
Synthetic Mulch vs Natural Mulch Illustration
Synthetic mulch, made from materials like plastic or rubber, offers long-lasting weed control and moisture retention but lacks soil enrichment benefits. Natural mulch, such as wood chips or straw, improves soil fertility and supports beneficial microorganisms while decomposing over time. Choosing between synthetic and natural mulch depends on garden goals, maintenance preferences, and environmental considerations.
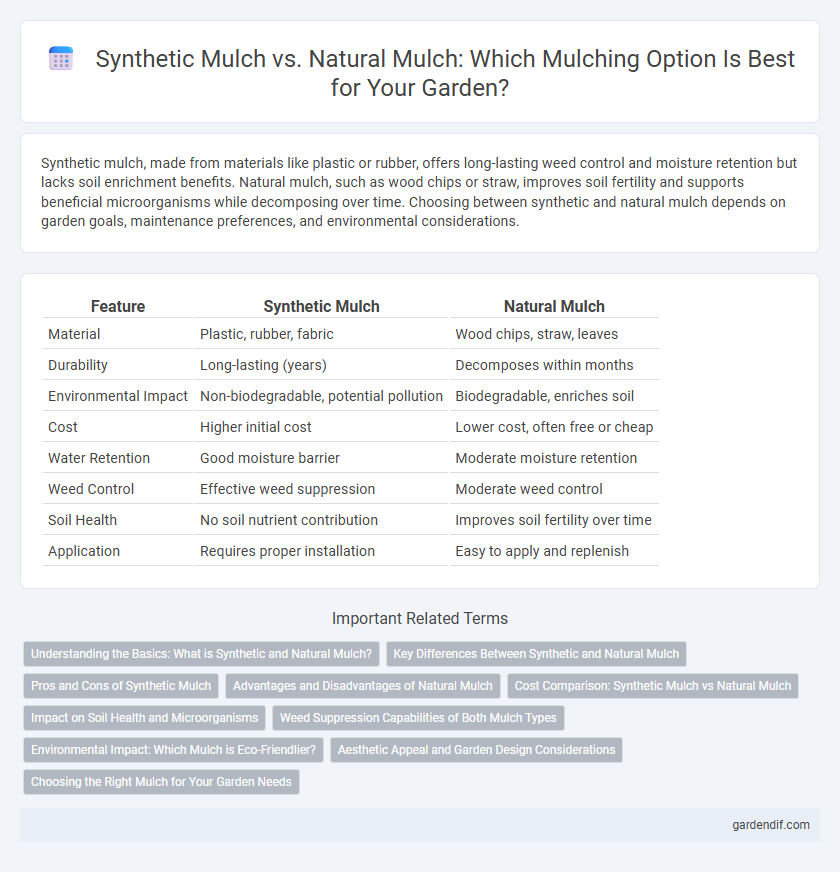
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Synthetic Mulch | Natural Mulch |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Plastic, rubber, fabric | Wood chips, straw, leaves |
| Durability | Long-lasting (years) | Decomposes within months |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable, potential pollution | Biodegradable, enriches soil |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower cost, often free or cheap |
| Water Retention | Good moisture barrier | Moderate moisture retention |
| Weed Control | Effective weed suppression | Moderate weed control |
| Soil Health | No soil nutrient contribution | Improves soil fertility over time |
| Application | Requires proper installation | Easy to apply and replenish |
Understanding the Basics: What is Synthetic and Natural Mulch?
Synthetic mulch consists of man-made materials like plastic, rubber, or landscape fabrics designed to suppress weeds, conserve moisture, and regulate soil temperature. Natural mulch includes organic substances such as wood chips, straw, leaves, and compost that decompose over time, enriching the soil with nutrients and improving its structure. Understanding these fundamental differences helps gardeners choose the right mulch based on environmental impact, soil health, and maintenance requirements.
Key Differences Between Synthetic and Natural Mulch
Synthetic mulch, often made from plastic or rubber, offers long-lasting weed control and moisture retention but lacks biodegradability and can negatively impact soil health. Natural mulch, derived from organic materials like wood chips, bark, or compost, enriches soil fertility through decomposition and supports beneficial microbial activity. Key differences include environmental impact, soil nutrient contribution, durability, and ease of installation.
Pros and Cons of Synthetic Mulch
Synthetic mulch offers advantages such as durability, low maintenance, and effective weed suppression, making it suitable for long-term landscaping projects. However, it lacks the ability to improve soil health or moisture retention like natural mulch and can contribute to environmental concerns due to its non-biodegradable nature. Its installation cost is higher initially, but the reduced frequency of replacement may offset expenses over time.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Natural Mulch
Natural mulch improves soil fertility by decomposing and adding organic matter, enhancing moisture retention and promoting beneficial microbial activity. It can be sourced sustainably from materials like wood chips, straw, or leaves, making it environmentally friendly and biodegradable, but it may require more frequent replacement compared to synthetic options. However, natural mulch can attract pests and harbor diseases if not properly managed, potentially impacting plant health.
Cost Comparison: Synthetic Mulch vs Natural Mulch
Synthetic mulch generally incurs a higher upfront cost compared to natural mulch due to the materials and manufacturing process involved. Natural mulch, such as wood chips or straw, is often less expensive initially but may require more frequent replacement, potentially increasing long-term expenses. Over time, synthetic mulch can offer cost savings through durability and reduced maintenance, making it a financially viable option depending on the project's duration and scale.
Impact on Soil Health and Microorganisms
Synthetic mulch, often made from plastic or rubber, inhibits natural soil aeration and water infiltration, leading to reduced microbial activity and poorer soil health over time. Natural mulch, such as wood chips or straw, enhances soil structure by promoting moisture retention, organic matter decomposition, and supporting diverse microbial communities essential for nutrient cycling. The use of natural mulch fosters a balanced ecosystem in the rhizosphere, improving soil fertility and plant growth sustainably.
Weed Suppression Capabilities of Both Mulch Types
Synthetic mulch, made from materials like plastic or rubber, offers superior weed suppression by creating a strong physical barrier that blocks sunlight and prevents weed germination more effectively than natural mulches. Natural mulch, such as wood chips or straw, suppresses weeds by covering the soil surface and limiting light but may decompose and require frequent replenishment, reducing its long-term weed control performance. The longevity and impermeability of synthetic mulch provide consistent weed inhibition, whereas natural mulch promotes soil health but offers less reliable weed suppression over time.
Environmental Impact: Which Mulch is Eco-Friendlier?
Synthetic mulch, typically made from plastic or rubber, contributes to long-term environmental pollution due to its non-biodegradable nature and potential to release harmful chemicals into the soil. Natural mulch, derived from organic materials like wood chips, leaves, or compost, improves soil health by enhancing moisture retention, promoting microbial activity, and eventually decomposing into nutrient-rich humus. Choosing natural mulch significantly reduces landfill waste and supports sustainable gardening practices, making it the eco-friendlier option for environmental impact.
Aesthetic Appeal and Garden Design Considerations
Synthetic mulch offers consistent color and texture that can enhance modern garden designs by maintaining a uniform aesthetic throughout the seasons. Natural mulch, such as bark or wood chips, provides a dynamic appearance that changes over time, complementing organic and rustic garden styles. Garden design considerations often weigh the long-term visual impact and integration with plant growth, favoring synthetic mulch for low-maintenance landscapes and natural mulch for ecological harmony.
Choosing the Right Mulch for Your Garden Needs
Synthetic mulch, such as rubber or plastic, offers long-lasting weed suppression and moisture retention but lacks nutrient contribution to soil health. Natural mulch, including wood chips, straw, or compost, enhances soil fertility by decomposing and enriching organic matter while improving microbial activity. Selecting the right mulch depends on garden goals, balancing durability and aesthetics with soil improvement and environmental impact.
Synthetic Mulch vs Natural Mulch Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com