
Living mulch vs synthetic mulch Illustration
Living mulch improves soil health by enhancing organic matter, promoting beneficial microbial activity, and reducing erosion, whereas synthetic mulch primarily serves as a barrier to suppress weeds and retain moisture without contributing to soil fertility. Living mulch offers a sustainable, eco-friendly option that supports biodiversity and requires less frequent replacement, in contrast to synthetic mulch, which may degrade over time and contribute to plastic waste. Choosing between living and synthetic mulch depends on long-term soil vitality goals and environmental impact considerations.
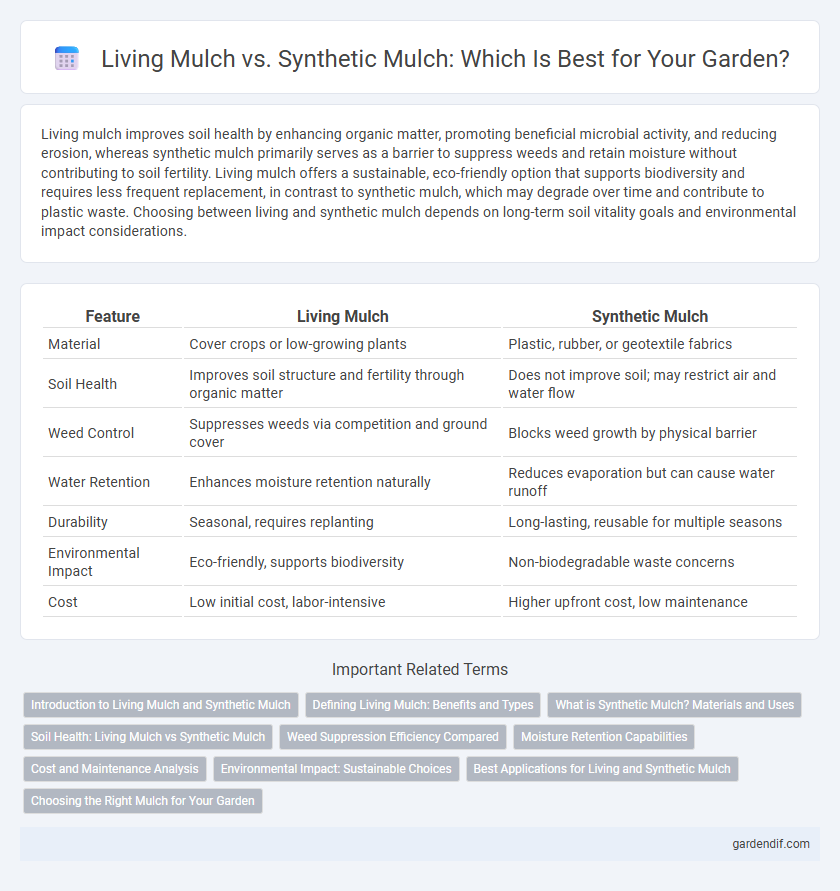
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Living Mulch | Synthetic Mulch |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Cover crops or low-growing plants | Plastic, rubber, or geotextile fabrics |
| Soil Health | Improves soil structure and fertility through organic matter | Does not improve soil; may restrict air and water flow |
| Weed Control | Suppresses weeds via competition and ground cover | Blocks weed growth by physical barrier |
| Water Retention | Enhances moisture retention naturally | Reduces evaporation but can cause water runoff |
| Durability | Seasonal, requires replanting | Long-lasting, reusable for multiple seasons |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, supports biodiversity | Non-biodegradable waste concerns |
| Cost | Low initial cost, labor-intensive | Higher upfront cost, low maintenance |
Introduction to Living Mulch and Synthetic Mulch
Living mulch consists of fast-growing ground cover plants that provide soil protection, moisture retention, and natural weed suppression while enhancing soil fertility through organic matter decomposition. Synthetic mulch, made from materials like plastic or rubber, offers durable weed control, moisture conservation, and temperature regulation but lacks the ecological benefits of living mulch. Choosing between living and synthetic mulch depends on long-term soil health goals, garden aesthetics, and maintenance preferences.
Defining Living Mulch: Benefits and Types
Living mulch consists of cover crops such as clover, vetch, or creeping thyme planted alongside main crops to provide natural weed suppression, moisture retention, and soil enrichment through nitrogen fixation. Benefits include improved soil structure, enhanced biodiversity, and reduced erosion, making it an eco-friendly alternative to synthetic mulch made from plastic or rubber. Common types of living mulch vary by region but generally include legumes for nutrient enhancement and grasses for ground cover.
What is Synthetic Mulch? Materials and Uses
Synthetic mulch consists of man-made materials such as plastic films, landscape fabrics, rubber, and geotextiles designed to control weed growth, retain soil moisture, and regulate soil temperature in agricultural and landscaping applications. Commonly used plastics include polyethylene and polypropylene, which provide durability and water resistance, while rubber mulches offer long-lasting cushioning for playgrounds and pathways. Synthetic mulch is favored for its ability to reduce erosion, minimize labor for maintenance, and improve crop yields by creating an optimal growing environment.
Soil Health: Living Mulch vs Synthetic Mulch
Living mulch enhances soil health by increasing organic matter, improving soil structure, and promoting beneficial microbial activity that supports nutrient cycling. Synthetic mulch, while effective at weed suppression and moisture retention, does not contribute to soil fertility or microbial diversity and can sometimes lead to soil compaction and reduced aeration. Choosing living mulch supports long-term soil vitality, whereas synthetic mulch provides short-term surface protection without improving soil biology.
Weed Suppression Efficiency Compared
Living mulch, composed of cover crops like clover or ryegrass, enhances weed suppression by outcompeting weeds through rapid ground coverage and root competition, reducing reliance on herbicides. Synthetic mulch, such as plastic or landscape fabric, offers a physical barrier that effectively blocks sunlight, preventing weed seed germination and growth with consistent suppression over the growing season. Studies reveal living mulches provide ecological benefits and improved soil health but may allow some weed infiltration, whereas synthetic mulches deliver superior immediate weed suppression but can impact soil moisture and temperature.
Moisture Retention Capabilities
Living mulch significantly enhances moisture retention by reducing soil evaporation through continuous ground cover and root interaction, which improves soil structure and water infiltration. Synthetic mulch, such as plastic or landscape fabric, provides an effective barrier against evaporation but lacks the natural benefits of soil aeration and organic matter contribution. Studies show living mulch can retain up to 30% more soil moisture over time compared to synthetic alternatives, making it a sustainable choice for water conservation in agriculture and gardening.
Cost and Maintenance Analysis
Living mulch generally incurs higher initial costs due to plant selection and establishment but offers long-term savings by improving soil health and reducing weed growth, decreasing the need for herbicides. Synthetic mulch usually has lower upfront expenses and requires minimal maintenance but can involve repeated replacement costs and potential environmental disposal fees. Maintenance of living mulch demands regular watering and management, whereas synthetic mulch requires occasional cleaning and inspection to maintain effectiveness.
Environmental Impact: Sustainable Choices
Living mulch enhances soil health by increasing organic matter and supporting biodiversity, reducing the need for chemical fertilizers and pesticides. Synthetic mulch, often made from non-biodegradable plastics, contributes to soil contamination and waste accumulation in landfills. Choosing living mulch promotes sustainable agriculture by improving carbon sequestration and minimizing environmental pollution.
Best Applications for Living and Synthetic Mulch
Living mulch excels in agricultural systems requiring soil erosion control, moisture retention, and biodiversity enhancement, particularly in organic farming and permaculture. Synthetic mulch is best suited for ornamental landscapes, urban gardening, and pathways where weed suppression, durability, and low maintenance are priorities. Choosing between living and synthetic mulch depends on specific crop needs, environmental conditions, and long-term soil health goals.
Choosing the Right Mulch for Your Garden
Living mulch enhances soil health by improving aeration, increasing organic matter, and supporting beneficial insects, while synthetic mulch offers superior weed control and moisture retention with less maintenance. Selecting the right mulch depends on garden goals, plant types, and local climate conditions; living mulch suits ecosystems focused on biodiversity and soil enrichment, whereas synthetic mulch excels in vegetable beds requiring consistent moisture and weed suppression. Balancing these factors ensures optimal growth, resource efficiency, and long-term plant vitality.
Living mulch vs synthetic mulch Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com