
NPK-heavy blend vs micronutrient blend Illustration
NPK-heavy blends deliver high concentrations of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, targeting primary nutrient needs for robust plant growth and yield. Micronutrient blends provide essential trace elements like iron, manganese, and zinc, crucial for enzymatic functions and overall plant health in smaller quantities. Selecting the right fertilizer depends on crop requirements, soil conditions, and nutrient deficiencies to optimize productivity and sustainability.
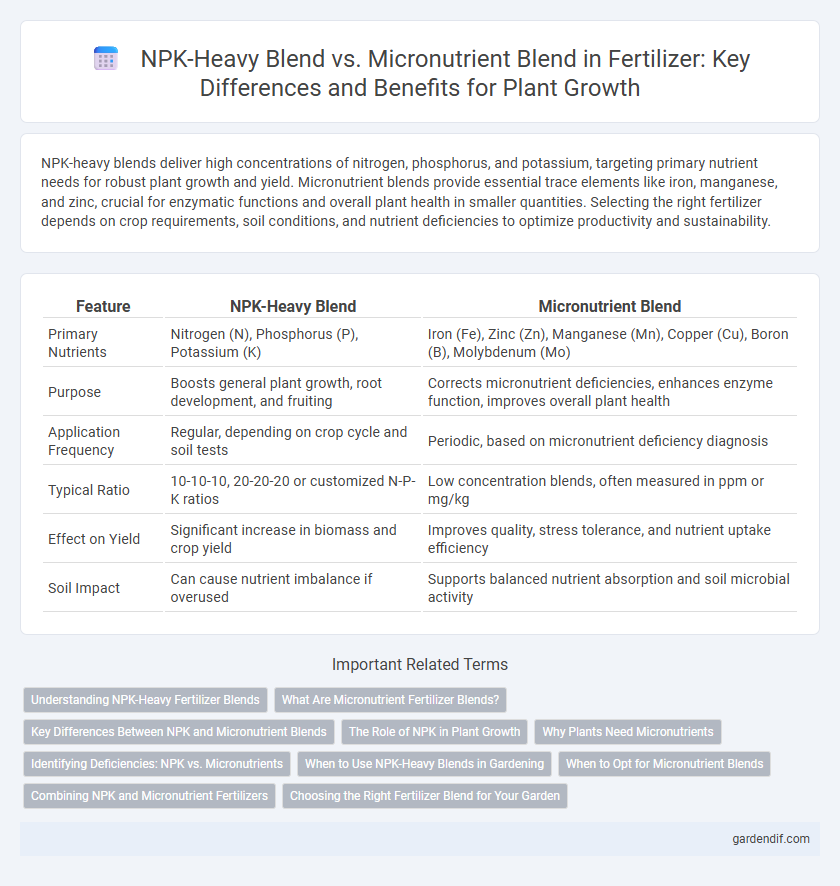
Table of Comparison
| Feature | NPK-Heavy Blend | Micronutrient Blend |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Nutrients | Nitrogen (N), Phosphorus (P), Potassium (K) | Iron (Fe), Zinc (Zn), Manganese (Mn), Copper (Cu), Boron (B), Molybdenum (Mo) |
| Purpose | Boosts general plant growth, root development, and fruiting | Corrects micronutrient deficiencies, enhances enzyme function, improves overall plant health |
| Application Frequency | Regular, depending on crop cycle and soil tests | Periodic, based on micronutrient deficiency diagnosis |
| Typical Ratio | 10-10-10, 20-20-20 or customized N-P-K ratios | Low concentration blends, often measured in ppm or mg/kg |
| Effect on Yield | Significant increase in biomass and crop yield | Improves quality, stress tolerance, and nutrient uptake efficiency |
| Soil Impact | Can cause nutrient imbalance if overused | Supports balanced nutrient absorption and soil microbial activity |
Understanding NPK-Heavy Fertilizer Blends
NPK-heavy fertilizer blends are formulated with high concentrations of nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K), essential macronutrients that drive plant growth, root development, and overall crop yield. These blends are designed to address primary nutrient deficiencies in soil, promoting vigorous vegetative growth and enhanced fruit or grain production. Unlike micronutrient blends, which supply trace elements like zinc, iron, and manganese for enzymatic function and chlorophyll synthesis, NPK-heavy fertilizers emphasize bulk nutrient replenishment critical for large-scale agricultural productivity.
What Are Micronutrient Fertilizer Blends?
Micronutrient fertilizer blends contain essential trace elements such as zinc, copper, manganese, iron, and boron, which are critical for plant development but required in smaller quantities than primary nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium (NPK). These blends improve soil fertility by addressing specific nutrient deficiencies that NPK-heavy blends may not cover, enhancing plant health, yield, and resistance to environmental stress. Farmers use micronutrient blends to balance soil nutrition, especially in areas with micronutrient-poor soils, ensuring optimal crop growth and nutrient uptake efficiency.
Key Differences Between NPK and Micronutrient Blends
NPK-heavy blends primarily provide essential macronutrients nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) to promote robust plant growth, root development, and fruiting, whereas micronutrient blends supply vital trace elements like iron, zinc, manganese, and copper, crucial for enzymatic and physiological plant functions. NPK blends typically have a higher nutrient concentration and are used to address major soil nutrient deficiencies, while micronutrient blends target specific micronutrient shortfalls that affect plant metabolic processes at lower doses. The main difference lies in their nutrient composition and role: NPK blends support general plant nutrition for growth and yield, whereas micronutrient blends optimize overall plant health and resistance to environmental stress.
The Role of NPK in Plant Growth
NPK-heavy blends provide essential macronutrients--nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K)--that drive critical plant growth processes such as leaf development, root formation, and fruit production. Nitrogen enhances chlorophyll synthesis and overall vegetative growth, phosphorus supports energy transfer and flowering, while potassium regulates water uptake and disease resistance. These primary nutrients form the foundation of plant nutrition, ensuring optimal growth and yield before micronutrient supplementation is considered.
Why Plants Need Micronutrients
Plants require micronutrients such as iron, manganese, zinc, copper, boron, molybdenum, and chlorine to support vital physiological functions including enzyme activation, chlorophyll synthesis, and nutrient absorption. While NPK-heavy blends supply essential macronutrients nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium for growth and energy, micronutrient blends ensure balanced nutrition that prevents deficiencies impacting plant health and crop yield. Effective fertilization combines both macronutrients and micronutrients to optimize plant development and improve resistance to environmental stress.
Identifying Deficiencies: NPK vs. Micronutrients
NPK-heavy blend fertilizers primarily address major nutrient deficiencies in nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium essential for plant growth, but often overlook subtle micronutrient shortages. Micronutrient blends target deficiencies in trace elements like iron, zinc, manganese, and copper, which are critical for enzyme function and overall plant health. Identifying specific nutrient deficiencies through soil testing is crucial to determine whether an NPK-heavy or micronutrient blend is needed for optimal crop yield.
When to Use NPK-Heavy Blends in Gardening
NPK-heavy blends are ideal for promoting vigorous growth during the early stages of plant development, as they provide essential macronutrients nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium in high concentrations. These fertilizers support leaf, root, and flower growth, making them suitable for vegetables, corn, and other nutrient-demanding crops. Avoid using NPK-heavy blends late in the growing season to prevent excessive foliage growth at the expense of fruit or flower production.
When to Opt for Micronutrient Blends
Micronutrient blends should be chosen when soil tests reveal deficiencies in essential trace elements like zinc, iron, manganese, and copper, which are not adequately supplied by NPK-heavy blends. These blends support crop health by improving enzymatic functions, chlorophyll production, and stress resistance, thereby enhancing yield quality rather than just quantity. Opt for micronutrient blends during growth stages sensitive to deficiency symptoms or in soils prone to micronutrient depletion due to intensive farming or specific crop requirements.
Combining NPK and Micronutrient Fertilizers
Combining NPK-heavy blends with micronutrient fertilizers enhances overall plant health by addressing both macronutrient and micronutrient deficiencies critical for optimal growth. This integrated approach improves nutrient uptake efficiency, leading to increased yield and better crop quality. Balanced fertilization strategies leverage the synergistic effects of nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, alongside essential micronutrients like zinc, iron, and manganese for sustainable soil fertility.
Choosing the Right Fertilizer Blend for Your Garden
Choosing the right fertilizer blend depends on your garden's specific nutrient needs, with NPK-heavy blends providing essential nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium for primary growth stages. Micronutrient blends supplement trace elements like iron, zinc, and manganese, critical for enzyme function and overall plant health. Soil testing is vital to determine deficiencies and select a balanced formula that supports vigorous growth and maximizes crop yield.
NPK-heavy blend vs micronutrient blend Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com