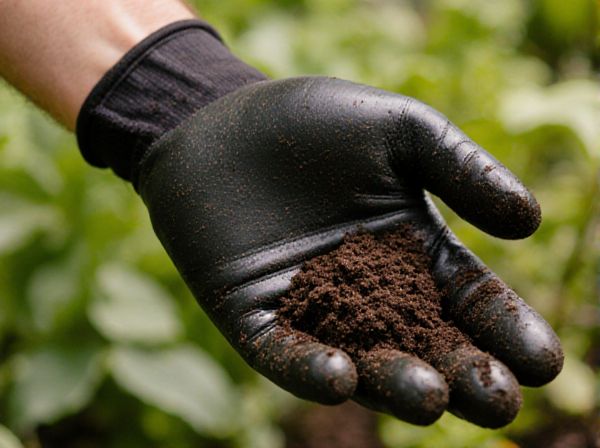

Manure application vs Green manure incorporation Illustration
Manure application enriches soil with essential nutrients and organic matter, promoting microbial activity and improving soil structure. Green manure incorporation involves growing cover crops that are plowed back into the soil, enhancing nitrogen content and increasing soil fertility naturally. Both methods boost crop productivity but differ in nutrient release timing and soil health benefits.
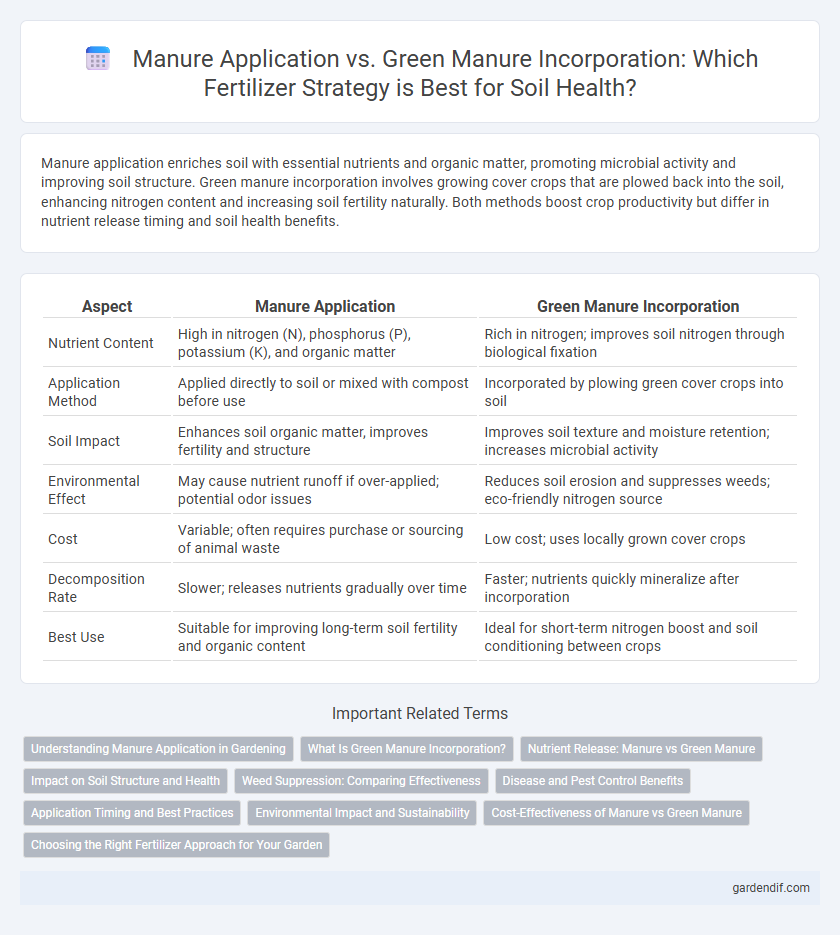
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Manure Application | Green Manure Incorporation |
|---|---|---|
| Nutrient Content | High in nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K), and organic matter | Rich in nitrogen; improves soil nitrogen through biological fixation |
| Application Method | Applied directly to soil or mixed with compost before use | Incorporated by plowing green cover crops into soil |
| Soil Impact | Enhances soil organic matter, improves fertility and structure | Improves soil texture and moisture retention; increases microbial activity |
| Environmental Effect | May cause nutrient runoff if over-applied; potential odor issues | Reduces soil erosion and suppresses weeds; eco-friendly nitrogen source |
| Cost | Variable; often requires purchase or sourcing of animal waste | Low cost; uses locally grown cover crops |
| Decomposition Rate | Slower; releases nutrients gradually over time | Faster; nutrients quickly mineralize after incorporation |
| Best Use | Suitable for improving long-term soil fertility and organic content | Ideal for short-term nitrogen boost and soil conditioning between crops |
Understanding Manure Application in Gardening
Manure application in gardening enriches soil with essential nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, promoting healthy plant growth and improving soil structure through increased organic matter. Unlike green manure incorporation, which relies on growing and tilling cover crops to boost soil fertility, manure provides immediate nutrient release, enhancing microbial activity and soil moisture retention. Proper timing and correct manure-to-soil ratios minimize nutrient leaching and prevent plant damage, making it a sustainable choice for maintaining garden productivity.
What Is Green Manure Incorporation?
Green manure incorporation involves growing specific crops, such as legumes or cover crops, and then plowing them into the soil to enhance nutrient content and soil structure. Unlike traditional manure application, which adds organic matter directly, green manure decomposes in situ, increasing nitrogen fixation and improving microbial activity. This sustainable practice reduces the need for synthetic fertilizers while promoting soil fertility and moisture retention.
Nutrient Release: Manure vs Green Manure
Manure application releases nutrients gradually, providing a steady supply of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium essential for crop growth over an extended period. Green manure incorporation accelerates nutrient availability, particularly nitrogen, due to rapid decomposition of fresh plant biomass that enhances soil fertility quickly. Understanding the nutrient release dynamics of both methods allows for optimized fertilization strategies tailored to specific crop nutrient demands and soil health goals.
Impact on Soil Structure and Health
Manure application enhances soil structure by increasing organic matter content, promoting microbial activity, and improving nutrient availability, which leads to better water retention and aeration. Green manure incorporation rapidly adds fresh biomass, stimulating soil microbial diversity and accelerating nutrient cycling, thereby enhancing soil fertility and reducing erosion risks. Both practices improve soil health, but manure provides a longer-term organic amendment while green manure offers immediate benefits through quick decomposition and nutrient release.
Weed Suppression: Comparing Effectiveness
Manure application provides essential nutrients but often lacks strong weed suppression properties, leading to potential weed proliferation in treated fields. Green manure incorporation enhances soil fertility while creating a physical mulch layer that effectively inhibits weed seed germination. Studies show that green manure crops like clover or rye, when incorporated, reduce weed density more significantly compared to conventional manure amendments.
Disease and Pest Control Benefits
Manure application enhances soil fertility and microbial diversity, which suppresses soil-borne diseases and improves pest resistance in crops. Green manure incorporation enriches soil organic matter and releases allelopathic compounds that inhibit pest populations and pathogen growth. Both methods contribute to sustainable disease and pest control through improved soil health and ecosystem balance.
Application Timing and Best Practices
Manure application is most effective when applied before planting or during early crop growth stages to maximize nutrient availability and reduce nitrogen losses. Green manure incorporation is best conducted well before sowing, ideally 3-4 weeks prior, to allow sufficient decomposition and improve soil organic matter. Optimizing timing for both practices ensures enhanced nutrient uptake, soil fertility, and crop yield.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Manure application enhances soil fertility by recycling nutrients and increasing organic matter, but it can lead to nutrient runoff and greenhouse gas emissions if not managed properly. Green manure incorporation improves soil structure and biodiversity while reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers, making it a more sustainable practice with lower environmental impact. Both methods contribute to sustainable agriculture, yet green manure offers better long-term soil health benefits and mitigates environmental risks more effectively.
Cost-Effectiveness of Manure vs Green Manure
Manure application provides a cost-effective fertilizer option due to the direct use of animal waste, reducing the need for synthetic inputs and lowering overall expenses. Green manure incorporation involves growing specific cover crops that require land, water, and labor investments before decomposition, often increasing short-term costs. Cost-effectiveness depends on factors such as availability, labor requirements, and nutrient release rates, with manure typically offering immediate nutrient benefits at lower expenses.
Choosing the Right Fertilizer Approach for Your Garden
Manure application enriches soil with organic matter and essential nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, promoting long-term soil fertility and improved crop yield. Green manure incorporation involves growing specific cover crops such as clover or legumes and then tilling them into the soil to enhance nitrogen fixation and soil structure. Selecting between manure application and green manure incorporation depends on soil nutrient status, crop requirements, and sustainability goals, ensuring optimal nutrient cycling and soil health for your garden.
Manure application vs Green manure incorporation Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com