
Hydroponic Fertilizer vs Organic Fertilizer Illustration
Hydroponic fertilizer provides precise nutrient delivery tailored for soilless systems, ensuring faster plant growth and higher yields compared to organic fertilizer. Organic fertilizer relies on natural decomposition processes, which can be slower and less predictable in hydroponic setups. Choosing hydroponic fertilizer optimizes nutrient availability and promotes efficient root uptake essential for hydroponic plant development.
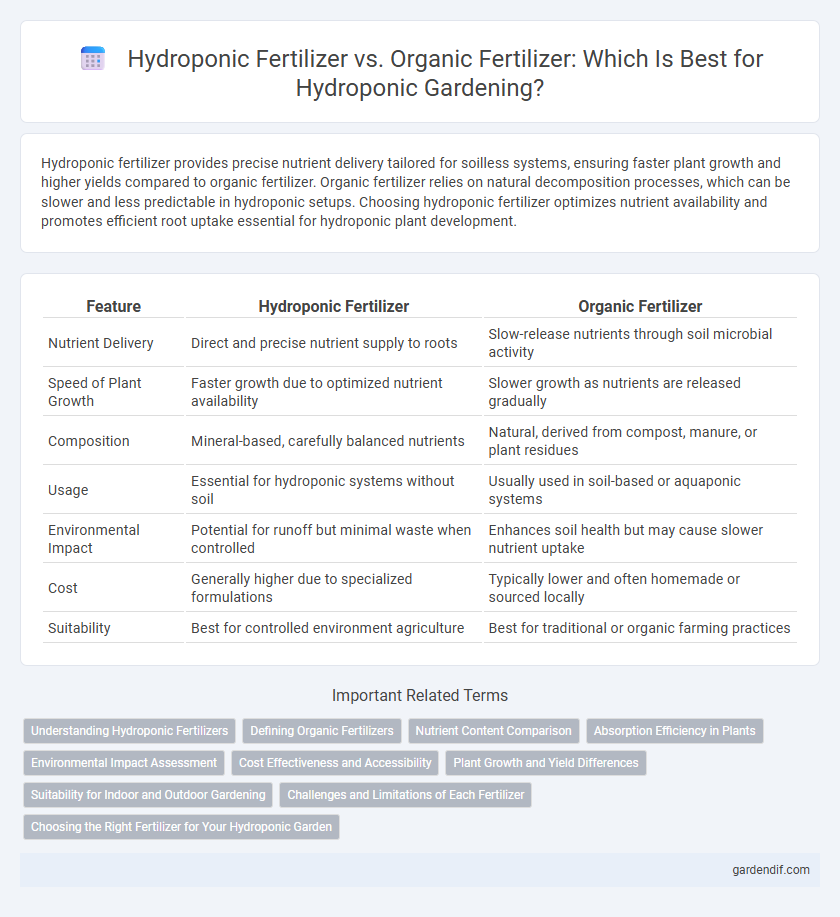
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Hydroponic Fertilizer | Organic Fertilizer |
|---|---|---|
| Nutrient Delivery | Direct and precise nutrient supply to roots | Slow-release nutrients through soil microbial activity |
| Speed of Plant Growth | Faster growth due to optimized nutrient availability | Slower growth as nutrients are released gradually |
| Composition | Mineral-based, carefully balanced nutrients | Natural, derived from compost, manure, or plant residues |
| Usage | Essential for hydroponic systems without soil | Usually used in soil-based or aquaponic systems |
| Environmental Impact | Potential for runoff but minimal waste when controlled | Enhances soil health but may cause slower nutrient uptake |
| Cost | Generally higher due to specialized formulations | Typically lower and often homemade or sourced locally |
| Suitability | Best for controlled environment agriculture | Best for traditional or organic farming practices |
Understanding Hydroponic Fertilizers
Hydroponic fertilizers provide plants with precise nutrient formulations essential for soil-less growth, delivering balanced macro- and micronutrients in readily available forms. Unlike organic fertilizers, which rely on microbial activity to release nutrients gradually, hydroponic nutrients dissolve directly in water, ensuring immediate uptake and optimal plant development. Understanding the composition and solubility of hydroponic fertilizers is crucial for maximizing yield and maintaining nutrient solution stability in controlled environments.
Defining Organic Fertilizers
Organic fertilizers consist of natural materials such as compost, manure, and plant residues that enrich soil by supplying essential nutrients and improving microbial activity. These fertilizers release nutrients slowly, promoting sustainable plant growth and enhancing soil structure over time. Unlike hydroponic fertilizers, organic fertilizers rely on biological processes to make nutrients available to plants rather than providing immediate nutrient solutions.
Nutrient Content Comparison
Hydroponic fertilizers provide precise nutrient formulations with easily absorbable minerals like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, optimized for plant growth in water-based systems. Organic fertilizers release nutrients more slowly, relying on microbial activity to convert complex compounds into available forms, often resulting in variable nutrient concentrations. The controlled nutrient content in hydroponic fertilizers ensures consistent and balanced feeding tailored to specific crop needs, enhancing growth efficiency compared to organic alternatives.
Absorption Efficiency in Plants
Hydroponic fertilizer delivers essential nutrients in a water-soluble form, enabling faster absorption and more efficient nutrient uptake by plants compared to organic fertilizer. Organic fertilizers rely on microbial activity for nutrient release, which can slow down absorption rates and reduce immediate availability. This controlled nutrient delivery in hydroponics results in optimized growth and higher yields due to improved absorption efficiency.
Environmental Impact Assessment
Hydroponic fertilizer typically yields less environmental runoff compared to traditional organic fertilizers, reducing water pollution and nutrient leaching into soil and waterways. Organic fertilizers, while biodegradable and supporting soil health with microorganisms, can contribute to greenhouse gas emissions during decomposition and require more land use. Assessing environmental impact reveals hydroponic systems often minimize resource waste and contamination, offering a sustainable alternative for efficient nutrient delivery in controlled environments.
Cost Effectiveness and Accessibility
Hydroponic fertilizers offer precise nutrient delivery, resulting in faster plant growth and higher yields, often reducing overall costs compared to traditional organic fertilizers. While organic fertilizers are typically more accessible and environmentally friendly, they may require larger quantities and longer application times, increasing labor and input expenses. Choosing hydroponic fertilizers can enhance cost effectiveness by minimizing waste and optimizing nutrient uptake, especially in controlled environments where resource efficiency is critical.
Plant Growth and Yield Differences
Hydroponic fertilizer delivers precise nutrient formulations directly to plant roots, promoting faster growth rates and higher yields compared to organic fertilizers, which release nutrients more slowly through microbial activity. The controlled nutrient availability in hydroponic systems supports optimal photosynthesis and root development, resulting in increased biomass and fruit production. Organic fertilizers can improve soil health and microbial diversity but often produce variable growth outcomes and lower immediate yields in hydroponic setups.
Suitability for Indoor and Outdoor Gardening
Hydroponic fertilizer offers precise nutrient control, making it ideal for indoor gardening where soil is absent and environmental variables are strictly managed. Organic fertilizer, rich in natural matter and beneficial microbes, suits outdoor gardening by improving soil health and supporting long-term ecosystem sustainability. Both fertilizers enhance plant growth, but hydroponic fertilizer excels in controlled indoor systems while organic fertilizer thrives in traditional outdoor environments.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Fertilizer
Hydroponic fertilizer requires precise nutrient balance and monitoring to avoid nutrient lockout and water pollution, posing challenges in maintaining optimal growth conditions. Organic fertilizers often face limitations in hydroponics due to their slower nutrient release, inconsistent nutrient concentration, and potential for microbial contamination in the closed system. Both fertilizers demand careful management to prevent nutrient deficiencies or toxicities, impacting plant health and yield efficiency.
Choosing the Right Fertilizer for Your Hydroponic Garden
Selecting the right fertilizer for your hydroponic garden hinges on nutrient availability and plant growth requirements. Hydroponic fertilizers are precisely formulated to provide essential minerals in a soluble form, ensuring rapid absorption and optimal plant development. Organic fertilizers, while beneficial for soil health, may lack the immediate nutrient availability needed in hydroponic systems, making synthetic hydroponic nutrients generally preferred for efficient and controlled feeding.
Hydroponic Fertilizer vs Organic Fertilizer Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com