
Sheet mulching vs broadcast mulching Illustration
Sheet mulching involves layering organic materials like cardboard or newspaper directly on the soil, creating a weed barrier and improving soil health over time. Broadcast mulching scatters loose organic materials such as bark chips or straw evenly across the surface, providing immediate moisture retention and temperature regulation. Choosing between sheet mulching and broadcast mulching depends on the specific gardening goals, with sheet mulching offering long-term soil benefits and broadcast mulching serving as a quicker, more superficial protective layer.
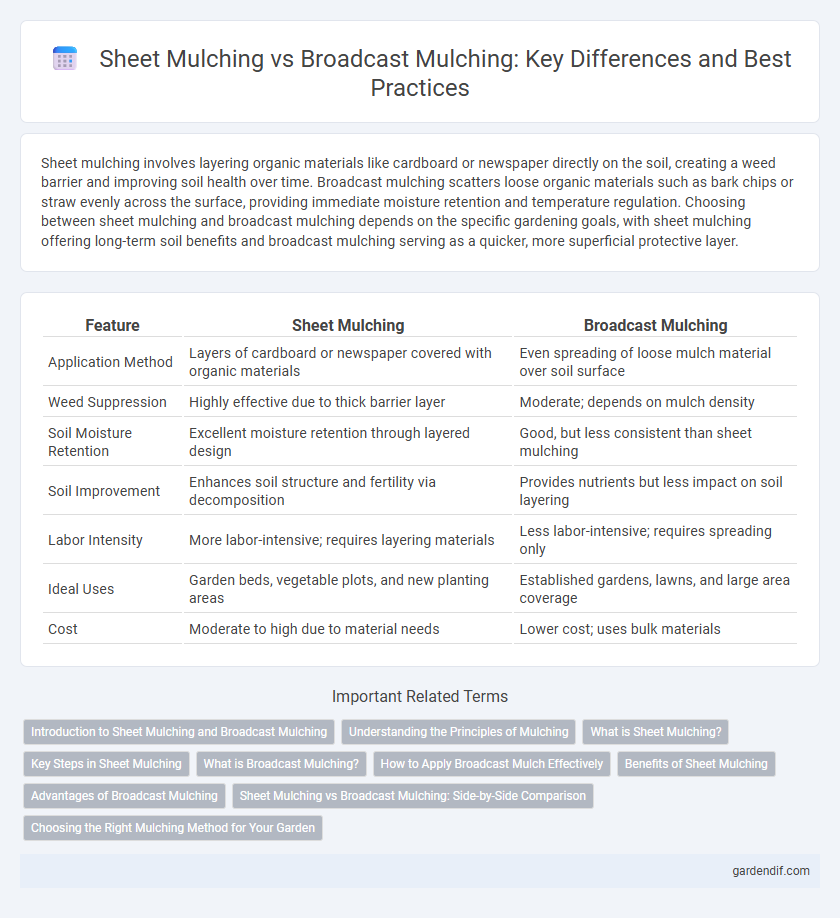
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Sheet Mulching | Broadcast Mulching |
|---|---|---|
| Application Method | Layers of cardboard or newspaper covered with organic materials | Even spreading of loose mulch material over soil surface |
| Weed Suppression | Highly effective due to thick barrier layer | Moderate; depends on mulch density |
| Soil Moisture Retention | Excellent moisture retention through layered design | Good, but less consistent than sheet mulching |
| Soil Improvement | Enhances soil structure and fertility via decomposition | Provides nutrients but less impact on soil layering |
| Labor Intensity | More labor-intensive; requires layering materials | Less labor-intensive; requires spreading only |
| Ideal Uses | Garden beds, vegetable plots, and new planting areas | Established gardens, lawns, and large area coverage |
| Cost | Moderate to high due to material needs | Lower cost; uses bulk materials |
Introduction to Sheet Mulching and Broadcast Mulching
Sheet mulching involves layering organic materials such as cardboard, compost, and mulch directly over the soil to suppress weeds and improve soil health by promoting microbial activity. Broadcast mulching spreads a uniform layer of mulch, like wood chips or straw, directly on the soil surface to retain moisture and reduce erosion. Both methods support sustainable gardening practices but differ in application techniques and impact on soil structure.
Understanding the Principles of Mulching
Sheet mulching involves layering cardboard or newspaper beneath organic materials to suppress weeds and retain soil moisture, creating a living mulch that improves soil health over time. Broadcast mulching spreads organic materials loosely across the soil surface, offering immediate moisture retention and temperature regulation but less effective weed control. Understanding these principles helps select the appropriate method based on garden goals, soil condition, and weed pressure for optimal plant growth.
What is Sheet Mulching?
Sheet mulching is an eco-friendly gardening technique that involves layering organic materials such as cardboard or newspaper directly on soil, followed by compost and mulch to suppress weeds and improve soil health. This method enhances moisture retention, promotes beneficial microbial activity, and gradually decomposes to enrich the soil structure. Unlike broadcast mulching, which distributes organic material loosely over the surface, sheet mulching creates a compact, layered system that effectively reduces weed growth and supports plant vitality.
Key Steps in Sheet Mulching
Sheet mulching involves layering cardboard or newspaper over soil, followed by organic materials like compost and mulch to suppress weeds and enrich soil health. Key steps include thoroughly removing existing vegetation, applying a nitrogen-rich layer to accelerate decomposition, and covering with a thick mulch layer to retain moisture and prevent erosion. This method promotes soil regeneration and reduces maintenance compared to broadcast mulching, which simply spreads mulch across the surface without underlying weed suppression layers.
What is Broadcast Mulching?
Broadcast mulching involves spreading organic materials like wood chips, straw, or leaves evenly across the soil surface to suppress weeds, retain moisture, and improve soil health. This method contrasts with sheet mulching, which layers biodegradable sheets beneath organic cover to enhance soil structure and nutrient content. Broadcast mulching is a quicker, less labor-intensive technique ideal for covering large areas and promoting microbial activity.
How to Apply Broadcast Mulch Effectively
Broadcast mulching requires spreading organic materials such as wood chips, straw, or leaves evenly across the soil surface at a depth of 2 to 4 inches to conserve moisture and suppress weeds. Ensuring the mulch layer is uniform and avoiding excessive thickness prevents fungal growth and soil smothering. Regularly replenishing broadcast mulch, especially after heavy rain or wind, maintains its effectiveness in enhancing soil health and temperature regulation.
Benefits of Sheet Mulching
Sheet mulching improves soil health by layering organic materials that decompose slowly, enhancing moisture retention and suppressing weeds more effectively than broadcast mulching. It creates a structured barrier that reduces soil erosion and promotes beneficial microbial activity, resulting in nutrient-rich soil. This method also minimizes the need for frequent mulch replenishment, making it a sustainable choice for long-term garden care.
Advantages of Broadcast Mulching
Broadcast mulching offers superior soil coverage by evenly distributing organic materials over large areas, which enhances moisture retention and weed suppression more effectively than sheet mulching. This method accelerates the breakdown of mulch into the soil, promoting improved nutrient cycling and soil fertility. Furthermore, broadcast mulching allows for easier application in uneven terrains and larger landscapes, reducing labor and time costs.
Sheet Mulching vs Broadcast Mulching: Side-by-Side Comparison
Sheet mulching involves layering organic materials such as cardboard or newspaper beneath mulch to suppress weeds, retain moisture, and improve soil fertility; it creates a barrier that gradually breaks down and enriches the soil. Broadcast mulching spreads mulch materials loosely over the soil surface without layering, offering moderate weed control and moisture retention but lesser soil enhancement compared to sheet mulching. Sheet mulching is preferable for long-term soil health and weed suppression, while broadcast mulching suits quick coverage and erosion control.
Choosing the Right Mulching Method for Your Garden
Sheet mulching creates a dense, moisture-retentive barrier using layers of cardboard or newspaper topped with organic matter, effectively suppressing weeds and enriching soil structure over time. Broadcast mulching involves spreading loose organic materials like straw, wood chips, or leaves directly over the soil surface, providing immediate moisture retention and temperature regulation but requiring more frequent replenishment. For vegetable gardens or areas with persistent weeds, sheet mulching offers long-term soil improvement, while broadcast mulching suits established beds needing quick, seasonal protection.
Sheet mulching vs broadcast mulching Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com