
Hydroponics vs Soil Gardening Illustration
Hydroponics offers precise control over nutrient delivery and water usage, resulting in faster plant growth compared to traditional soil gardening. Soil gardening depends on natural processes and soil health, which can lead to variable yields and pests management challenges. Choosing between these methods depends on resource availability, crop type, and desired growing conditions within a greenhouse environment.
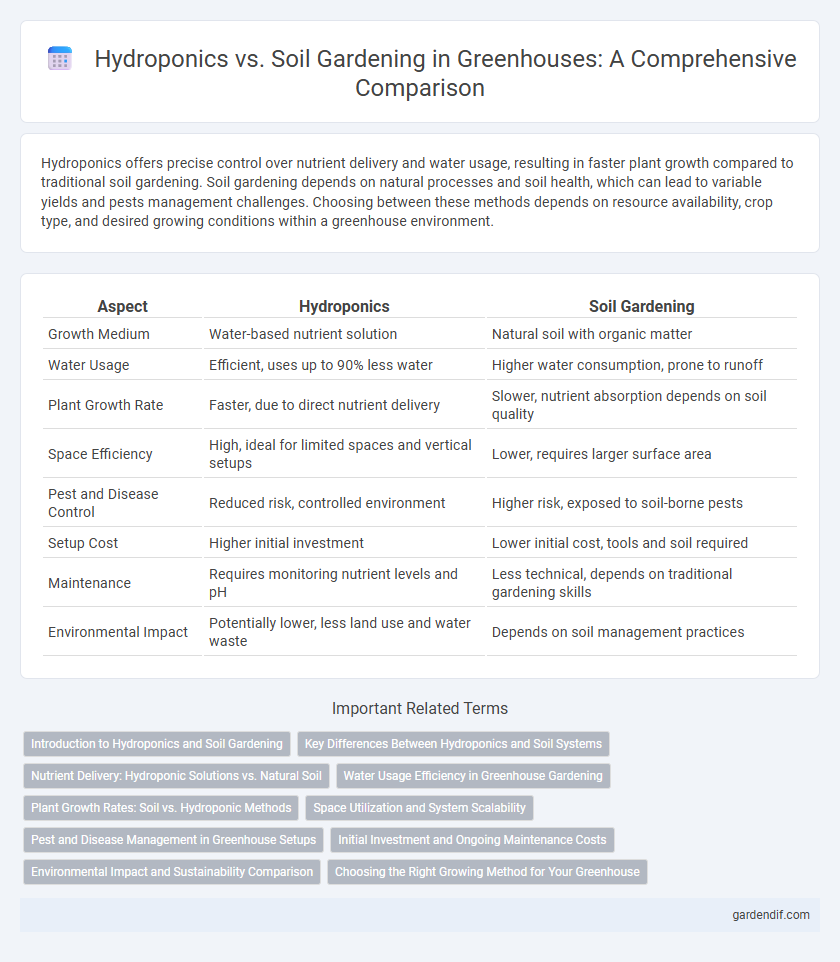
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Hydroponics | Soil Gardening |
|---|---|---|
| Growth Medium | Water-based nutrient solution | Natural soil with organic matter |
| Water Usage | Efficient, uses up to 90% less water | Higher water consumption, prone to runoff |
| Plant Growth Rate | Faster, due to direct nutrient delivery | Slower, nutrient absorption depends on soil quality |
| Space Efficiency | High, ideal for limited spaces and vertical setups | Lower, requires larger surface area |
| Pest and Disease Control | Reduced risk, controlled environment | Higher risk, exposed to soil-borne pests |
| Setup Cost | Higher initial investment | Lower initial cost, tools and soil required |
| Maintenance | Requires monitoring nutrient levels and pH | Less technical, depends on traditional gardening skills |
| Environmental Impact | Potentially lower, less land use and water waste | Depends on soil management practices |
Introduction to Hydroponics and Soil Gardening
Hydroponics is a soil-less cultivation technique where plants grow in nutrient-rich water solutions, allowing precise control over nutrient delivery and faster growth rates. Soil gardening relies on natural soil as the medium, providing organic matter and beneficial microbes that support plant health and root development. Both methods offer unique advantages, but hydroponics maximizes space efficiency and resource use, while soil gardening promotes biodiversity and traditional cultivation practices.
Key Differences Between Hydroponics and Soil Systems
Hydroponics systems use nutrient-rich water solutions to grow plants without soil, enabling faster growth rates and more efficient nutrient uptake compared to traditional soil gardening. Soil gardening relies on natural soil composition and microorganisms to provide nutrients, often resulting in slower plant development and greater susceptibility to pests and diseases. Hydroponics offers precise control over environmental factors, leading to higher yields and resource efficiency, whereas soil gardening depends on natural soil conditions and weather variability.
Nutrient Delivery: Hydroponic Solutions vs. Natural Soil
Hydroponic systems deliver nutrients directly to plant roots through water-based solutions enriched with precise mineral concentrations, ensuring optimized nutrient uptake and faster growth rates. In contrast, natural soil provides a complex ecosystem where nutrients are released through organic matter decomposition and microbial activity, offering a slower but balanced nutrient supply. Hydroponic nutrient delivery allows for controlled pH and nutrient levels, minimizing deficiencies and maximizing yield efficiency compared to traditional soil gardening.
Water Usage Efficiency in Greenhouse Gardening
Hydroponics in greenhouse gardening significantly reduces water usage by recirculating nutrient-rich solutions, using up to 90% less water compared to traditional soil gardening. Soil gardening often experiences high water loss due to evaporation and runoff, making it less efficient in controlled environments. Optimizing water efficiency through hydroponic systems supports sustainable greenhouse practices and enhances crop yield with minimal resource consumption.
Plant Growth Rates: Soil vs. Hydroponic Methods
Hydroponic methods significantly accelerate plant growth rates compared to traditional soil gardening due to optimized nutrient delivery directly to roots in controlled environments. Studies demonstrate hydroponic systems can increase growth speed by 25-50% for various crops like lettuce, tomatoes, and herbs. Enhanced oxygen availability and precise water management in hydroponics further boost photosynthesis efficiency and root development, outperforming soil-based cultivation.
Space Utilization and System Scalability
Hydroponics maximizes space utilization by enabling vertical stacking and higher plant density within controlled environments, making it ideal for limited-area greenhouses. Soil gardening requires more horizontal space due to root depth and plant spacing needs, limiting scalability in compact settings. Hydroponic systems offer greater scalability through modular components and automation capabilities, facilitating expansion without proportional land increase.
Pest and Disease Management in Greenhouse Setups
Hydroponics in greenhouse setups reduces pest and disease issues by eliminating soil-borne pathogens and allowing precise control of nutrient solutions, minimizing pathogen spread. Soil gardening remains more susceptible to pests like root weevils and fungal diseases such as Fusarium wilt, requiring vigilant monitoring and organic or chemical treatments. Integrated pest management (IPM) strategies tailored to hydroponic systems often include biological controls and sanitation protocols that further reduce disease outbreaks.
Initial Investment and Ongoing Maintenance Costs
Hydroponics typically requires a higher initial investment due to the need for specialized equipment such as pumps, grow lights, and nutrient solutions, whereas soil gardening has lower startup costs with basic tools and soil. Ongoing maintenance costs for hydroponics include electricity for pumps and lights, as well as regular nutrient replenishment, which can be more expensive compared to soil gardening's costs of compost, water, and occasional pest control. In greenhouses, hydroponic systems can offer more efficient resource use but demand consistent monitoring and technical upkeep, leading to potentially higher long-term expenses than traditional soil gardening.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Comparison
Hydroponics uses up to 90% less water than traditional soil gardening, significantly reducing water waste and conserving resources. The controlled environment in hydroponic systems minimizes pesticide use and nutrient runoff, lowering environmental pollution compared to soil gardening. While soil gardening supports natural ecosystems and biodiversity, hydroponics offers a more sustainable solution for urban areas by maximizing space and reducing carbon footprints through localized production.
Choosing the Right Growing Method for Your Greenhouse
Hydroponics offers faster plant growth and higher yields by delivering nutrients directly through a water-based system, making it ideal for limited space and controlled environments within a greenhouse. Soil gardening supports natural microbial ecosystems and improves plant resilience, which benefits crops that thrive in rich organic matter and require minimal technological input. Selecting the right growing method depends on crop type, resource availability, and desired management intensity in your greenhouse setup.
Hydroponics vs Soil Gardening Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com