
Clay soil vs Silt soil Illustration
Clay soil has fine particles that retain water well but drain poorly, often becoming compacted, while silt soil has medium-sized particles that hold moisture efficiently and provide better aeration. Clay soil is nutrient-rich but can be challenging for root penetration, whereas silt soil is fertile and easier to cultivate due to its smoother texture. Understanding these differences helps gardeners choose the right amendments for improved soil structure and plant growth.
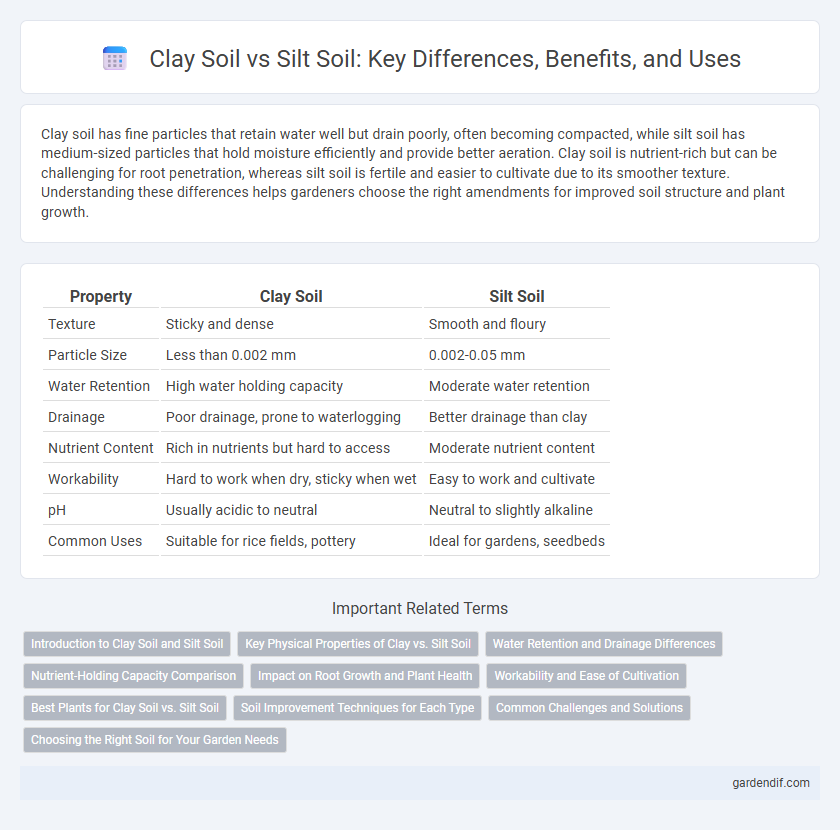
Table of Comparison
| Property | Clay Soil | Silt Soil |
|---|---|---|
| Texture | Sticky and dense | Smooth and floury |
| Particle Size | Less than 0.002 mm | 0.002-0.05 mm |
| Water Retention | High water holding capacity | Moderate water retention |
| Drainage | Poor drainage, prone to waterlogging | Better drainage than clay |
| Nutrient Content | Rich in nutrients but hard to access | Moderate nutrient content |
| Workability | Hard to work when dry, sticky when wet | Easy to work and cultivate |
| pH | Usually acidic to neutral | Neutral to slightly alkaline |
| Common Uses | Suitable for rice fields, pottery | Ideal for gardens, seedbeds |
Introduction to Clay Soil and Silt Soil
Clay soil consists of very fine mineral particles that compact tightly, resulting in poor drainage and high nutrient retention. Silt soil has medium-sized particles, feels smooth and floury, and retains moisture longer than sandy soil while providing moderate fertility. Both soil types play distinct roles in agriculture and horticulture, influencing water retention, aeration, and plant root development.
Key Physical Properties of Clay vs. Silt Soil
Clay soil features very fine particles that retain water tightly, leading to poor drainage and slow drying, while silt soil has medium-sized particles that provide moderate water retention and better drainage. Clay soil's texture is sticky when wet and hardens as it dries, whereas silt soil feels smooth and floury, maintaining a loose structure. The high plasticity and density of clay contrasts with the more friable and easily eroded nature of silt, significantly influencing aeration and root penetration.
Water Retention and Drainage Differences
Clay soil retains water effectively due to its fine particles and low permeability, causing slow drainage and potentially waterlogged conditions. Silt soil, with medium-sized particles, holds moisture well but drains more efficiently than clay, balancing water retention and aeration. Understanding these differences is essential for agricultural practices and plant health management.
Nutrient-Holding Capacity Comparison
Clay soil has a higher nutrient-holding capacity due to its fine texture and greater surface area, which allows it to retain essential minerals such as potassium, calcium, and magnesium more effectively than silt soil. Silt soil, though smoother and more porous, tends to leach nutrients faster because of its larger particles, resulting in lower cation exchange capacity compared to clay. The increased nutrient retention in clay soils supports better fertility and plant growth under proper moisture conditions.
Impact on Root Growth and Plant Health
Clay soil's fine particles create dense, compact layers that restrict root penetration and reduce oxygen availability, often leading to poor plant health and slower growth. In contrast, silt soil has medium-sized particles that improve moisture retention without excessive compaction, promoting healthier root development and more vigorous plant growth. Understanding the differences in texture and drainage between clay and silt soils is crucial for optimizing root growth and overall plant vitality.
Workability and Ease of Cultivation
Clay soil has fine particles that compact tightly, making it dense and heavy, which can restrict root growth and reduce aeration, thus requiring significant effort to till and improve its workability. Silt soil features medium-sized particles that retain moisture better than sand but drain more efficiently than clay, offering a smoother texture and easier cultivation due to enhanced soil aeration and nutrient availability. Gardeners prefer silt soil for its balance between moisture retention and ease of tilling, while clay soil often demands soil amendments like organic matter to enhance its structure and ease of cultivation.
Best Plants for Clay Soil vs. Silt Soil
Clay soil supports plants like daylilies, hostas, and asters that thrive in dense, moisture-retentive conditions, while silt soil is ideal for herbs such as basil, cilantro, and lemon balm due to its smooth texture and good drainage. Both soil types benefit from the addition of organic matter to enhance fertility and structure, promoting healthier root development. Understanding the distinct water retention and aeration properties of clay and silt soils helps in selecting plants that maximize growth and yield.
Soil Improvement Techniques for Each Type
Clay soil benefits from soil improvement techniques such as adding organic matter like compost or peat moss to enhance drainage and aeration, while gypsum application can help reduce compaction. Silt soil requires loosening through deep tillage and incorporation of coarse materials like sand or perlite to improve texture and prevent waterlogging. Both soil types respond well to cover cropping and regular mulching to maintain structure and fertility.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Clay soil often faces issues with poor drainage and compaction, limiting root growth and aeration. Silt soil tends to have erosion problems due to its fine particles being easily washed away by water. Incorporating organic matter improves soil structure, enhances water retention in clay, and reduces erosion in silt soils, promoting healthier plant development.
Choosing the Right Soil for Your Garden Needs
Clay soil retains water effectively due to its fine particles, making it ideal for plants requiring consistent moisture but prone to compaction and poor drainage. Silt soil, with medium-sized particles, offers excellent fertility and moderate water retention, supporting a wide range of garden plants while improving aeration. Selecting between clay and silt depends on your garden's drainage requirements and plant water needs, ensuring optimal growth and soil health.
Clay soil vs Silt soil Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com