
NPK ratio adjustment vs Micronutrient supplementation Illustration
Adjusting the NPK ratio in fertilizers targets the primary nutrients--nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium--essential for plant growth and yield optimization. Micronutrient supplementation addresses secondary elements like iron, zinc, and manganese, which are crucial for metabolic processes and deficiency correction. Effective fertilization strategies combine precise NPK balancing with targeted micronutrient delivery to enhance crop health and maximize productivity.
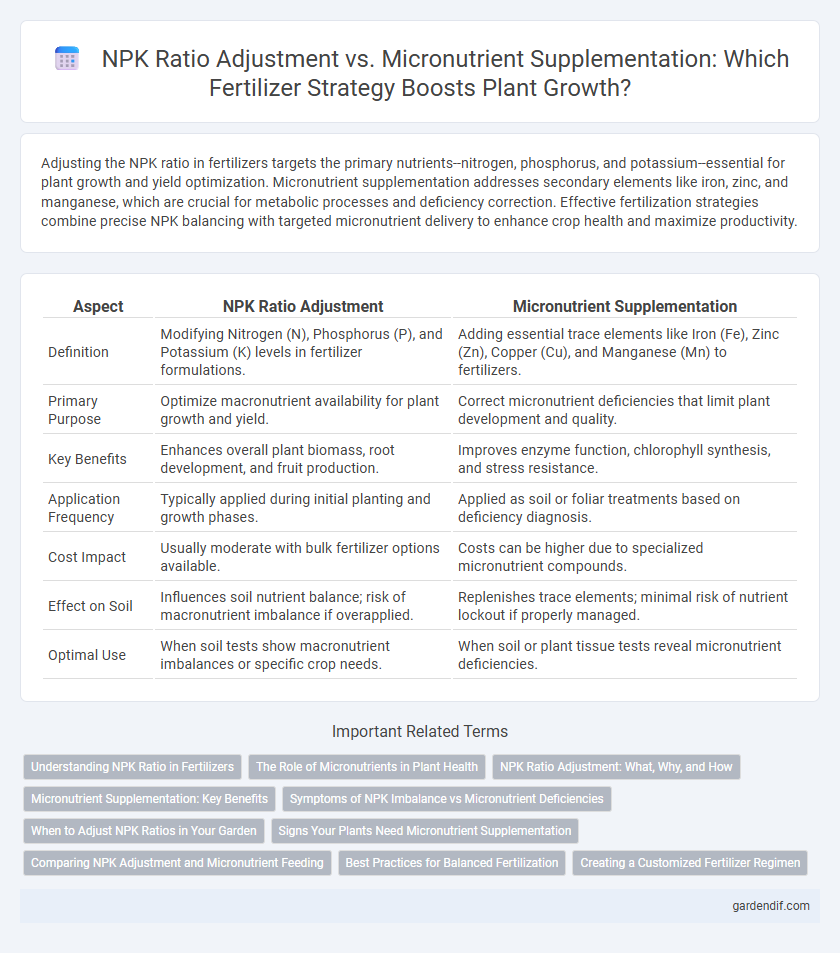
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | NPK Ratio Adjustment | Micronutrient Supplementation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Modifying Nitrogen (N), Phosphorus (P), and Potassium (K) levels in fertilizer formulations. | Adding essential trace elements like Iron (Fe), Zinc (Zn), Copper (Cu), and Manganese (Mn) to fertilizers. |
| Primary Purpose | Optimize macronutrient availability for plant growth and yield. | Correct micronutrient deficiencies that limit plant development and quality. |
| Key Benefits | Enhances overall plant biomass, root development, and fruit production. | Improves enzyme function, chlorophyll synthesis, and stress resistance. |
| Application Frequency | Typically applied during initial planting and growth phases. | Applied as soil or foliar treatments based on deficiency diagnosis. |
| Cost Impact | Usually moderate with bulk fertilizer options available. | Costs can be higher due to specialized micronutrient compounds. |
| Effect on Soil | Influences soil nutrient balance; risk of macronutrient imbalance if overapplied. | Replenishes trace elements; minimal risk of nutrient lockout if properly managed. |
| Optimal Use | When soil tests show macronutrient imbalances or specific crop needs. | When soil or plant tissue tests reveal micronutrient deficiencies. |
Understanding NPK Ratio in Fertilizers
Understanding the NPK ratio in fertilizers is crucial for optimizing plant growth, as it directly indicates the proportions of nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) essential for photosynthesis, root development, and overall plant health. Adjusting the NPK ratio allows for targeted nutrient supply that matches specific crop growth stages, improving yield and nutrient use efficiency. While NPK ratios address macronutrient needs, micronutrient supplementation fills essential trace element gaps like zinc, iron, and manganese, ensuring comprehensive plant nutrition beyond primary nutrients.
The Role of Micronutrients in Plant Health
Micronutrients such as iron, zinc, and manganese are essential for enzymatic functions and chlorophyll synthesis in plants, directly impacting growth and yield. Adjusting the NPK ratio primarily addresses macronutrient needs but often overlooks deficiencies in these critical trace elements. Integrating micronutrient supplementation ensures balanced nutrition, enhancing plant resilience against diseases and environmental stress.
NPK Ratio Adjustment: What, Why, and How
NPK ratio adjustment involves modifying the proportions of nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) in fertilizers to match specific crop nutrient requirements, optimizing plant growth and yield. This process addresses nutrient imbalances in soil, enhancing nutrient uptake efficiency and preventing deficiencies or toxicities that can limit crop productivity. Farmers achieve NPK ratio adjustment through soil testing, targeted fertilizer application, and precision agriculture techniques that tailor nutrient delivery to crop and soil conditions.
Micronutrient Supplementation: Key Benefits
Micronutrient supplementation enhances crop resilience and yield by providing essential elements like zinc, iron, and manganese that are often deficient in soils despite balanced NPK ratios. Improved nutrient uptake efficiency and better enzymatic functions contribute to healthier plants and higher quality produce. Targeted micronutrient application addresses specific soil deficiencies, promoting sustainable agricultural productivity beyond standard NPK fertilization.
Symptoms of NPK Imbalance vs Micronutrient Deficiencies
NPK imbalance in plants typically manifests as stunted growth, yellowing leaves, and poor fruit development due to insufficient nitrogen, phosphorus, or potassium levels. Micronutrient deficiencies cause specific symptoms such as chlorosis from iron deficiency, necrosis from calcium shortage, and interveinal yellowing linked to magnesium lack. Identifying these distinct symptoms enables precise adjustment of NPK ratios versus targeted micronutrient supplementation for optimal crop health and yield.
When to Adjust NPK Ratios in Your Garden
Adjust NPK ratios in your garden when soil tests indicate nutrient imbalances affecting plant growth, such as nitrogen deficiency causing yellowing leaves or phosphorus scarcity reducing root development. Tailoring the NPK ratio optimizes macronutrient availability, directly enhancing crop yield and health. Micronutrient supplementation is essential only when specific trace element deficiencies are identified, as improper NPK adjustments alone won't correct these specialized nutrient gaps.
Signs Your Plants Need Micronutrient Supplementation
Yellowing leaves with green veins, known as chlorosis, often indicate a deficiency in iron, manganese, or zinc, signaling the need for micronutrient supplementation. Stunted growth and poor flowering can result from inadequate boron or molybdenum levels, while leaf tip burn and curling frequently reflect calcium or copper shortages. Monitoring these specific symptoms helps determine when micronutrient supplementation is essential alongside proper NPK ratio adjustment for optimal plant health.
Comparing NPK Adjustment and Micronutrient Feeding
Adjusting the NPK ratio directly enhances macronutrient availability essential for plant growth, focusing on nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium balance to optimize yield. Micronutrient supplementation targets trace elements like zinc, iron, and manganese, critical for enzyme function and disease resistance but required in smaller quantities. Comparing the two, NPK adjustment impacts overall biomass production, while micronutrient feeding improves plant health and quality by addressing specific nutritional deficiencies.
Best Practices for Balanced Fertilization
Adjusting the NPK ratio is essential for addressing primary nutrient needs, ensuring optimal crop growth and yield by providing adequate nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium levels tailored to specific soil and crop requirements. Micronutrient supplementation targets critical trace elements such as zinc, iron, manganese, and copper, which are vital for enzymatic functions and overall plant health but needed in smaller quantities. Best practices for balanced fertilization integrate both NPK ratio adjustments and precise micronutrient applications based on soil testing and crop-specific deficiencies to enhance nutrient use efficiency and promote sustainable agriculture.
Creating a Customized Fertilizer Regimen
Adjusting the NPK ratio targets primary nutrient balance critical for crop growth, while micronutrient supplementation addresses trace elements essential for enzymatic functions and overall plant health. A customized fertilizer regimen integrates soil test results, crop type, and growth stages to optimize both macronutrient proportions and micronutrient availability. Precision in nutrient management enhances yield quality, nutrient use efficiency, and sustainable soil fertility over time.
NPK ratio adjustment vs Micronutrient supplementation Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com