
Mulching flower beds vs Mulching vegetable beds Illustration
Mulching flower beds enhances soil moisture retention and suppresses weeds, promoting vibrant blooms by maintaining consistent nutrient levels. Vegetable bed mulching improves soil temperature regulation, reduces erosion, and prevents soil-borne diseases, contributing to healthier and more productive crops. Choosing the appropriate mulch type and thickness tailored to the specific bed type optimizes plant growth and soil health.
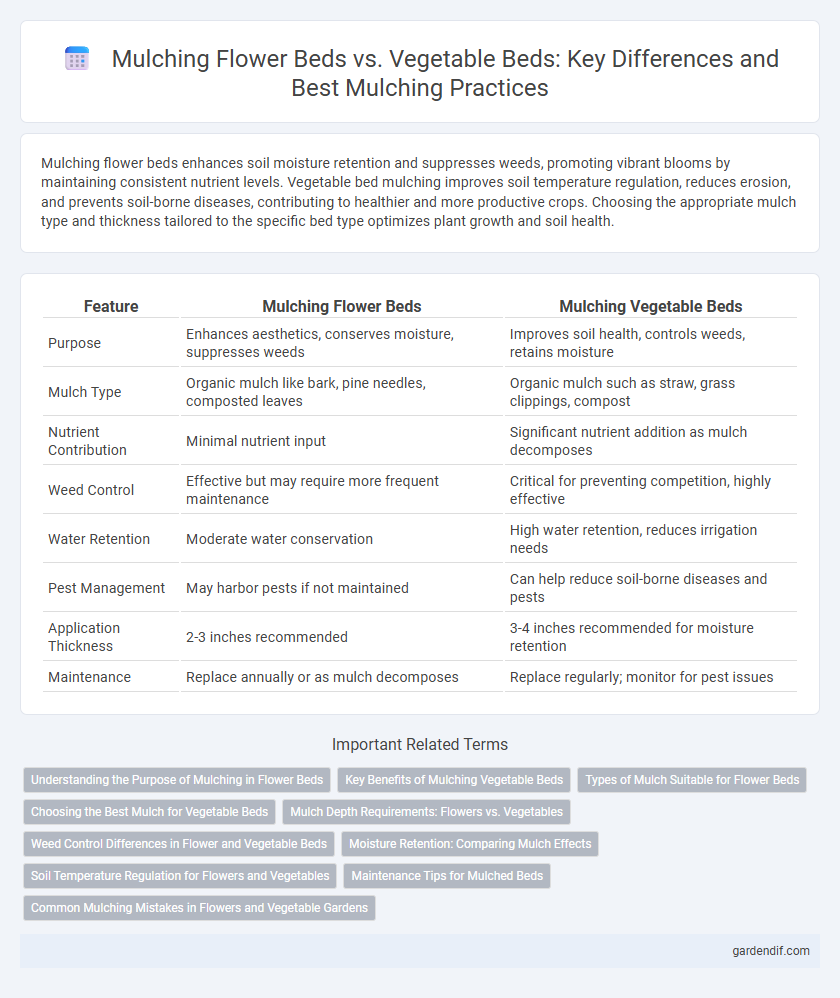
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Mulching Flower Beds | Mulching Vegetable Beds |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Enhances aesthetics, conserves moisture, suppresses weeds | Improves soil health, controls weeds, retains moisture |
| Mulch Type | Organic mulch like bark, pine needles, composted leaves | Organic mulch such as straw, grass clippings, compost |
| Nutrient Contribution | Minimal nutrient input | Significant nutrient addition as mulch decomposes |
| Weed Control | Effective but may require more frequent maintenance | Critical for preventing competition, highly effective |
| Water Retention | Moderate water conservation | High water retention, reduces irrigation needs |
| Pest Management | May harbor pests if not maintained | Can help reduce soil-borne diseases and pests |
| Application Thickness | 2-3 inches recommended | 3-4 inches recommended for moisture retention |
| Maintenance | Replace annually or as mulch decomposes | Replace regularly; monitor for pest issues |
Understanding the Purpose of Mulching in Flower Beds
Mulching flower beds primarily aims to enhance aesthetic appeal, retain soil moisture, and suppress weed growth, promoting healthier, more vibrant blooms. Unlike vegetable beds where nutrient cycling and pest control are critical, mulching flower beds focuses on maintaining proper soil temperature and preventing erosion. Organic mulches like bark or composted leaves are preferred for flower beds due to their ability to improve soil structure and support beneficial microorganisms.
Key Benefits of Mulching Vegetable Beds
Mulching vegetable beds enhances soil moisture retention, reduces weed growth, and regulates soil temperature, leading to healthier plant development and higher yields. Organic mulches like straw or compost improve soil fertility by slowly decomposing, enriching the nutrient content essential for vegetable growth. Mulching also minimizes soil erosion and prevents disease by creating a barrier between soil and plant leaves, promoting sustainable and productive vegetable gardening.
Types of Mulch Suitable for Flower Beds
Organic mulches such as shredded bark, pine needles, and composted leaves are ideal for flower beds because they improve soil fertility and enhance moisture retention while allowing proper aeration. Inorganic mulches like rubber mulch or landscape fabric are less common for flower beds as they do not contribute nutrients but can be used for long-term weed suppression. Choosing mulch types that balance aesthetic appeal and soil health promotes vibrant blooms and healthy root systems in flower beds.
Choosing the Best Mulch for Vegetable Beds
Choosing the best mulch for vegetable beds involves selecting materials that enhance soil moisture retention, suppress weeds, and improve soil fertility without introducing harmful chemicals. Organic mulches such as straw, shredded leaves, or composted bark are ideal for vegetable beds as they decompose, adding nutrients to the soil and fostering healthy plant growth. Unlike flower beds where aesthetics might guide mulch choice, vegetable garden mulching prioritizes soil health and safe, edible crop production.
Mulch Depth Requirements: Flowers vs. Vegetables
Mulch depth requirements differ between flower beds and vegetable beds, with flowers generally benefiting from a thicker mulch layer of 3 to 4 inches to conserve moisture and suppress weeds effectively. Vegetable beds typically require a thinner mulch layer of about 2 to 3 inches to prevent excess moisture that can cause rot and to allow easier access for harvesting and soil warming. Proper mulch depth enhances soil health, promotes plant growth, and optimizes water retention tailored to the specific needs of flowers and vegetables.
Weed Control Differences in Flower and Vegetable Beds
Mulching flower beds typically involves using organic materials like bark or wood chips, which create a thick barrier to suppress weeds effectively while enhancing soil moisture and temperature control. In vegetable beds, mulch selection often favors straw or shredded leaves that not only control weeds but also decompose quickly, enriching soil fertility essential for crop growth. The primary weed control difference lies in the mulch composition and thickness, tailored for flower beds to prioritize aesthetics and for vegetable beds to optimize soil health and ease of harvesting.
Moisture Retention: Comparing Mulch Effects
Mulching flower beds typically uses organic materials like shredded bark or pine needles that retain moisture by reducing evaporation and regulating soil temperature, benefiting delicate blooms. Vegetable beds often require mulch types such as straw or compost that not only preserve soil moisture but also improve nutrient content and soil health for faster vegetable growth. Both flower and vegetable mulches significantly enhance moisture retention, but vegetable bed mulch prioritizes nutrient enrichment alongside water conservation.
Soil Temperature Regulation for Flowers and Vegetables
Mulching flower beds helps maintain a stable soil temperature that promotes consistent blooming by protecting delicate roots from extreme heat or cold. In vegetable beds, mulch regulates soil warmth crucial for seed germination and root development, particularly enhancing growth in early spring or late fall. Both flower and vegetable mulches improve moisture retention, reducing temperature fluctuations that can stress plants and impede growth.
Maintenance Tips for Mulched Beds
Mulching flower beds requires regular monitoring to prevent weed growth and maintain soil moisture, recommending organic mulches like bark or compost that decompose slowly and enrich soil nutrients. Vegetable beds benefit from mulch types such as straw or shredded leaves, which help regulate soil temperature and reduce pest infiltration, with frequent reapplication necessary to maintain effectiveness during the growing season. Proper maintenance involves consistent watering, avoiding mulch pile-ups around plant stems, and periodic fluffing to enhance air circulation and prevent mold or rot in both flower and vegetable beds.
Common Mulching Mistakes in Flowers and Vegetable Gardens
Applying mulch too thickly in flower beds can suffocate roots and promote fungal diseases, while in vegetable gardens, improper mulch thickness may hinder seedling emergence and reduce soil warmth. Using dyed or chemically treated mulch near edible plants can introduce harmful substances into vegetable beds, whereas in flower beds, organic mulch is preferred to enhance soil fertility. Neglecting to replenish mulch regularly results in weed growth in both flower and vegetable gardens, undermining plant health and soil moisture retention.
Mulching flower beds vs Mulching vegetable beds Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com