
Active Ventilation vs Passive Ventilation Illustration
Active ventilation in greenhouses relies on mechanical systems like fans and vents to regulate temperature and humidity, providing precise environmental control. Passive ventilation uses natural airflow through strategically placed vents and openings, promoting energy-efficient air exchange without electrical input. Choosing between active and passive ventilation depends on climate conditions, crop requirements, and energy availability.
Table of Comparison
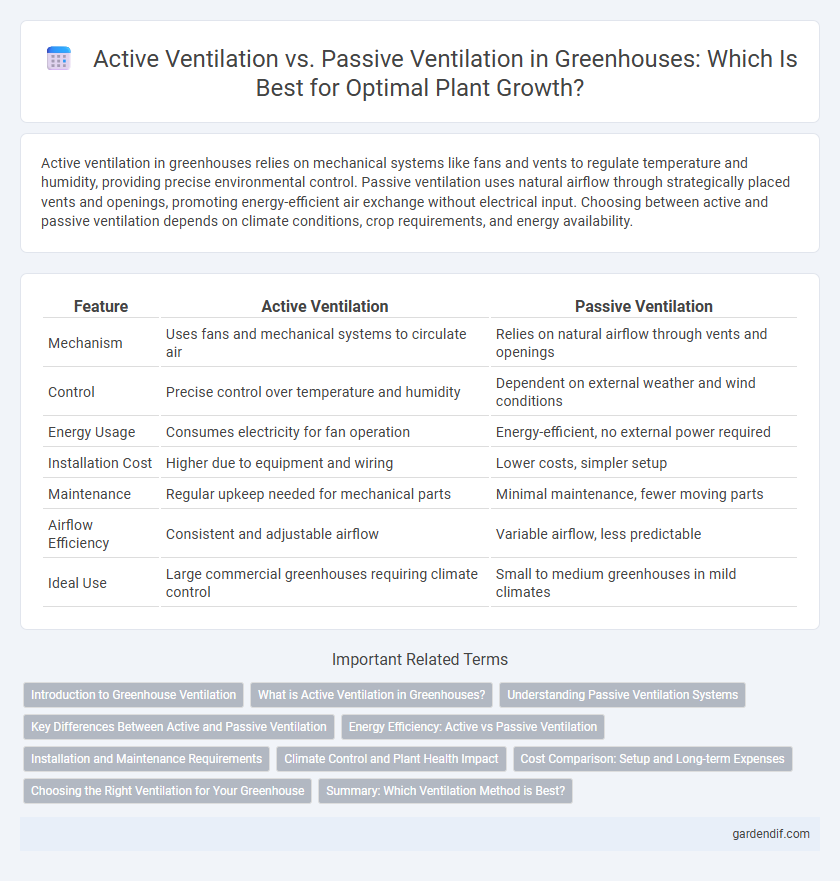
| Feature | Active Ventilation | Passive Ventilation |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanism | Uses fans and mechanical systems to circulate air | Relies on natural airflow through vents and openings |
| Control | Precise control over temperature and humidity | Dependent on external weather and wind conditions |
| Energy Usage | Consumes electricity for fan operation | Energy-efficient, no external power required |
| Installation Cost | Higher due to equipment and wiring | Lower costs, simpler setup |
| Maintenance | Regular upkeep needed for mechanical parts | Minimal maintenance, fewer moving parts |
| Airflow Efficiency | Consistent and adjustable airflow | Variable airflow, less predictable |
| Ideal Use | Large commercial greenhouses requiring climate control | Small to medium greenhouses in mild climates |
Introduction to Greenhouse Ventilation
Active ventilation in greenhouses uses mechanical systems such as fans and vents to regulate temperature and humidity, ensuring optimal plant growth by maintaining consistent airflow. Passive ventilation relies on natural air movement through strategically placed vents and openings, promoting energy-efficient climate control without electrical input. Both methods are essential for preventing heat stress and controlling moisture levels, with the choice depending on greenhouse size, location, and crop requirements.
What is Active Ventilation in Greenhouses?
Active ventilation in greenhouses involves mechanically powered systems such as fans and exhausts that regulate airflow and temperature. This method ensures consistent air exchange and helps control humidity levels, promoting optimal growing conditions and preventing diseases. Compared to passive ventilation, active systems provide precise environmental control regardless of external wind conditions.
Understanding Passive Ventilation Systems
Passive ventilation systems in greenhouses rely on natural airflow driven by temperature differences and wind pressure, eliminating the need for mechanical fans and reducing energy costs. These systems typically use roof vents, sidewall openings, and adjustable louvers strategically placed to enhance air movement and maintain optimal temperature and humidity levels. Understanding the design and placement of these components is essential for maximizing ventilation efficiency and promoting healthy plant growth.
Key Differences Between Active and Passive Ventilation
Active ventilation in greenhouses relies on mechanical systems such as fans and vents to control air circulation, offering precise temperature and humidity management. Passive ventilation depends on natural airflow driven by wind and temperature differences, requiring no energy input but providing less control over internal conditions. Key differences include the energy consumption, control level, and installation complexity, with active systems enabling consistent climate control and passive systems offering cost-effective, maintenance-free operation.
Energy Efficiency: Active vs Passive Ventilation
Active ventilation systems in greenhouses utilize mechanical fans and controls to regulate airflow, consuming electricity but providing precise climate control. Passive ventilation relies on natural airflow through vents and openings, eliminating energy costs but offering less consistent environmental regulation. Energy efficiency favors passive ventilation due to zero electrical consumption, though active systems optimize plant growth by maintaining stable internal conditions.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Active ventilation systems in greenhouses require electrical components such as fans and automated controls, demanding professional installation and routine maintenance to ensure optimal performance and prevent mechanical failure. Passive ventilation relies on strategically placed vents and natural airflow, resulting in simpler installation without electrical infrastructure and minimal upkeep, often limited to occasional cleaning and adjustment. Choosing between the two depends on factors like greenhouse size, climate control needs, and budget for ongoing maintenance.
Climate Control and Plant Health Impact
Active ventilation in greenhouses uses mechanical systems like fans and vents to regulate temperature and humidity precisely, ensuring optimal climate control that reduces plant stress and promotes healthy growth. Passive ventilation relies on natural airflow through strategically placed openings, which is energy-efficient but less consistent in maintaining stable conditions, potentially exposing plants to temperature fluctuations and pests. Effective climate management balances ventilation methods to improve air circulation, reduce disease risk, and enhance photosynthesis for healthier plants.
Cost Comparison: Setup and Long-term Expenses
Active ventilation systems in greenhouses require higher initial setup costs due to the need for fans, motors, and electrical installations, while passive ventilation relies on natural airflow through vents and louvers, making setup expenses significantly lower. Long-term expenses for active systems include ongoing energy consumption and maintenance of mechanical components, which can increase operational costs over time. Passive ventilation offers minimal maintenance and no energy costs, resulting in lower total long-term expenses but may be less effective in climate control compared to active systems.
Choosing the Right Ventilation for Your Greenhouse
Effective greenhouse ventilation hinges on selecting between active and passive systems based on climate control needs and energy efficiency. Active ventilation employs fans and mechanical components to regulate airflow, offering precise temperature and humidity control essential for high-value crops. Passive ventilation relies on natural airflow through strategically placed vents, ideal for energy savings and low-maintenance environments but less effective in extreme weather conditions.
Summary: Which Ventilation Method is Best?
Active ventilation in greenhouses utilizes fans and mechanical systems to regulate air circulation and temperature efficiently, making it ideal for larger or climate-sensitive operations. Passive ventilation relies on natural airflow through vents and openings, offering an energy-efficient and low-maintenance solution suitable for small to medium-sized greenhouses in mild climates. The best method depends on greenhouse size, climate control needs, and energy consumption priorities.
Active Ventilation vs Passive Ventilation Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com