
Pelletized fertilizer vs Powdered fertilizer Illustration
Pelletized fertilizer offers controlled nutrient release, reducing runoff and enhancing soil absorption compared to powdered fertilizer. Its ease of handling and minimal dust production make it ideal for precise application in both agricultural and gardening settings. Powdered fertilizer dissolves quickly, providing rapid nutrient availability but requires careful management to prevent nutrient loss and uneven distribution.
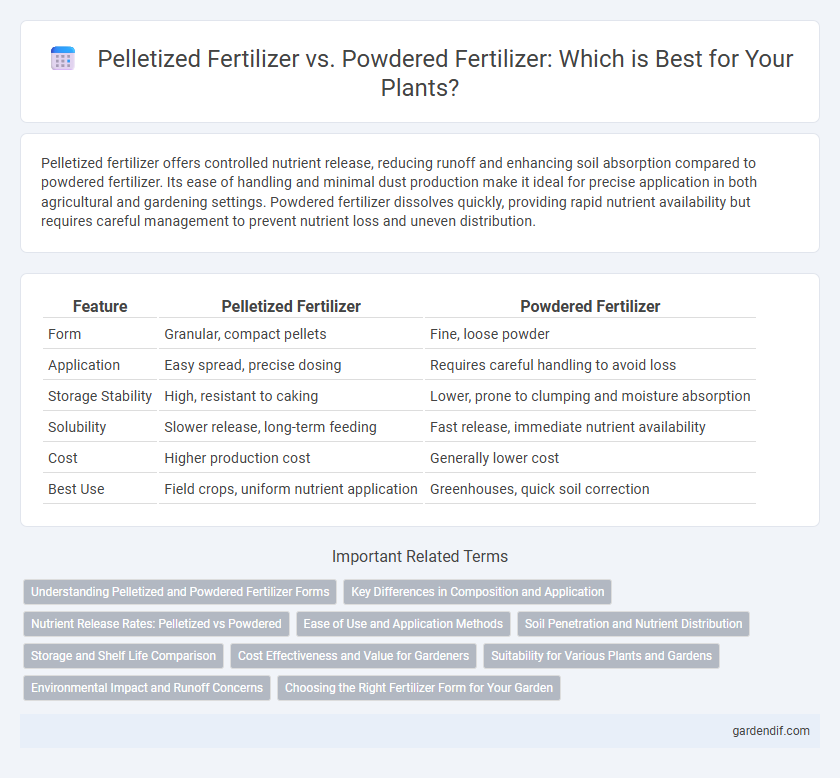
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Pelletized Fertilizer | Powdered Fertilizer |
|---|---|---|
| Form | Granular, compact pellets | Fine, loose powder |
| Application | Easy spread, precise dosing | Requires careful handling to avoid loss |
| Storage Stability | High, resistant to caking | Lower, prone to clumping and moisture absorption |
| Solubility | Slower release, long-term feeding | Fast release, immediate nutrient availability |
| Cost | Higher production cost | Generally lower cost |
| Best Use | Field crops, uniform nutrient application | Greenhouses, quick soil correction |
Understanding Pelletized and Powdered Fertilizer Forms
Pelletized fertilizers offer uniform nutrient distribution and reduced dust, enhancing ease of handling and application compared to powdered fertilizers, which provide faster nutrient release due to their increased surface area. Powdered fertilizers dissolve quickly in soil, promoting immediate nutrient availability, while pelletized forms improve nutrient retention and reduce leaching. Understanding these differences allows for optimized fertilization strategies tailored to specific crop needs and soil conditions.
Key Differences in Composition and Application
Pelletized fertilizer consists of granulated nutrient particles, providing uniform nutrient release and easier handling compared to powdered fertilizer, which is a fine, dust-like form that dissolves quickly for immediate plant absorption. Pelletized fertilizers typically contain binding agents that enhance soil contact and reduce nutrient loss via volatilization, whereas powdered fertilizers offer faster nutrient availability but require more precise application to avoid runoff or overuse. The choice between pelletized and powdered fertilizers depends on crop type, soil condition, and desired nutrient delivery speed.
Nutrient Release Rates: Pelletized vs Powdered
Pelletized fertilizer offers a slower, controlled nutrient release rate, enhancing nutrient availability over an extended period and reducing leaching losses. Powdered fertilizer, by comparison, dissolves rapidly, delivering nutrients quickly but increasing the risk of nutrient runoff and requiring more frequent applications. Understanding these distinct release patterns is critical for optimizing fertilization schedules and improving crop nutrient uptake efficiency.
Ease of Use and Application Methods
Pelletized fertilizer offers superior ease of use due to its uniform size and reduced dust, allowing precise application with spreaders and minimizing waste. Powdered fertilizer requires careful handling to avoid inhalation risks and often needs to be dissolved or mixed before application, complicating the process. The granular nature of pelletized fertilizer supports more efficient application methods, enhancing nutrient delivery and reducing labor time compared to powdered forms.
Soil Penetration and Nutrient Distribution
Pelletized fertilizer offers improved soil penetration due to its compact form, allowing nutrients to reach deeper root zones more effectively than powdered fertilizer. Powdered fertilizer tends to distribute nutrients more quickly on the soil surface but may face challenges with uneven dispersion and runoff. Enhanced nutrient availability from pelletized fertilizers supports sustained plant growth by promoting consistent root absorption.
Storage and Shelf Life Comparison
Pelletized fertilizer offers superior storage stability due to its compact form, reducing the risks of moisture absorption and caking compared to powdered fertilizer. Powdered fertilizers are more prone to clumping and nutrient degradation over time when exposed to humidity and air. Pelletized forms typically maintain their nutrient potency for longer periods, enhancing shelf life and ease of handling during storage.
Cost Effectiveness and Value for Gardeners
Pelletized fertilizer offers superior cost effectiveness by reducing application waste and providing slow-release nutrients, which promote consistent plant growth and minimize the need for frequent reapplication. Powdered fertilizer, while generally cheaper upfront, often requires more frequent applications and careful handling to avoid nutrient runoff and uneven distribution, potentially increasing long-term costs. Gardeners benefit most from pelletized fertilizer due to its balanced nutrient delivery, reducing labor and enhancing overall value through improved plant health and yield.
Suitability for Various Plants and Gardens
Pelletized fertilizer offers controlled nutrient release ideal for slow-growing plants and established gardens, minimizing nutrient runoff and promoting steady root development. Powdered fertilizer provides rapid nutrient availability suited for fast-growing plants and greenhouse crops requiring immediate nutrient uptake. Selecting between pelletized and powdered fertilizer depends on plant growth rate, garden type, and nutrient management needs for optimal crop yield.
Environmental Impact and Runoff Concerns
Pelletized fertilizer releases nutrients gradually, reducing the risk of runoff and minimizing environmental contamination compared to powdered fertilizer, which dissolves quickly and can lead to nutrient leaching into water bodies. The compact form of pelletized fertilizer improves nutrient use efficiency, lowering the potential for groundwater pollution and eutrophication. Powdered fertilizers, while easier to apply, often increase the likelihood of soil erosion and waterway pollution due to their higher solubility and faster nutrient release rates.
Choosing the Right Fertilizer Form for Your Garden
Pelletized fertilizer offers controlled nutrient release and ease of application, making it ideal for sustained feeding in garden beds and lawns. Powdered fertilizer provides fast nutrient availability and is often preferred for quick correction of nutrient deficiencies or for foliar feeding. Selecting the right form depends on your garden's needs, soil type, and desired nutrient release speed to optimize plant growth and yield.
Pelletized fertilizer vs Powdered fertilizer Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com