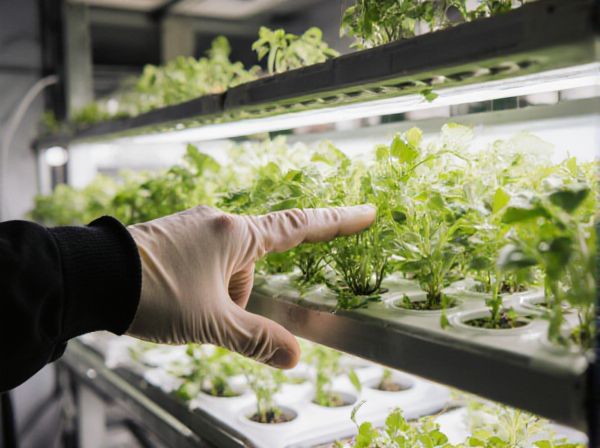

Hydroponics vs soil Illustration
Hydroponics offers faster plant growth and higher yield compared to traditional soil methods by delivering nutrients directly to the roots through water. Soil cultivation relies on natural microorganisms and organic matter to support plant health, which can result in variable nutrient availability and slower growth. Choosing hydroponics reduces water usage and minimizes pest issues, making it a sustainable option for greenhouse farming.
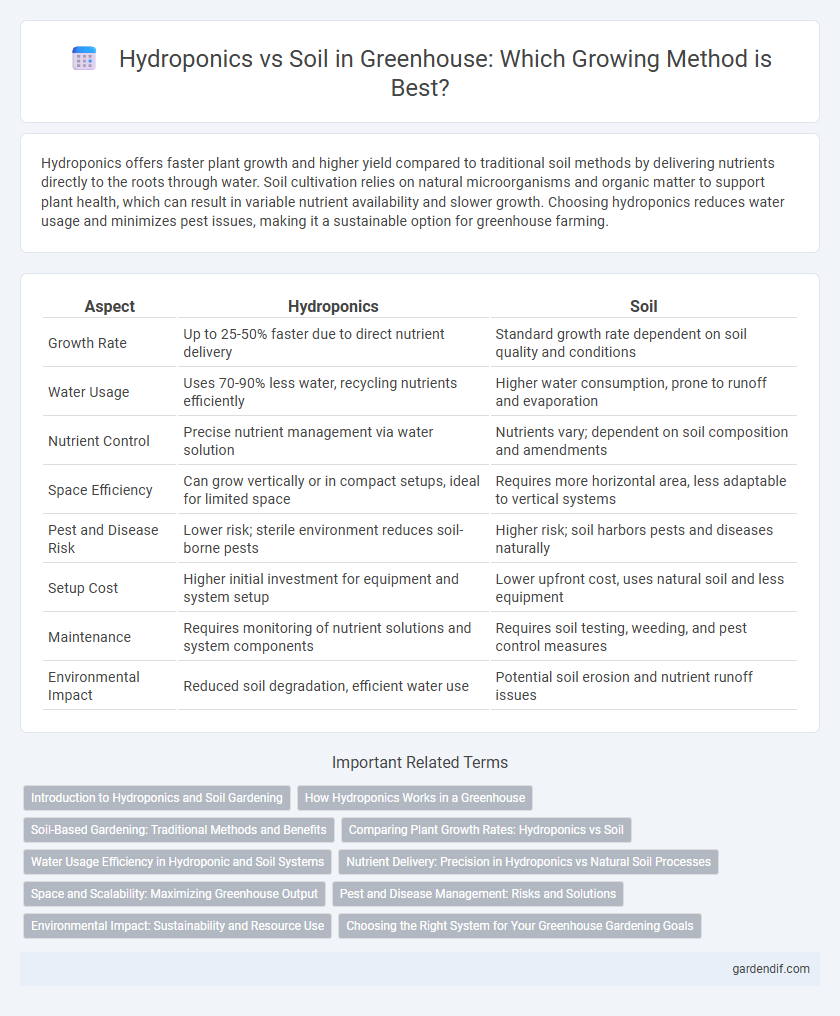
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Hydroponics | Soil |
|---|---|---|
| Growth Rate | Up to 25-50% faster due to direct nutrient delivery | Standard growth rate dependent on soil quality and conditions |
| Water Usage | Uses 70-90% less water, recycling nutrients efficiently | Higher water consumption, prone to runoff and evaporation |
| Nutrient Control | Precise nutrient management via water solution | Nutrients vary; dependent on soil composition and amendments |
| Space Efficiency | Can grow vertically or in compact setups, ideal for limited space | Requires more horizontal area, less adaptable to vertical systems |
| Pest and Disease Risk | Lower risk; sterile environment reduces soil-borne pests | Higher risk; soil harbors pests and diseases naturally |
| Setup Cost | Higher initial investment for equipment and system setup | Lower upfront cost, uses natural soil and less equipment |
| Maintenance | Requires monitoring of nutrient solutions and system components | Requires soil testing, weeding, and pest control measures |
| Environmental Impact | Reduced soil degradation, efficient water use | Potential soil erosion and nutrient runoff issues |
Introduction to Hydroponics and Soil Gardening
Hydroponics is a soilless cultivation method where plants grow in nutrient-rich water solutions, enabling faster growth and higher yields compared to traditional soil gardening. Soil gardening relies on natural soil containing organic matter, microorganisms, and minerals essential for plant development but may face challenges like soil-borne diseases and variable nutrient content. Both methods have unique advantages, with hydroponics offering precise nutrient control and soil gardening providing a natural ecosystem for plant roots.
How Hydroponics Works in a Greenhouse
Hydroponics in a greenhouse involves growing plants without soil by circulating nutrient-rich water directly to the roots through a controlled environment. This system optimizes resource efficiency, enhances growth rates, and allows precise control over factors such as pH, temperature, and nutrient concentration. Compared to soil-based cultivation, hydroponics reduces water usage by up to 90% and minimizes pest-related issues, making it ideal for sustainable greenhouse farming.
Soil-Based Gardening: Traditional Methods and Benefits
Soil-based gardening remains a foundational method in greenhouses, leveraging natural nutrients and microbial activity to promote plant health and growth. This traditional approach enhances soil structure, improves water retention, and supports diverse ecosystems crucial for nutrient cycling. Gardeners benefit from lower startup costs and easier integration of compost and organic matter, fostering sustainable and resilient plant cultivation.
Comparing Plant Growth Rates: Hydroponics vs Soil
Hydroponic systems typically enable faster plant growth rates compared to soil cultivation due to precise nutrient delivery and optimal oxygen availability at the roots. Studies show hydroponic plants can grow up to 25-50% faster, benefiting from controlled environments that minimize stress factors like pests and soil-borne diseases. Soil-grown plants often have slower growth due to variable nutrient accessibility and microbial competition, despite potentially richer organic matter content.
Water Usage Efficiency in Hydroponic and Soil Systems
Hydroponic systems use up to 90% less water than traditional soil cultivation by recycling nutrient-rich water directly to plant roots, significantly reducing water waste. Soil systems often lose water through evaporation, runoff, and deep percolation, leading to less efficient water usage. Optimizing water delivery in hydroponics enhances sustainability and resource conservation in controlled greenhouse environments.
Nutrient Delivery: Precision in Hydroponics vs Natural Soil Processes
Hydroponics offers precise nutrient delivery by directly supplying a balanced solution to plant roots, optimizing growth rates and reducing nutrient waste. In contrast, natural soil relies on microbial activity and organic matter decomposition, which can result in variable nutrient availability and slower uptake. The controlled environment of hydroponics ensures consistent nutrient levels, enhancing plant health and yield compared to the fluctuating conditions in soil-based cultivation.
Space and Scalability: Maximizing Greenhouse Output
Hydroponics systems in greenhouses significantly optimize space by allowing vertical stacking and closer plant spacing, enabling higher crop density compared to traditional soil methods. Scalability is enhanced through modular designs, facilitating easy expansion without extensive land requirements, which is crucial for maximizing output in limited greenhouse areas. This efficient use of space and scalable setup makes hydroponics ideal for intensifying production while minimizing environmental footprint.
Pest and Disease Management: Risks and Solutions
Hydroponics significantly reduces the risk of soil-borne pests and diseases since plants grow in a controlled, soilless environment, minimizing exposure to common pathogens like nematodes and soil fungi. However, hydroponic systems are vulnerable to waterborne diseases such as Pythium and algae buildup, requiring rigorous water sterilization and monitoring protocols. In contrast, soil cultivation demands regular crop rotation, organic amendments, and integrated pest management strategies to manage soil pests and fungal infections effectively.
Environmental Impact: Sustainability and Resource Use
Hydroponics uses up to 90% less water than traditional soil farming by recirculating nutrient solutions, significantly reducing water waste and runoff pollution. Soil cultivation often leads to soil degradation, erosion, and higher pesticide use, contributing to environmental harm and reduced biodiversity. Hydroponic systems minimize land use and enable year-round production, enhancing sustainability and resource efficiency in controlled environments.
Choosing the Right System for Your Greenhouse Gardening Goals
Hydroponics offers faster growth rates and higher yields by delivering nutrients directly to plant roots, making it ideal for maximizing space and resource efficiency in greenhouses. Soil cultivation promotes natural microbial activity and improves plant resilience, which benefits those prioritizing organic growth and long-term soil health. Selecting the right system depends on factors such as crop type, available resources, maintenance capacity, and your specific greenhouse gardening goals.
Hydroponics vs soil Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com