
Mulching vs Bare soil Illustration
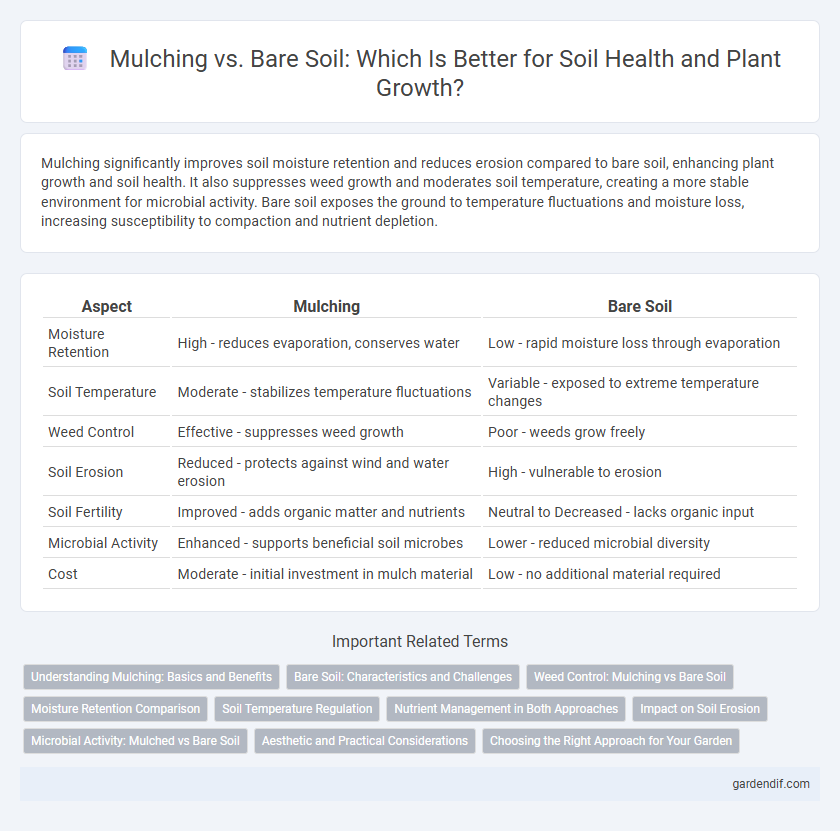
Mulching significantly improves soil moisture retention and reduces erosion compared to bare soil, enhancing plant growth and soil health. It also suppresses weed growth and moderates soil temperature, creating a more stable environment for microbial activity. Bare soil exposes the ground to temperature fluctuations and moisture loss, increasing susceptibility to compaction and nutrient depletion.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Mulching | Bare Soil |
|---|---|---|
| Moisture Retention | High - reduces evaporation, conserves water | Low - rapid moisture loss through evaporation |
| Soil Temperature | Moderate - stabilizes temperature fluctuations | Variable - exposed to extreme temperature changes |
| Weed Control | Effective - suppresses weed growth | Poor - weeds grow freely |
| Soil Erosion | Reduced - protects against wind and water erosion | High - vulnerable to erosion |
| Soil Fertility | Improved - adds organic matter and nutrients | Neutral to Decreased - lacks organic input |
| Microbial Activity | Enhanced - supports beneficial soil microbes | Lower - reduced microbial diversity |
| Cost | Moderate - initial investment in mulch material | Low - no additional material required |
Understanding Mulching: Basics and Benefits
Mulching involves covering soil with organic or inorganic materials like straw, wood chips, or plastic to conserve moisture, regulate temperature, and suppress weeds. This practice improves soil structure and fertility by adding organic matter and preventing erosion, enhancing microbial activity and nutrient retention. Compared to bare soil, mulching significantly reduces water evaporation and soil compaction, promoting healthier plant growth and sustainable land management.
Bare Soil: Characteristics and Challenges
Bare soil exposes the ground surface to erosion by wind and water, leading to nutrient loss and diminished soil structure. This condition increases evaporation rates, reducing moisture retention vital for plant growth. Without protective cover, bare soil is more susceptible to compaction and temperature fluctuations, which negatively impact microbial activity and overall soil health.
Weed Control: Mulching vs Bare Soil
Mulching significantly reduces weed growth by blocking sunlight and creating a physical barrier that inhibits seed germination, whereas bare soil provides an ideal environment for weeds to sprout and spread rapidly. Organic mulches also improve soil moisture retention and temperature regulation, further discouraging weed establishment compared to exposed bare soil. Effective weed control through mulching minimizes the need for herbicides and manual weeding, promoting healthier plant growth and sustainable soil management.
Moisture Retention Comparison
Mulching significantly enhances soil moisture retention by reducing evaporation rates compared to bare soil, maintaining humidity levels critical for plant health. Studies show that mulched soils retain up to 30% more moisture than exposed soils, promoting sustained water availability during dry periods. This moisture conservation supports root development and reduces irrigation frequency, improving overall water-use efficiency in agricultural practices.
Soil Temperature Regulation
Mulching significantly improves soil temperature regulation by insulating the soil, reducing temperature fluctuations between day and night, and maintaining a more consistent microclimate for plant roots. Bare soil is more susceptible to extreme temperature variations, which can stress plants and disrupt root development. Organic mulches such as straw, wood chips, or compost also enhance moisture retention while protecting soil microbial activity essential for healthy soil structure.
Nutrient Management in Both Approaches
Mulching enhances nutrient management by slowly releasing organic matter, improving soil fertility and reducing nutrient leaching compared to bare soil. Bare soil often experiences accelerated nutrient depletion due to erosion and lack of organic residue to replenish nutrients. Mulched soils maintain better moisture retention, promoting microbial activity that aids nutrient cycling and availability.
Impact on Soil Erosion
Mulching significantly reduces soil erosion by protecting the soil surface from the direct impact of raindrops and minimizing water runoff, thus preserving soil structure and fertility. Bare soil is highly vulnerable to erosion as it lacks protective cover, leading to increased sediment loss and nutrient depletion. Studies show mulched areas can reduce soil erosion rates by up to 70% compared to bare soil conditions.
Microbial Activity: Mulched vs Bare Soil
Mulching significantly enhances microbial activity by providing organic matter that serves as a food source for soil microbes, promoting diverse and abundant microbial populations. In contrast, bare soil often experiences reduced microbial activity due to exposure to environmental stresses like temperature fluctuations and moisture loss. This increased microbial activity under mulch improves soil structure, nutrient cycling, and overall soil health.
Aesthetic and Practical Considerations
Mulching enhances aesthetic appeal by providing a uniform, tidy appearance that contrasts nicely with plants and garden features, while bare soil often looks patchy and uneven. Practically, mulching conserves soil moisture, suppresses weeds, and regulates temperature, leading to healthier plant growth compared to exposed, bare soil that dries out quickly and invites erosion. This combination of visual improvement and functional benefits makes mulching a preferred choice in both residential and commercial landscaping.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Garden
Mulching improves soil moisture retention, reduces erosion, and suppresses weeds, making it ideal for healthy garden growth. Bare soil can lead to nutrient loss, increased evaporation, and soil compaction, which negatively impact plant development. Assess your garden's specific needs, climate, and plant types to choose between mulching or leaving soil bare for optimal soil health and productivity.
Mulching vs Bare soil Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com