison
| Property | Claybreaker | Gypsum |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Improves soil structure by breaking down heavy clay | Enhances soil permeability and adds calcium |
| Soil Types | Heavy clay soils | Clay and saline soils |
| Main Ingredient | Organic acids and minerals | Calcium sulfate dihydrate (CaSO4*2H2O) |
| Effect on Soil pH | Neutral to slightly acidic | Neutral to slightly alkaline |
| Calcium Content | Low to moderate | High, supplies essential calcium |
| Application Rate | Varies, typically 1-3 tons per acre | 1-2 tons per acre |
| Benefits | Breaks clay particles, improves aeration and drainage | Reduces soil crusting, improves nutrient availability |
| Cost | Moderate | Low to moderate |
Understanding Clay Soil Challenges
Claybreaker improves soil structure by breaking up compacted clay layers, enhancing aeration and drainage essential for healthy root growth. Gypsum, a calcium sulfate compound, mitigates soil compaction by displacing sodium ions in sodic clay, promoting better aggregation and water infiltration. Understanding the specific clay soil challenge--whether poor aeration or sodium toxicity--guides the choice between Claybreaker and gypsum for effective soil remediation.
What is Claybreaker?
Claybreaker is a soil amendment designed to improve heavy clay soils by enhancing drainage and reducing compaction. It typically contains a blend of gypsum, organic matter, and other minerals that promote soil structure and aeration. Unlike pure gypsum, Claybreaker also helps increase microbial activity, boosting overall soil health and fertility.
What is Gypsum?
Gypsum is a naturally occurring mineral composed of calcium sulfate dihydrate, widely used in soil management to improve structure and reduce compaction. It enhances soil permeability by displacing sodium ions, promoting better water infiltration and root growth in clay soils. Unlike claybreakers, gypsum does not physically break up soil aggregates but chemically conditions the soil to improve aeration and nutrient availability.
How Claybreaker Works in Soil
Claybreaker improves soil structure by chemically dispersing clay particles, preventing compaction and enhancing aeration and water infiltration. It works by exchanging sodium ions in the clay with calcium ions, reducing soil salinity and promoting aggregation of soil particles into crumb-like structures. This process increases nutrient availability and root penetration, supporting healthier plant growth.
How Gypsum Improves Clay Soil
Gypsum enhances clay soil by reducing its compact structure through calcium sulfate, which displaces sodium ions and improves soil aggregation. This process increases permeability, allowing better water infiltration and root penetration in dense clay soils. Unlike claybreaker, gypsum does not break soil physically but chemically improves soil texture and fertility for healthier plant growth.
Key Differences: Claybreaker vs Gypsum
Claybreaker is primarily a soil conditioner designed to loosen heavy clay soils by flocculating clay particles and improving water infiltration, while gypsum mainly supplies calcium and sulfur to enhance soil structure and reduce sodium levels. Claybreaker works by physically breaking up dense clay clumps, whereas gypsum chemically alters soil properties to mitigate sodicity and improve permeability. The key difference lies in Claybreaker's focus on mechanical soil loosening compared to gypsum's role in chemical soil amendment and nutrient supplementation.
Application Methods for Claybreaker
Claybreaker is primarily applied by broadcasting or incorporation into the soil to improve drainage and reduce clay compaction. Gypsum is often used as a soil amendment to supply calcium and improve soil structure but differs by being more effective in sodic soils. Application methods for Claybreaker typically involve tilling it into the topsoil layer to enhance permeability and root penetration.
Application Methods for Gypsum
Gypsum application methods for soil amendment include broadcasting, surface application, and subsurface incorporation, ensuring effective calcium delivery and soil structure improvement. Broadcasting spreads gypsum evenly over the field, while subsurface incorporation involves mixing gypsum into the soil profile to enhance permeability and reduce compaction. These methods optimize gypsum's ability to offset sodium effects, improve water infiltration, and promote healthier root development in sodic or saline soils.
Pros and Cons: Claybreaker and Gypsum
Claybreaker improves soil structure by breaking up compacted clay, enhancing aeration and water infiltration, but it may take time to show significant results and can be costly for large areas. Gypsum adds calcium and sulfur, helping to reduce soil salinity and improve water penetration in sodic soils, but it is less effective on heavily compacted clay and can lead to nutrient imbalances if overused. Both amendments contribute to better soil health, yet selecting between Claybreaker and Gypsum depends on specific soil conditions and crop requirements.
Which Amendment is Best for Your Garden Soil?
Claybreaker improves garden soil by breaking up heavy clay particles, enhancing aeration and drainage for healthier root growth. Gypsum adds calcium and sulfur to soil, reducing compaction and improving water infiltration without altering soil pH. For soils with dense clay, Claybreaker excels in improving texture, while Gypsum is ideal for sodic soils needing calcium and sulfur enrichment.
Claybreaker vs Gypsum Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com