
Liquid fertilizer vs Solid fertilizer Illustration
Liquid fertilizer offers faster nutrient absorption due to its immediate availability to plants, enhancing growth and yield efficiency. Solid fertilizer provides a slow-release nutrient supply, promoting prolonged soil nourishment and reducing the frequency of application. Choosing between liquid and solid fertilizers depends on crop type, soil condition, and desired nutrient delivery speed.
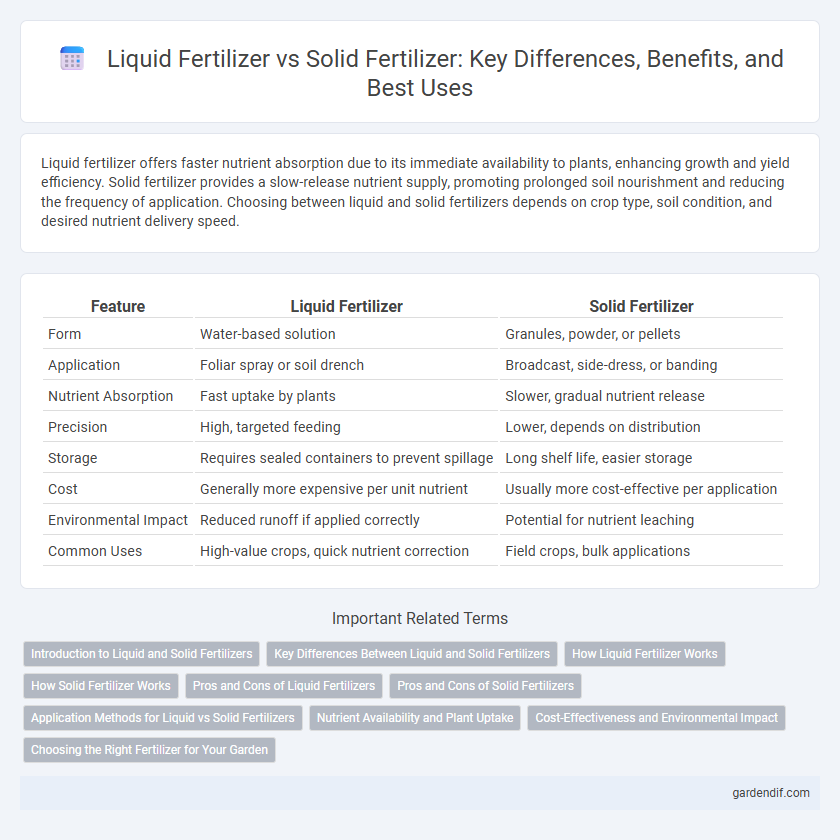
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Liquid Fertilizer | Solid Fertilizer |
|---|---|---|
| Form | Water-based solution | Granules, powder, or pellets |
| Application | Foliar spray or soil drench | Broadcast, side-dress, or banding |
| Nutrient Absorption | Fast uptake by plants | Slower, gradual nutrient release |
| Precision | High, targeted feeding | Lower, depends on distribution |
| Storage | Requires sealed containers to prevent spillage | Long shelf life, easier storage |
| Cost | Generally more expensive per unit nutrient | Usually more cost-effective per application |
| Environmental Impact | Reduced runoff if applied correctly | Potential for nutrient leaching |
| Common Uses | High-value crops, quick nutrient correction | Field crops, bulk applications |
Introduction to Liquid and Solid Fertilizers
Liquid fertilizers offer rapid nutrient availability and uniform application, making them ideal for foliar feeding and fertigation systems. Solid fertilizers, including granular and pellet forms, provide controlled nutrient release and ease of storage, often used for soil incorporation and long-term nutrient supply. Selecting between liquid and solid fertilizers depends on crop type, soil conditions, and application methods to optimize nutrient efficiency and crop yield.
Key Differences Between Liquid and Solid Fertilizers
Liquid fertilizers offer faster nutrient absorption due to their immediate solubility, enhancing plant growth efficiency, while solid fertilizers release nutrients gradually, providing long-term soil enrichment. Liquid forms allow precise application and are ideal for foliar feeding, whereas solid fertilizers are more cost-effective and easier to store. The choice between liquid and solid fertilizers depends on crop needs, soil type, and desired nutrient release speed for optimal agricultural productivity.
How Liquid Fertilizer Works
Liquid fertilizer delivers nutrients directly to plant roots through soil or foliar application, allowing for rapid absorption and immediate availability. Its dissolved nutrients enable precise, uniform distribution, enhancing nutrient uptake efficiency compared to solid formulations. This targeted delivery supports optimal plant growth and stress resilience by providing essential elements exactly when and where plants need them.
How Solid Fertilizer Works
Solid fertilizer releases nutrients gradually as it dissolves in soil moisture, providing a steady nutrient supply to plant roots over time. Its slow-release properties improve nutrient absorption efficiency and reduce the risk of nutrient leaching compared to liquid fertilizers. Solid fertilizers also promote sustained soil fertility by enhancing microbial activity and maintaining balanced nutrient levels in the root zone.
Pros and Cons of Liquid Fertilizers
Liquid fertilizers offer rapid nutrient absorption and uniform application, improving crop growth efficiency. They can be easily mixed with pesticides and applied through irrigation systems, but may require frequent applications due to faster nutrient depletion. However, the risk of leaching and higher initial costs compared to solid fertilizers can limit their practicality in some agricultural settings.
Pros and Cons of Solid Fertilizers
Solid fertilizers offer precise nutrient control with slow-release properties, promoting long-term soil enrichment and reducing leaching risks. Their storage and transportation are cost-effective due to lower water content, but application can be labor-intensive and less uniform compared to liquid alternatives. Slow nutrient availability may limit immediate plant uptake, making them less ideal for rapid-growth crops or emergency nutrient supplementation.
Application Methods for Liquid vs Solid Fertilizers
Liquid fertilizers deliver nutrients through foliar sprays, fertigation, or soil drenching, enabling rapid nutrient uptake and precise application rates. Solid fertilizers are typically applied by broadcasting, side-dressing, or banding, requiring incorporation into the soil for gradual nutrient release. Selection of application method depends on crop type, soil properties, and timing to optimize nutrient availability and minimize losses.
Nutrient Availability and Plant Uptake
Liquid fertilizers offer faster nutrient availability and quicker plant uptake due to their immediate solubility and easier root absorption. Solid fertilizers release nutrients more slowly as they break down in the soil, providing longer-term nutrient supply but delayed uptake. Optimizing nutrient timing and type enhances plant growth efficiency and yield quality in varied agricultural systems.
Cost-Effectiveness and Environmental Impact
Liquid fertilizers often offer greater cost-effectiveness by enabling precise nutrient application, reducing waste and improving crop yield efficiency. Solid fertilizers generally have lower upfront costs but can lead to nutrient runoff and environmental pollution if improperly applied. Choosing between liquid and solid fertilizers requires balancing financial investment with minimizing ecological impact to promote sustainable agriculture.
Choosing the Right Fertilizer for Your Garden
Liquid fertilizer offers rapid nutrient absorption and precise application, ideal for correcting deficiencies quickly in growing plants. Solid fertilizer provides a slow-release nutrient supply, enhancing soil structure and promoting long-term plant health. Selecting the right fertilizer depends on your garden's specific needs, soil condition, and crop type to maximize growth and yield.
Liquid fertilizer vs Solid fertilizer Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com