
Pine Needles vs Leaf Mold Illustration
Pine needles create a lightweight, acidic mulch that improves soil drainage and deters weeds, while leaf mold offers a nutrient-rich, moisture-retentive layer that enhances soil structure and fertility. Choosing pine needles benefits acid-loving plants like azaleas and blueberries, whereas leaf mold is ideal for enriching garden beds and supporting diverse plant growth. Both mulches contribute to healthy soil ecosystems but serve different horticultural purposes based on plant needs and soil conditions.
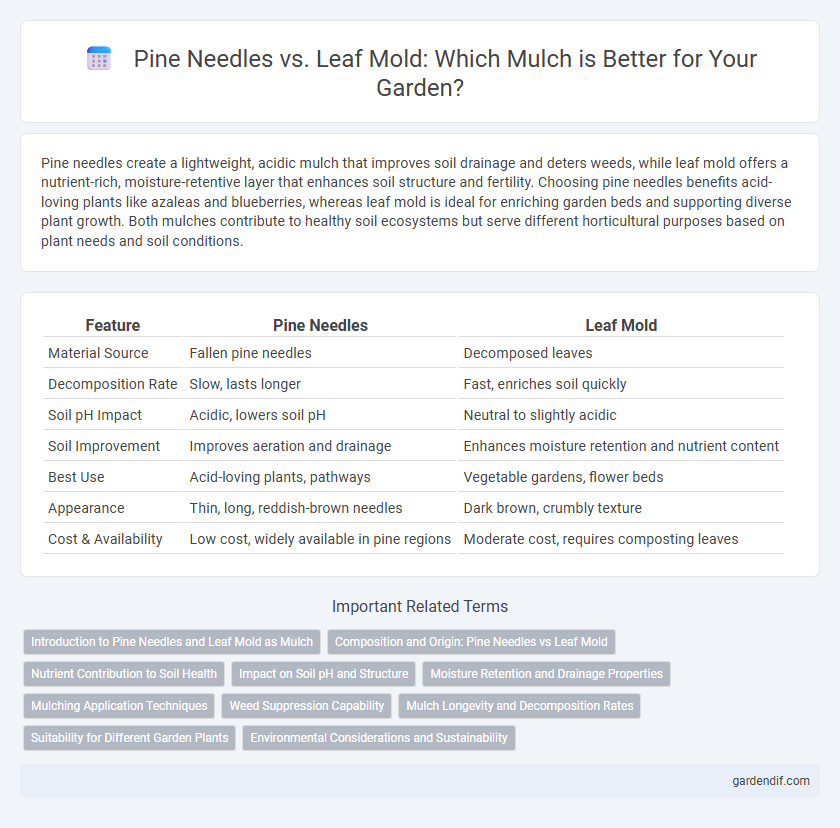
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Pine Needles | Leaf Mold |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Fallen pine needles | Decomposed leaves |
| Decomposition Rate | Slow, lasts longer | Fast, enriches soil quickly |
| Soil pH Impact | Acidic, lowers soil pH | Neutral to slightly acidic |
| Soil Improvement | Improves aeration and drainage | Enhances moisture retention and nutrient content |
| Best Use | Acid-loving plants, pathways | Vegetable gardens, flower beds |
| Appearance | Thin, long, reddish-brown needles | Dark brown, crumbly texture |
| Cost & Availability | Low cost, widely available in pine regions | Moderate cost, requires composting leaves |
Introduction to Pine Needles and Leaf Mold as Mulch
Pine needles and leaf mold serve as effective organic mulches with distinct properties. Pine needles, known for their acidic quality and slow decomposition, are ideal for acid-loving plants such as azaleas and blueberries. Leaf mold, created from decomposed leaves, enriches soil with nutrients and improves moisture retention, benefiting a wide range of garden plants.
Composition and Origin: Pine Needles vs Leaf Mold
Pine needles consist primarily of lignin and cellulose from coniferous trees, offering acidic organic matter that decomposes slowly, ideal for acid-loving plants. Leaf mold originates from decomposed deciduous tree leaves, rich in humus and beneficial microbes, providing a neutral to slightly acidic pH that improves soil structure and moisture retention. The contrasting composition and origin of pine needles and leaf mold influence their nutrient release rates and suitability for different garden ecosystems.
Nutrient Contribution to Soil Health
Pine needles contribute acidic organic matter that slowly releases nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, enhancing soil acidity and structure, especially beneficial for acid-loving plants. Leaf mold, composed of decomposed leaves, provides a rich source of diverse micronutrients and improves soil moisture retention and aeration, promoting overall soil fertility. Both mulches support soil microbial activity, but leaf mold offers a more balanced nutrient profile ideal for general soil health maintenance.
Impact on Soil pH and Structure
Pine needles create an acidic mulch that lowers soil pH, benefiting acid-loving plants but potentially harming neutral or alkaline soil ecosystems. Leaf mold decomposes into a neutral to slightly acidic humus, enriching soil structure by improving aeration and water retention without significantly altering pH levels. Both mulches enhance soil organic matter; however, pine needles actively modify soil chemistry, while leaf mold primarily boosts physical soil properties.
Moisture Retention and Drainage Properties
Pine needles provide excellent drainage properties due to their coarse texture, preventing waterlogging while allowing moisture to reach plant roots efficiently. Leaf mold excels at moisture retention because it absorbs and holds water like a sponge, maintaining consistent soil moisture levels ideal for plant growth. Combining pine needles and leaf mold can create a balanced mulch that optimizes both drainage and moisture retention for healthier soil conditions.
Mulching Application Techniques
Pine needles create a lightweight, acidic mulch that improves soil aeration and drains quickly, ideal for acid-loving plants like azaleas and blueberries. Leaf mold offers excellent moisture retention and enriches soil with organic matter, making it suitable for water-loving gardens and shaded areas. Applying pine needles in thin, even layers prevents matting, while leaf mold should be spread thickly to maximize moisture control and soil enrichment.
Weed Suppression Capability
Pine needles provide effective weed suppression by creating a dense, acidic mulch layer that inhibits weed seed germination and growth. Leaf mold also suppresses weeds but to a lesser extent due to its looser structure and higher moisture retention, which can encourage some weed seeds to sprout. Gardeners seeking maximum weed control often prefer pine needle mulch for its durability and natural allelopathic properties.
Mulch Longevity and Decomposition Rates
Pine needles decompose slowly due to their waxy coating and high lignin content, providing longer-lasting mulch that suppresses weeds effectively. Leaf mold, composed of decomposed deciduous leaves, breaks down faster, enriching the soil with organic matter but requiring more frequent replenishment. Choosing between pine needles and leaf mold mulch depends on the desired balance between mulch longevity and soil nutrient enhancement.
Suitability for Different Garden Plants
Pine needles create an acidic mulch ideal for acid-loving plants such as blueberries, azaleas, and rhododendrons, promoting healthy growth by maintaining soil pH levels. Leaf mold provides a neutral to slightly acidic environment rich in organic matter, benefiting a wide range of garden plants including vegetables, perennials, and shrubs by improving soil structure and moisture retention. Choosing between pine needles and leaf mold depends on the specific pH and nutrient needs of your garden plants for optimal growth and health.
Environmental Considerations and Sustainability
Pine needles and leaf mold serve as sustainable mulches with distinct environmental impacts; pine needles decompose slowly, reducing soil erosion and providing long-lasting acidity suitable for acid-loving plants, while leaf mold enriches soil structure by boosting microbial activity and moisture retention. Pine needle mulch is renewable and readily available in conifer-rich regions, minimizing waste and promoting sustainable landscaping practices. Leaf mold, created from decomposed leaf litter, recycles organic waste and enhances carbon sequestration in soil, supporting eco-friendly gardening and healthier ecosystems.
Pine Needles vs Leaf Mold Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com