
Silty Soil vs Sandy Soil Illustration
Silty soil retains moisture better and has finer particles compared to sandy soil, which is coarse and drains water quickly. Silty soil is more fertile and supports plant growth due to its nutrient-holding capacity, while sandy soil often requires frequent watering and fertilization. Understanding these differences helps gardeners choose the right soil type for optimal crop yield and soil management.
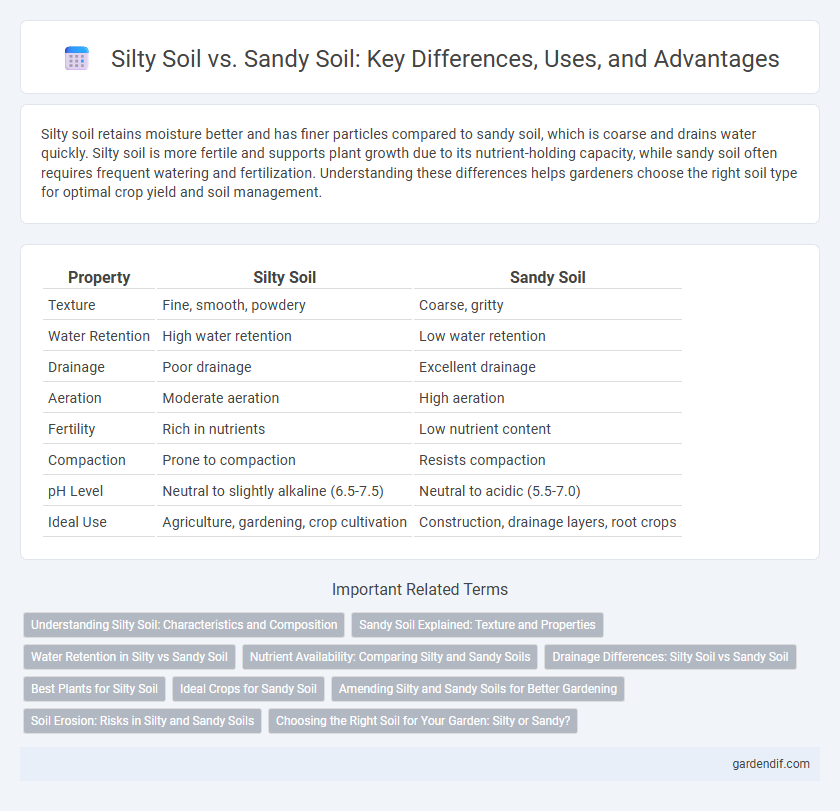
Table of Comparison
| Property | Silty Soil | Sandy Soil |
|---|---|---|
| Texture | Fine, smooth, powdery | Coarse, gritty |
| Water Retention | High water retention | Low water retention |
| Drainage | Poor drainage | Excellent drainage |
| Aeration | Moderate aeration | High aeration |
| Fertility | Rich in nutrients | Low nutrient content |
| Compaction | Prone to compaction | Resists compaction |
| pH Level | Neutral to slightly alkaline (6.5-7.5) | Neutral to acidic (5.5-7.0) |
| Ideal Use | Agriculture, gardening, crop cultivation | Construction, drainage layers, root crops |
Understanding Silty Soil: Characteristics and Composition
Silty soil consists of fine particles ranging from 0.002 to 0.05 millimeters in diameter, offering a smooth texture and high nutrient retention ideal for agriculture. Its composition includes a significant amount of minerals such as quartz and feldspar, which enhance fertility but also increase water retention, leading to poor drainage and potential root rot if unmanaged. Understanding these properties helps optimize silty soil use in gardening and farming by improving aeration and preventing compaction.
Sandy Soil Explained: Texture and Properties
Sandy soil is characterized by its coarse texture and large particle size, allowing excellent drainage and aeration but poor water and nutrient retention. Its gritty feel results from the dominance of sand particles ranging from 0.05 to 2 mm in diameter, which create large pore spaces between particles. This soil type is ideal for plants requiring well-drained conditions but often necessitates organic matter amendments to enhance fertility and moisture retention.
Water Retention in Silty vs Sandy Soil
Silty soil exhibits higher water retention due to its fine particles and greater surface area, enabling it to hold moisture longer than sandy soil. Sandy soil, composed of larger particles with larger pore spaces, drains water quickly, resulting in lower moisture retention. This difference significantly impacts irrigation strategies, with silty soil requiring less frequent watering compared to sandy soil.
Nutrient Availability: Comparing Silty and Sandy Soils
Silty soil holds higher nutrient availability than sandy soil due to its fine particles and greater cation exchange capacity, which enhance nutrient retention and accessibility for plants. In contrast, sandy soil has large particles and poor nutrient-holding capacity, leading to faster nutrient leaching and lower fertility. This makes silty soil more suitable for crops requiring consistent nutrient supply, while sandy soil often needs frequent fertilization to maintain productivity.
Drainage Differences: Silty Soil vs Sandy Soil
Sandy soil has large particles and well-connected pore spaces, allowing water to drain quickly and preventing waterlogging. Silty soil, composed of finer particles, retains moisture longer due to smaller pore spaces, resulting in slower drainage and higher water retention. These drainage differences influence irrigation needs and plant root oxygen availability in silty versus sandy soils.
Best Plants for Silty Soil
Silty soil, known for its fine texture and high nutrient content, supports a wide variety of plants such as lettuce, cabbage, and broccoli that thrive in moisture-retentive environments. Unlike sandy soil, which drains quickly and suits drought-tolerant species, silty soil retains water, promoting healthier growth for moisture-loving plants. Optimal plant selection for silty soil includes perennials and vegetables that benefit from its fertility and moderate drainage characteristics.
Ideal Crops for Sandy Soil
Sandy soil, characterized by large particles and excellent drainage, is ideal for crops such as carrots, potatoes, peanuts, and watermelons that thrive in well-aerated environments. These crops benefit from sandy soil's ability to warm quickly in the spring, promoting faster root development and preventing waterlogging. Farmers often choose sandy soil for cultivating drought-tolerant plants due to its low water retention capacity.
Amending Silty and Sandy Soils for Better Gardening
Amend silty soil by incorporating organic matter such as compost or well-rotted manure to improve drainage and prevent compaction, enhancing root growth and nutrient uptake. Sandy soil benefits from the addition of organic mulch and clay-rich amendments to increase moisture retention and nutrient-holding capacity, reducing water loss and promoting healthier plant development. Regularly testing soil pH and nutrient levels ensures tailored amendments that optimize soil structure and fertility for superior gardening results.
Soil Erosion: Risks in Silty and Sandy Soils
Silty soil, with its fine particles, is highly susceptible to water erosion due to poor drainage and low permeability, causing rapid loss of topsoil and nutrients. Sandy soil, characterized by coarse grains and high infiltration rates, experiences less surface runoff but is prone to wind erosion, leading to displacement of loose particles. Effective soil conservation strategies must account for these erosion risks to maintain soil fertility and prevent land degradation.
Choosing the Right Soil for Your Garden: Silty or Sandy?
Silty soil retains moisture and nutrients more effectively, making it ideal for gardens with water-loving plants and requiring good fertility. Sandy soil drains quickly, preventing root rot but necessitates frequent watering and nutrient supplementation for optimal plant growth. Selecting between silty and sandy soil depends on your garden's water retention needs and the types of plants you intend to cultivate.
Silty Soil vs Sandy Soil Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com