
Hydroponic substrate vs Organic soil Illustration
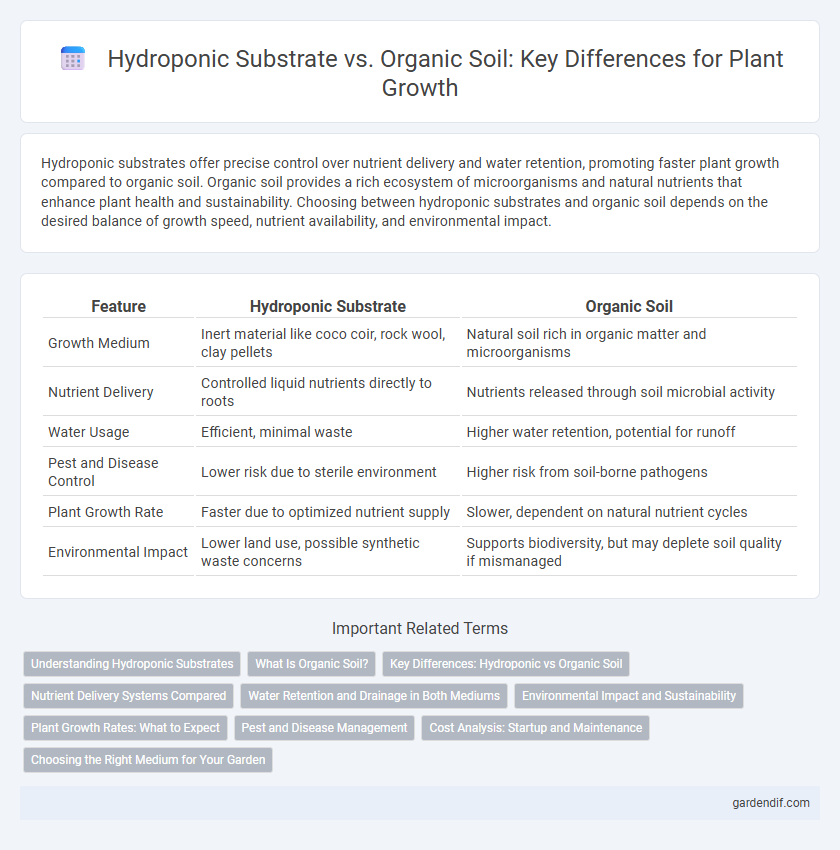
Hydroponic substrates offer precise control over nutrient delivery and water retention, promoting faster plant growth compared to organic soil. Organic soil provides a rich ecosystem of microorganisms and natural nutrients that enhance plant health and sustainability. Choosing between hydroponic substrates and organic soil depends on the desired balance of growth speed, nutrient availability, and environmental impact.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Hydroponic Substrate | Organic Soil |
|---|---|---|
| Growth Medium | Inert material like coco coir, rock wool, clay pellets | Natural soil rich in organic matter and microorganisms |
| Nutrient Delivery | Controlled liquid nutrients directly to roots | Nutrients released through soil microbial activity |
| Water Usage | Efficient, minimal waste | Higher water retention, potential for runoff |
| Pest and Disease Control | Lower risk due to sterile environment | Higher risk from soil-borne pathogens |
| Plant Growth Rate | Faster due to optimized nutrient supply | Slower, dependent on natural nutrient cycles |
| Environmental Impact | Lower land use, possible synthetic waste concerns | Supports biodiversity, but may deplete soil quality if mismanaged |
Understanding Hydroponic Substrates
Hydroponic substrates are inert growing mediums such as coco coir, perlite, or rockwool that provide structural support for plant roots without contributing nutrients, relying on nutrient-rich water solutions for growth. Unlike organic soil, which contains natural microorganisms and organic matter that supply nutrients and improve soil structure, hydroponic substrates offer precise control over nutrient delivery, reducing variability and potential soil-borne diseases. Understanding the properties of hydroponic substrates, including porosity, water retention, and aeration, is essential for optimizing plant health and maximizing crop yields in soilless cultivation systems.
What Is Organic Soil?
Organic soil consists of natural materials like decomposed plant matter, compost, and microorganisms that enhance nutrient availability and soil structure. It supports healthy root development by retaining moisture and promoting beneficial microbial activity. Unlike hydroponic substrates, organic soil provides a living ecosystem that sustains long-term plant growth and fertility.
Key Differences: Hydroponic vs Organic Soil
Hydroponic substrate offers a soilless medium primarily composed of inert materials such as coconut coir, perlite, or rockwool, enabling precise nutrient control and faster plant growth compared to organic soil. Organic soil contains natural components like decomposed plant matter, microorganisms, and minerals that enhance soil fertility and support ecosystem biodiversity. Key differences include nutrient delivery methods, microbial activity levels, water retention capacity, and environmental sustainability impacts.
Nutrient Delivery Systems Compared
Hydroponic substrates enable precise control over nutrient delivery by directly supplying a balanced nutrient solution to plant roots, resulting in faster absorption and enhanced growth rates compared to organic soil. Organic soil relies on microbial activity to break down organic matter, gradually releasing nutrients which can lead to variable availability and slower nutrient uptake. The efficient and targeted nutrient delivery in hydroponic systems reduces nutrient waste and supports optimal plant development.
Water Retention and Drainage in Both Mediums
Hydroponic substrates typically offer superior water retention and precise drainage control compared to organic soil, ensuring roots receive optimal moisture without waterlogging. Organic soil retains water through its natural organic matter and porosity, but its drainage varies based on composition, often leading to inconsistent moisture levels. Effective water management in hydroponic media enhances nutrient uptake efficiency, while organic soil requires regular monitoring to prevent root rot and maintain aeration balance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Hydroponic substrates significantly reduce water consumption and nutrient runoff compared to organic soil, promoting efficient resource use and minimizing environmental pollution. Organic soil supports biodiversity and carbon sequestration but often requires more water and chemical inputs, which can increase its ecological footprint. Choosing hydroponic systems can enhance sustainability by optimizing nutrient delivery and reducing land degradation while organic soil maintains ecosystem health through natural processes.
Plant Growth Rates: What to Expect
Hydroponic substrates typically promote faster plant growth rates compared to organic soil due to their optimized nutrient delivery and aeration, enabling roots to absorb essential minerals more efficiently. Organic soil offers slower but more sustainable growth through natural microbial activity and nutrient cycling, which enhances plant resilience and long-term health. Expect hydroponic systems to accelerate growth by up to 30-50% while organic soil supports steady development with improved flavor and nutrient density.
Pest and Disease Management
Hydroponic substrates offer enhanced control over pest and disease management by reducing soil-borne pathogen risks commonly found in organic soil. Organic soil can harbor a wide range of pests and diseases, making preventative measures like crop rotation and biological controls essential. The sterile environment of hydroponic systems minimizes contamination, improving plant health and reducing the need for chemical treatments.
Cost Analysis: Startup and Maintenance
Hydroponic substrates typically require higher initial investment for specialized materials like inert media and nutrient solutions, whereas organic soil involves lower upfront costs due to natural availability. Maintenance expenses in hydroponics are driven by continuous nutrient solution replenishment and system monitoring, contrasted with organic soil requiring periodic amendments and less frequent input replacement. Over time, hydroponic systems may offer cost efficiency through faster plant growth and water conservation compared to traditional soil gardening.
Choosing the Right Medium for Your Garden
Hydroponic substrates offer precise control over nutrient delivery and water retention, promoting faster plant growth in soilless systems. Organic soil provides a rich microbial ecosystem and natural nutrient cycling, enhancing plant health and soil structure over time. Selecting the right medium depends on factors like crop type, growth speed, resource availability, and environmental sustainability goals.
Hydroponic substrate vs Organic soil Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com