
Benching vs Ground Planting Illustration
Benching in greenhouses allows for better air circulation and easier pest control compared to ground planting, which can lead to healthier plants. Ground planting maximizes space and soil benefits but may increase susceptibility to soil-borne diseases and weeds. Choosing between benching and ground planting depends on factors like crop type, disease management, and available space.
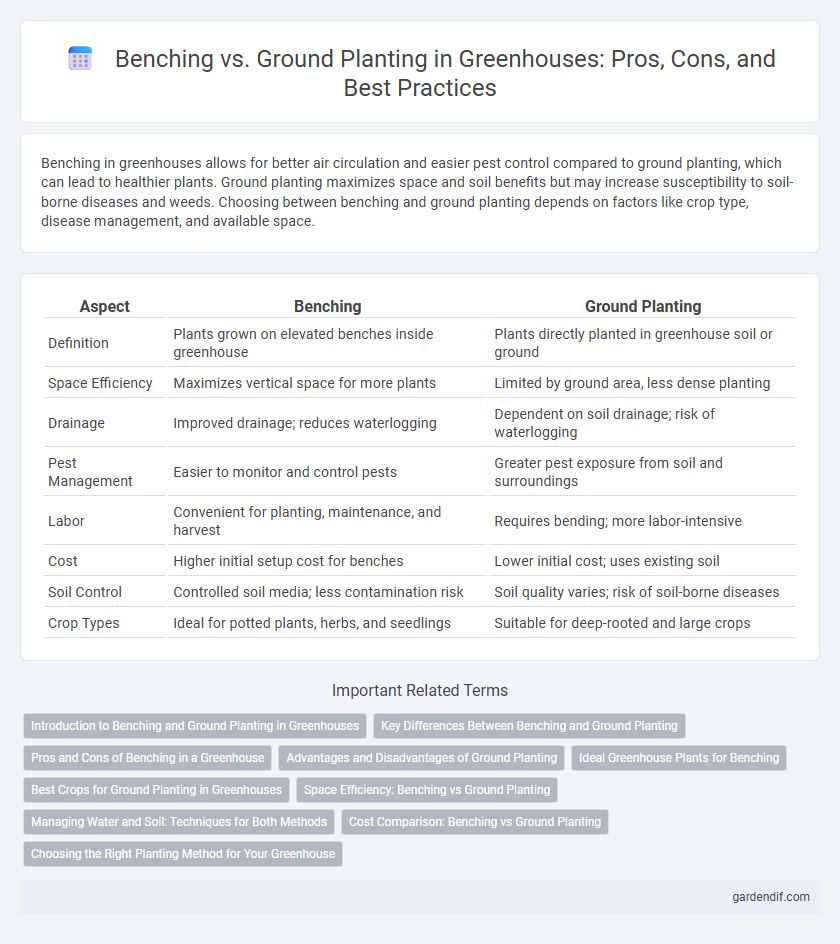
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Benching | Ground Planting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Plants grown on elevated benches inside greenhouse | Plants directly planted in greenhouse soil or ground |
| Space Efficiency | Maximizes vertical space for more plants | Limited by ground area, less dense planting |
| Drainage | Improved drainage; reduces waterlogging | Dependent on soil drainage; risk of waterlogging |
| Pest Management | Easier to monitor and control pests | Greater pest exposure from soil and surroundings |
| Labor | Convenient for planting, maintenance, and harvest | Requires bending; more labor-intensive |
| Cost | Higher initial setup cost for benches | Lower initial cost; uses existing soil |
| Soil Control | Controlled soil media; less contamination risk | Soil quality varies; risk of soil-borne diseases |
| Crop Types | Ideal for potted plants, herbs, and seedlings | Suitable for deep-rooted and large crops |
Introduction to Benching and Ground Planting in Greenhouses
Benching in greenhouses involves arranging plants on raised platforms or shelves to maximize space utilization and improve air circulation, which enhances growth conditions and reduces disease risk. Ground planting places crops directly in the soil beds within the greenhouse, offering benefits such as natural temperature regulation and easier access for deep-rooted plants. Selecting between benching and ground planting depends on crop type, greenhouse design, and desired maintenance efficiency.
Key Differences Between Benching and Ground Planting
Benching in greenhouses involves growing plants on elevated platforms, allowing improved air circulation, drainage, and ease of maintenance, while ground planting uses the soil or floor substrate directly, leading to more natural root expansion and moisture retention. Benching facilitates better pest control and crop organization versus ground planting's advantage in utilizing the greenhouse's thermal mass for temperature regulation. Selecting between benching and ground planting impacts irrigation practices, disease management, and space efficiency within controlled environment agriculture.
Pros and Cons of Benching in a Greenhouse
Benching in a greenhouse offers enhanced air circulation and optimized space utilization, allowing for better control of microclimates and easier access for plant maintenance. It facilitates improved drainage compared to ground planting, reducing the risk of root diseases and improving overall plant health. However, benching requires higher initial investment and ongoing structural maintenance, and it may restrict root growth for certain plant species compared to planting directly in the ground.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Ground Planting
Ground planting in greenhouses offers deep soil access, promoting robust root development and natural nutrient absorption, which enhances plant growth and yields. However, it poses challenges such as potential soil-borne diseases, limited soil control, and difficulty in managing moisture levels compared to benching systems. Despite these drawbacks, ground planting supports larger crops and reduces infrastructure costs, making it suitable for long-term cultivation and high-volume production.
Ideal Greenhouse Plants for Benching
Ideal greenhouse plants for benching include compact, high-value crops such as herbs like basil and parsley, seedlings, and small flowering plants like African violets. Benching allows optimal space utilization, better air circulation, and easier pest management, making it suitable for plants that require controlled environments and frequent handling. Compared to ground planting, benching supports faster growth and higher yield by providing uniform light and temperature conditions.
Best Crops for Ground Planting in Greenhouses
Root vegetables such as carrots, radishes, and beets thrive best with ground planting in greenhouses due to their need for deep, loose soil to develop properly. Leafy greens like spinach and lettuce also perform well when planted directly into the ground, benefiting from stable moisture levels and natural soil nutrients. Ground planting maximizes space and soil health, leading to higher yields and better crop quality for these types.
Space Efficiency: Benching vs Ground Planting
Benching in greenhouses maximizes space efficiency by utilizing vertical layers, allowing for increased plant density without expanding the greenhouse footprint. Ground planting consumes more horizontal space, limiting the number of plants per square meter and often making maintenance and irrigation less efficient. Optimizing bench systems can lead to higher crop yields per square meter compared to traditional ground planting methods.
Managing Water and Soil: Techniques for Both Methods
Benching in greenhouses allows precise water management through controlled irrigation systems that minimize runoff and soil erosion, ensuring nutrient retention. Ground planting requires well-drained soil and efficient drip irrigation to prevent waterlogging and promote uniform moisture distribution. Both methods benefit from mulching and regular soil testing to optimize moisture levels and maintain soil health.
Cost Comparison: Benching vs Ground Planting
Benching systems in greenhouses often involve higher initial costs due to materials and construction but offer efficient space utilization and improved plant management. Ground planting typically requires lower upfront investment but may incur higher ongoing costs related to soil maintenance and pest control. Evaluating overall expenditure depends on factors like crop type, scale, and long-term operational goals.
Choosing the Right Planting Method for Your Greenhouse
Benching maximizes space utilization and improves airflow, promoting healthier plant growth by elevating plants off the ground and facilitating better disease control. Ground planting allows for deeper root development and natural soil interactions but requires more vigilant soil management to prevent pathogens and moisture issues. Selecting the right method depends on greenhouse size, crop type, and operational goals, balancing efficiency with optimal growing conditions.
Benching vs Ground Planting Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com