
Submersible Pump vs External Pump Illustration
Submersible pumps are designed to operate underwater, making them ideal for hydroponic systems where space-saving and quiet operation are priorities. External pumps, positioned outside the water reservoir, offer easier maintenance and generally higher flow rates, suitable for larger setups requiring robust circulation. Choosing between submersible and external pumps depends on factors like system size, noise tolerance, and ease of access for servicing in hydroponic cultivation.
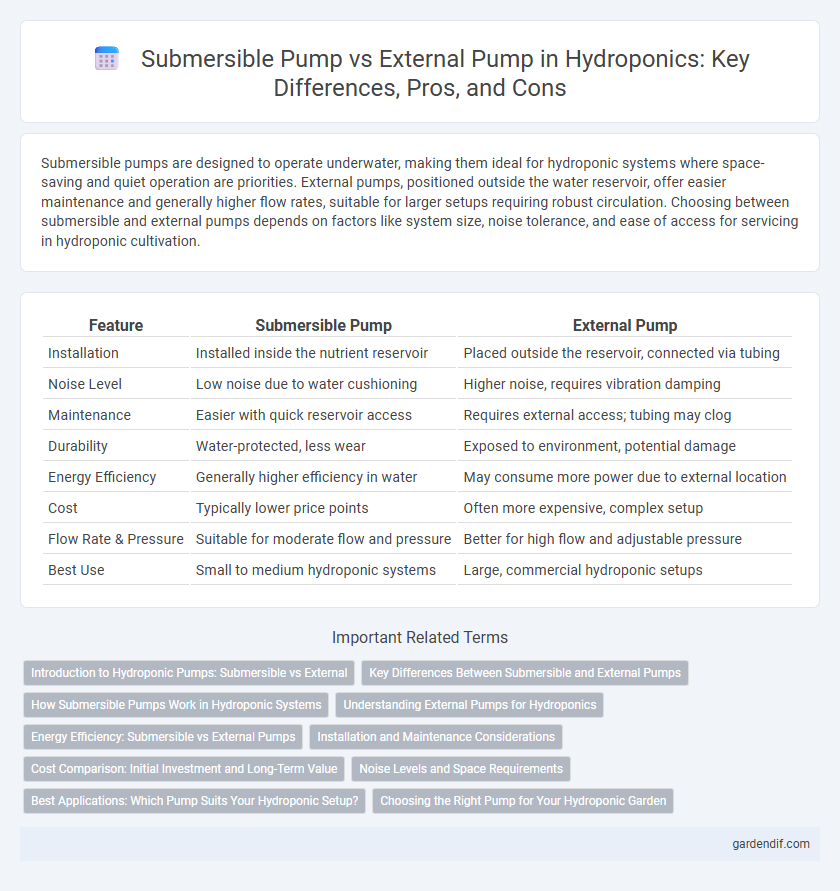
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Submersible Pump | External Pump |
|---|---|---|
| Installation | Installed inside the nutrient reservoir | Placed outside the reservoir, connected via tubing |
| Noise Level | Low noise due to water cushioning | Higher noise, requires vibration damping |
| Maintenance | Easier with quick reservoir access | Requires external access; tubing may clog |
| Durability | Water-protected, less wear | Exposed to environment, potential damage |
| Energy Efficiency | Generally higher efficiency in water | May consume more power due to external location |
| Cost | Typically lower price points | Often more expensive, complex setup |
| Flow Rate & Pressure | Suitable for moderate flow and pressure | Better for high flow and adjustable pressure |
| Best Use | Small to medium hydroponic systems | Large, commercial hydroponic setups |
Introduction to Hydroponic Pumps: Submersible vs External
Hydroponic systems rely on efficient water circulation, where submersible pumps operate underwater within the nutrient reservoir, providing quiet and space-saving water flow. External pumps are installed outside the reservoir, offering higher pressure and easier maintenance, suitable for complex or larger setups requiring robust water delivery. Choosing between submersible and external pumps depends on system size, noise preferences, and maintenance accessibility in hydroponic farming.
Key Differences Between Submersible and External Pumps
Submersible pumps are designed to be placed underwater within the nutrient solution, offering quiet operation and efficient water circulation directly from the reservoir. External pumps operate outside the water, providing easier maintenance and better heat dissipation but may generate more noise and require priming. Key differences include placement, noise levels, maintenance accessibility, and cooling efficiency, which influence their suitability for various hydroponic system setups.
How Submersible Pumps Work in Hydroponic Systems
Submersible pumps operate by being fully submerged in the nutrient solution, using an impeller to push water through the hydroponic system, ensuring efficient circulation and oxygenation. These pumps are often quieter and more energy-efficient compared to external pumps because the water's natural cooling effect prevents overheating. Their compact design allows for easy placement inside reservoirs, reducing the risk of leaks and making maintenance straightforward in hydroponic setups.
Understanding External Pumps for Hydroponics
External pumps for hydroponics offer enhanced durability and higher flow rates compared to submersible pumps, making them ideal for larger or more complex systems. These pumps operate outside the nutrient solution, reducing the risk of clogging and simplifying maintenance tasks. Their robust design supports precise control over water circulation, ensuring optimal oxygenation and nutrient delivery to hydroponic crops.
Energy Efficiency: Submersible vs External Pumps
Submersible pumps are typically more energy-efficient than external pumps because they operate directly within the water, reducing energy loss from friction and heat. External pumps often require more energy to move water through hoses and additional fittings, increasing operational costs. Optimizing pump selection for hydroponic systems can significantly impact overall energy consumption and sustainability.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Submersible pumps in hydroponic systems are installed directly inside the nutrient solution reservoir, offering a compact setup with minimal space requirements and easy integration, while external pumps require separate placement outside the reservoir, often necessitating additional plumbing and secure mounting. Maintenance for submersible pumps involves routine cleaning to prevent clogging from nutrient buildup and ensuring waterproof seals remain intact, whereas external pumps demand regular inspection of external hoses, connections, and filters, with easier access for repairs but potentially more complex initial setup. Choosing between the two depends on the grower's preference for ease of installation versus accessibility for maintenance and system customization.
Cost Comparison: Initial Investment and Long-Term Value
Submersible pumps typically have a lower initial investment cost, making them ideal for small to medium-scale hydroponic systems. External pumps, while more expensive upfront, offer greater durability and easier maintenance, potentially reducing long-term operational expenses. Evaluating total cost of ownership reveals that external pumps often provide better value in large-scale hydroponic setups due to enhanced efficiency and longevity.
Noise Levels and Space Requirements
Submersible pumps operate quietly as they are submerged in water, significantly reducing noise levels, while external pumps tend to generate more audible motor sound due to their placement outside the reservoir. Space-wise, submersible pumps occupy minimal room inside the hydroponic system, making them ideal for compact setups, whereas external pumps require extra space outside the reservoir for installation. Choosing between these pumps depends on balancing the need for a quiet environment with available spatial constraints in hydroponic cultivation.
Best Applications: Which Pump Suits Your Hydroponic Setup?
Submersible pumps are ideal for small to medium-sized hydroponic systems where space efficiency and quiet operation are crucial, as they sit directly in the nutrient reservoir ensuring consistent water flow. External pumps suit larger hydroponic setups requiring higher pressure and flow rates, offering easier maintenance and better heat dissipation outside the nutrient solution. Selecting the right pump depends on system size, reservoir placement, and desired water circulation intensity.
Choosing the Right Pump for Your Hydroponic Garden
Submersible pumps operate underwater within the nutrient solution, offering quieter performance and easy installation, ideal for smaller hydroponic systems or deep-water culture setups. External pumps sit outside the reservoir and deliver stronger pressure, making them suitable for larger or more complex hydroponic gardens requiring greater water circulation and nutrient distribution. Selecting the right pump depends on system size, reservoir depth, and water flow needs to ensure optimal oxygenation and nutrient delivery for healthy plant growth.
Submersible Pump vs External Pump Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com